Modular Construction for Affordable Residential Units

Sustainable Practices and Environmental Considerations
Minimizing Environmental Impact Through Material Selection
Modular construction offers a unique opportunity to significantly reduce environmental impact by carefully selecting materials. Prioritizing recycled, reclaimed, and locally sourced materials minimizes transportation distances, reducing carbon emissions associated with material delivery. This approach also decreases the overall energy consumption required to produce the materials, a crucial aspect of a sustainable building process. Furthermore, choosing materials with low embodied energy – the energy used in their extraction, processing, and manufacturing – is vital for minimizing the overall environmental footprint of the constructed module.
Employing sustainable materials like bamboo, timber, or recycled plastics reduces the dependence on virgin resources and promotes a circular economy. Careful consideration of the lifecycle of each material, from extraction to disposal, is crucial to ensuring minimal environmental damage throughout the entire construction process. By making conscious choices regarding materials, modular construction can move towards environmentally friendly and responsible building practices, setting a precedent for future projects.
Waste Reduction and Efficient Resource Management
Modular construction inherently lends itself to waste reduction. Pre-fabrication in a controlled factory environment allows for precise material cutting and assembly, minimizing on-site waste generation. This precision also contributes to efficient resource management, as materials are used optimally, reducing material overruns common in traditional construction. Effective planning and meticulous design are essential elements in achieving a low-waste modular construction process.
Advanced design software and digital fabrication techniques further enhance waste reduction by enabling precise material calculations and minimizing material waste. The standardized nature of modular construction facilitates the recovery and reuse of leftover materials, further minimizing the environmental impact. This process of continuous improvement in waste management is crucial for the overall sustainability of modular construction projects.
Energy Efficiency in Modular Design
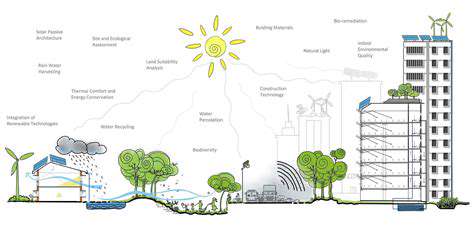
Modular construction offers significant opportunities for energy efficiency. The controlled factory environment allows for the incorporation of high-performance insulation materials and energy-efficient systems, such as solar panels or geothermal heating and cooling systems, into the modules. This pre-assembly process enables greater precision and control compared to traditional construction, resulting in optimized energy performance. Integrating these elements into the modules from the design stage helps achieve optimized energy efficiency throughout the building's lifecycle. The standardized nature of modular construction allows for the consistent application of these measures across multiple projects.
Design considerations for optimal energy efficiency in modular construction include strategic placement of windows for natural light and ventilation, optimized building orientation, and careful selection of energy-efficient appliances. These detailed planning stages, coupled with the factory-based nature of modular construction, set the stage for substantial energy savings. The incorporation of energy-efficient components during the module design phase ensures that the finished structure performs to a high standard, minimizing long-term energy consumption and reducing the building's carbon footprint.
Transportation and Logistics Optimization
Minimizing the environmental impact of transportation is vital for sustainable modular construction. Optimized delivery routes, using sustainable transportation methods like electric vehicles or rail, can significantly reduce carbon emissions associated with transporting materials and modules. Careful consideration of the logistics involved, including the use of efficient packaging and appropriate load capacity, is crucial for minimizing environmental impact. Modular construction, by its nature, often allows for the pre-assembly of components at a centralized location, reducing the number of trips required and the associated emissions.
Strategically locating manufacturing facilities close to construction sites, when possible, can further reduce transportation distances and emissions. This approach, coupled with efficient inventory management, minimizes the need for repeated trips and the environmental impact associated with the transport of materials. By focusing on sustainable transportation methods and logistics, modular construction can significantly reduce its carbon footprint and promote more environmentally friendly building practices.
Read more about Modular Construction for Affordable Residential Units
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing