Smart Building Cybersecurity Best Practices
Implementing Multi-Layered Security Measures
Implementing Robust Access Control
A crucial aspect of multi-layered security in smart buildings is implementing robust access control mechanisms. This involves not only controlling physical access to the building but also meticulously managing digital access to various systems and applications. Effective access control systems should employ strong authentication protocols, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to verify the identities of users and prevent unauthorized access. This layer of security ensures that only authorized personnel can interact with sensitive building systems, data, and resources, significantly reducing the risk of breaches and data compromises.
Beyond user authentication, access control should be granular, allowing administrators to precisely define which individuals have permission to perform specific tasks within the building's systems. This granular control mitigates the risk of privilege escalation, where an attacker gains unauthorized access to more sensitive functionalities due to a compromised account with higher privileges. Detailed audit trails are essential to track all access attempts and activities, enabling swift identification and response to any suspicious or unauthorized actions.
Enhancing Network Security Infrastructure
A secure network infrastructure is the bedrock of a smart building's cybersecurity posture. This entails employing robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor and block malicious traffic. These systems should be configured to identify and respond to emerging threats, adapting to the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity risks. Furthermore, the network should be segmented to isolate different building systems and applications, limiting the impact of a potential breach to a specific area rather than spreading across the entire network.
Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing are crucial to proactively identify and address weaknesses in the network infrastructure. These assessments should be conducted periodically to ensure that the network remains resilient against evolving threats. Properly configuring network devices, including routers, switches, and access points, with secure configurations is also essential to enhance network security. This proactive approach helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Protecting Data with Encryption and Backup Procedures
Data protection is paramount in a smart building environment. All sensitive data, including building management system (BMS) data, sensor readings, and user information, should be encrypted both in transit and at rest. Strong encryption protocols protect data from unauthorized access even if a breach occurs. Regular data backups should be performed, stored securely, and tested regularly to ensure data recovery in case of a disaster or data loss incident.
Employing Advanced Threat Detection and Response Systems
Implementing advanced threat detection and response systems is vital for rapidly identifying and mitigating potential security threats. These systems can include sophisticated security information and event management (SIEM) tools that collect, analyze, and correlate security events to detect anomalies and suspicious activities. Real-time threat intelligence feeds can also be integrated to provide up-to-date information about emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
A robust incident response plan should be in place to guide the swift and effective handling of security incidents. This plan should outline procedures for containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned, ensuring minimal disruption and damage in the event of a security breach. Effective communication channels and protocols are essential to ensure timely information sharing among stakeholders and facilitate swift response.
Maintaining Security Awareness and Training Programs
A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy must include ongoing security awareness training for all building personnel. Regular training programs should educate users about common security threats, phishing scams, and best practices for safe online behavior. This empowers employees to recognize and report suspicious activities, reducing the risk of human error in security protocols.
Regular security audits and assessments should be conducted to identify and address any gaps in security procedures and protocols. This continuous improvement process ensures the building's cybersecurity posture remains resilient and adapts to emerging threats and evolving technologies. Building a culture of security awareness and empowering all stakeholders to play a role in the security process is crucial for maintaining a strong security posture.
Securing IoT Devices and Networks
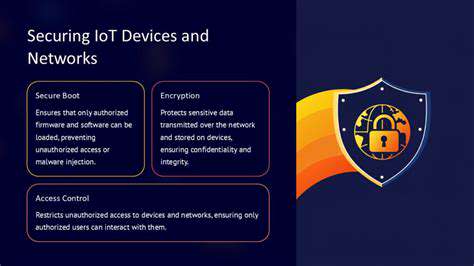
Protecting Against Common Vulnerabilities
IoT devices often lack robust security measures, making them vulnerable to exploitation by malicious actors. This lack of security can lead to a cascade of problems, from data breaches and unauthorized access to complete system compromise. Addressing these vulnerabilities is crucial to mitigating potential risks and ensuring the safety of interconnected systems. The proliferation of IoT devices across various sectors, including critical infrastructure and consumer products, necessitates a proactive approach to security. This involves implementing strong authentication protocols, employing secure communication channels, and regularly updating firmware to patch known vulnerabilities.
A significant vulnerability lies in the use of default passwords. Many IoT devices ship with easily guessed default credentials. Attackers often use automated tools to probe for these weak passwords, gaining unauthorized access to the device and potentially the entire network. Implementing strong, unique passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication where possible is essential to fortify these vulnerable points. Additionally, inadequate or outdated encryption protocols can be exploited by attackers to intercept and decrypt sensitive data. Implementing robust encryption, particularly end-to-end encryption, is a critical step in protecting data transmitted over various networks.
Implementing Robust Security Protocols
Implementing robust security protocols is critical for safeguarding IoT devices and networks. These protocols should incorporate strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to verify the identity of users and devices attempting to access the network. Employing secure communication protocols, like HTTPS, for data transmission is essential to protect sensitive information from interception and manipulation. Regularly updating firmware and software is paramount for addressing known vulnerabilities and patching potential security flaws.
Security protocols should be implemented at every level of the IoT ecosystem, from individual devices to the overarching network infrastructure. This includes establishing clear security policies and procedures that govern device access, data handling, and network management. Regular security audits and penetration testing can help identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. These assessments can help in evaluating the effectiveness of existing security measures and pinpoint areas needing improvement.
Securing Network Communications
Securing network communications is a crucial aspect of IoT security. This involves encrypting data transmitted between devices and the network, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches. Employing secure communication protocols, such as TLS/SSL, is paramount to protect sensitive data from interception and manipulation. Utilizing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can establish a secure connection between devices and the network, ensuring that communications remain confidential and authenticated.
Implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems is another critical step in securing network communications. These systems can monitor network traffic for malicious activity, alerting administrators to potential threats and allowing for timely intervention. Network segmentation, separating sensitive devices and networks from less critical ones, can further limit the impact of a successful attack. Regularly updating and maintaining these security measures is critical to their effectiveness.
Addressing the Human Factor
Security in the IoT extends beyond technical measures. User education and awareness play a vital role in preventing security breaches. Users need to be educated on best practices for creating strong passwords, recognizing phishing attempts, and reporting suspicious activity. Encouraging users to follow these guidelines is crucial to mitigating potential security risks. Regular security awareness training can reinforce these best practices and empower users to make informed decisions that contribute to the overall security posture of the system.
Furthermore, implementing strong access controls and user authentication policies can limit the impact of insider threats. This involves establishing clear guidelines for user access privileges and regularly reviewing and updating these policies. Strong user training and awareness, combined with robust technical security measures, are the key to building a comprehensive and resilient IoT security strategy.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Employee Training Program Design
A comprehensive employee training program should be meticulously designed to address specific organizational needs and ensure the effectiveness of the training. This involves identifying critical skills gaps within the workforce and tailoring training modules to bridge these gaps. Clearly defined learning objectives are crucial for measuring the program's success and ensuring that employees gain the necessary knowledge and skills. The program should also incorporate various learning methodologies, such as interactive workshops, online modules, and hands-on practice, to cater to diverse learning styles and enhance engagement.
Effective training programs should be evaluated regularly to assess their impact on employee performance and identify areas for improvement. This can involve collecting feedback from trainees, tracking changes in productivity, and analyzing the effectiveness of different training methods. Regular evaluations help ensure the program remains relevant and adaptable to evolving business needs.
Importance of Awareness Programs
Employee awareness programs are essential for fostering a positive and productive work environment. These programs aim to educate employees about relevant company policies, procedures, and ethical guidelines. Training programs should promote a culture of safety and compliance within the organization.
By promoting awareness of company values, employees can better understand their roles and responsibilities within the organization. This fosters a sense of shared purpose and enhances overall team performance. Building a strong foundation of awareness is essential for preventing misunderstandings and promoting open communication.
Training Delivery Methods
The delivery of employee training should incorporate a variety of methods to cater to different learning styles. This could include traditional classroom settings, interactive workshops, online learning platforms, and on-the-job training. An effective training program recognizes the benefits of diverse delivery methods for maximizing knowledge retention and application.
The selection of the most appropriate training method should depend on the specific learning objectives and the nature of the material being taught. The use of technology, such as simulations and virtual reality, can enhance the learning experience and create a more engaging environment for employees. Careful consideration must be given to the chosen method to ensure that it is suitable for the target audience and promotes effective knowledge transfer.
Training Evaluation and Feedback
Evaluating employee training programs is essential to measure their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. A thorough evaluation helps determine if the training objectives were met and if the training materials were relevant and engaging. Gathering feedback from trainees is crucial for understanding their perspectives and experiences with the training program.
Regular feedback loops allow for adjustments to training content and delivery methods, leading to a more tailored and impactful learning experience. Collecting data on employee performance after training can provide valuable insights into the program's overall impact and help optimize future training initiatives.
Training Schedule and Resources
A well-structured training schedule is crucial for ensuring that training sessions are delivered effectively and efficiently. The schedule should consider employee availability, training duration, and the overall learning objectives. Planning for adequate time for questions and discussions is essential to maximize knowledge retention and understanding.
Providing the necessary resources, such as training materials, equipment, and support staff, is vital for successful training delivery. This ensures that employees have access to the tools and support needed to effectively absorb the training content. Adequate resources and a well-planned schedule ensure that the training program meets its objectives and improves employee performance.
Read more about Smart Building Cybersecurity Best Practices
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing