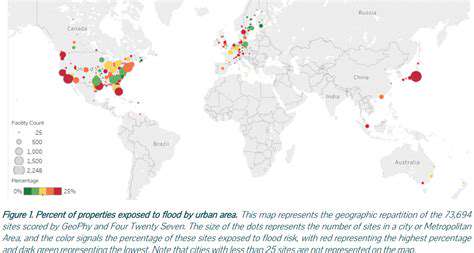
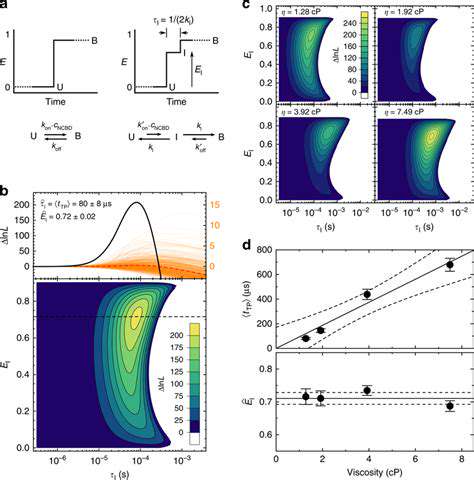
Climate Risk Disclosure in Real Estate Financing
Disclosure Requirements for Financial Statements
Accurate and transparent financial reporting is paramount for maintaining investor confidence and upholding ethical business practices. Companies must adhere to strict disclosure requirements to ensure that all material information is presented truthfully and completely in their financial statements. This includes details on revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and any significant events that could affect the company's financial position. Failure to disclose such information can lead to significant penalties and reputational damage.
Standardized Accounting Principles
Standardized accounting principles, like Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) in the United States or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), provide a common framework for financial reporting. These frameworks dictate how transactions should be recorded, classified, and presented in financial statements, ensuring comparability across different companies and industries. This allows investors and other stakeholders to understand the financial performance and position of various businesses more effectively.
Materiality Thresholds
Determining what information is material is crucial in financial reporting. Materiality refers to the significance of an item or event that could influence the economic decisions of investors and stakeholders. Items below a certain threshold, often based on quantitative or qualitative factors, are typically not required to be disclosed. Clearly defining and applying materiality thresholds is essential for maintaining transparency without overwhelming the reporting with insignificant details.
Disclosure of Conflicts of Interest
Companies must disclose any potential conflicts of interest that could impact their financial reporting or decision-making. This includes situations where a company's management or board members have personal interests that could clash with their fiduciary duties to shareholders. Disclosure of such conflicts is essential for maintaining trust and promoting ethical business practices, as it allows stakeholders to assess potential biases in financial reporting. It's a critical component of transparency.
Compliance with Regulatory Bodies
Companies are obligated to adhere to regulations set by various governmental and regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States. These regulations outline specific requirements for financial reporting, including the format, content, and timing of disclosures. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in significant legal and financial repercussions. The SEC, for example, closely monitors adherence to reporting standards. Thus, compliance is a crucial aspect of responsible business operations.
External Audits and Independent Verification
Independent audits are crucial to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. Independent auditors, who are not affiliated with the company, examine the financial records and evaluate the company's compliance with accounting standards. This independent verification process helps build confidence in the reported financial information and protects the interests of investors and creditors. Accurate financial statements build trust and confidence. This process, performed by an external party, adds credibility to the financial reports.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
Financial reporting standards and disclosure requirements are subject to continuous evolution. Changes in the economic landscape, advancements in technology, and evolving stakeholder needs necessitate adaptations in the disclosure requirements. Companies must proactively engage with and adapt to these evolving standards to maintain compliance and ensure the relevance and accuracy of their financial reporting. Staying current with evolving regulations is not just a legal obligation but a crucial business practice. This dynamic environment requires continuous monitoring and adjustments to ensure reporting remains useful and credible.

Read more about Climate Risk Disclosure in Real Estate Financing
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing