Modular Green Homes: Affordability and Sustainability

Prefabrication's Impact on Construction Efficiency
Prefabrication, the process of assembling building components in a controlled factory environment, is revolutionizing the construction industry. This method significantly streamlines the construction process, reducing on-site labor and increasing the overall efficiency of building projects. Prefabricated components are often pre-tested and pre-assembled, leading to faster installation times and minimizing costly delays on-site. This allows for a more predictable construction schedule, making it easier to manage project timelines and budgets.
By prefabricating elements like walls, floors, and roofs, construction teams can focus on the assembly and finishing touches on-site. This focused approach leads to a more organized construction site, reduced material waste, and improved safety standards. The reduced on-site time also minimizes the disruption to the surrounding environment and local communities.
Reduced Construction Time and Costs
One of the most significant advantages of prefabrication is the reduction in construction time. Prefabricated components can be manufactured and assembled significantly faster than traditional methods, leading to faster project completion. This translates directly to lower overall project costs, as the reduced time spent on-site translates to lower labor expenses and fewer material handling costs. This makes prefabrication a particularly attractive option for projects with tight deadlines or limited budgets.
Improved Quality Control and Safety
Prefabricated components are often manufactured in controlled factory environments, which allows for superior quality control. This leads to more precise measurements, better material handling, and a higher standard of quality than often achieved on-site. The prefabrication process also fosters a safer work environment on the construction site, as complex tasks are handled in a controlled factory setting, reducing the potential for on-site accidents. This results in fewer injuries and mitigates potential risks significantly.
Enhanced Design Flexibility and Innovation
Prefabrication allows for more design flexibility than traditional construction methods. The ability to manufacture components off-site enables the use of complex designs and innovative building materials that might be difficult or impossible to implement on a traditional construction site. This translates to more creative and customized building solutions. Prefabricated components can be designed to meet specific architectural requirements and aesthetic preferences, offering greater design freedom for project developers.
Sustainable Practices and Environmental Impact
Prefabrication often promotes sustainable practices in construction. The controlled environment of a factory facilitates better material management and reduces waste. By minimizing on-site activities, prefabrication also reduces the environmental impact of construction projects, including noise pollution, air and water contamination, and waste generation. This commitment to sustainability aligns with growing global concerns about responsible and environmentally friendly construction practices.
Material Efficiency and Waste Reduction
Prefabrication optimizes material usage, leading to significant waste reduction. Precise measurements and controlled environments in the factory minimize material waste and improve efficiency. This reduction in waste is not only economically beneficial but also aligns with sustainable construction practices, contributing to a greener future for the construction industry. The improved material management in prefabrication also reduces the overall cost of the project by minimizing material expenses and waste disposal costs.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
While prefabrication offers numerous advantages, there are also potential challenges to consider. Transporting large and complex prefabricated components can be challenging, and careful planning is crucial to ensure timely delivery and efficient on-site assembly. Furthermore, the initial investment in specialized equipment and skilled labor for prefabrication may be higher than for traditional construction methods. However, the long-term cost savings and efficiency gains often outweigh these initial considerations.
Sustainable Materials and Energy Efficiency: Key Components
Sustainable Materials: A Foundation for Eco-Friendly Homes
Choosing sustainable materials is paramount in constructing modular green homes. These materials, sourced responsibly and minimizing environmental impact, are crucial to the overall eco-friendliness of the structure. This includes opting for timber harvested from responsibly managed forests, recycled and reclaimed materials for various components, and incorporating locally sourced materials whenever possible. The selection process must consider the entire life cycle of the material, from extraction to disposal, ensuring minimal harm to the environment.
Furthermore, sustainable materials often exhibit inherent qualities that contribute to energy efficiency. For instance, timber frames, with their inherent insulation properties, can significantly reduce the need for additional insulation measures. Using materials with high thermal mass can help regulate temperature fluctuations, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling.
Energy Efficiency in Design: Optimizing Performance
Smart design principles are essential for maximizing energy efficiency in modular green homes. Careful consideration of solar orientation, maximizing natural light and ventilation, and minimizing thermal bridging are key strategies. Using passive solar design techniques can drastically reduce reliance on active heating and cooling systems, leading to significant energy savings.
Employing advanced building envelope technologies, such as high-performance windows and insulation, further enhances energy efficiency. These strategies not only reduce energy consumption but also contribute to a more comfortable and healthy indoor environment.
Passive Solar Design Strategies: Harnessing Natural Resources
Passive solar design strategies are fundamental to energy-efficient modular green homes. By strategically positioning windows and walls to maximize sunlight in winter and minimize it in summer, significant reductions in heating and cooling demands can be achieved. Careful consideration of shading devices and thermal mass materials further enhances the effectiveness of these strategies.
Understanding local climate conditions is crucial for optimizing passive solar design. Factors such as solar radiation patterns, prevailing winds, and temperature variations must be taken into account to ensure the design effectively harnesses natural resources.
Modular Construction Techniques: Streamlining the Process
Modular construction, inherent in these green homes, offers significant advantages in terms of sustainability. Pre-fabrication in controlled factory environments minimizes waste, reduces on-site construction time, and allows for precise quality control. This approach minimizes disruption to the surrounding environment and optimizes material use.
Moreover, modular construction facilitates the use of innovative and sustainable building materials and techniques that might not be readily available or practical for conventional construction methods. The standardized nature of modules also allows for more precise energy modeling and performance analysis, further enhancing the overall sustainability of the structure.
Renewable Energy Integration: Powering the Future
Integrating renewable energy sources is vital for creating truly sustainable modular green homes. Solar photovoltaic panels, wind turbines, and geothermal systems can significantly reduce reliance on the grid. The integration of these systems should be carefully planned and optimized for the specific location and energy needs of the home.
Furthermore, smart energy management systems can monitor and optimize energy use, ensuring that the home operates as efficiently as possible, maximizing the benefits of renewable energy sources.
Indoor Environmental Quality: Prioritizing Health and Wellbeing
A crucial aspect of sustainable modular green homes is prioritizing indoor environmental quality (IEQ). This involves selecting materials that minimize off-gassing of harmful VOCs, ensuring adequate ventilation, and controlling humidity levels to create a healthy and comfortable living environment. Proper air filtration systems can further enhance IEQ, improving air quality and reducing the risk of respiratory issues.
Implementing these strategies not only improves the health and well-being of occupants but also contributes to the overall sustainability of the home by reducing the need for energy-intensive air conditioning and heating systems.
Addressing Affordability Concerns Through Efficient Construction

Understanding the Financial Strain
Many individuals and families face significant financial challenges in today's economy, impacting their ability to access essential resources and opportunities. These challenges often stem from a combination of factors, including rising living costs, stagnant wages, and increasing debt burdens. This financial strain can lead to a cycle of hardship, making it difficult to improve one's economic situation.
The rising cost of housing, healthcare, and education is a significant contributor to affordability issues. These expenses can quickly consume a large portion of a household's income, leaving little room for savings or investments. Consequently, individuals and families may find themselves struggling to meet their basic needs.
Exploring Solutions for Housing Affordability
Addressing housing affordability requires a multifaceted approach. One crucial element is implementing policies that incentivize the development of affordable housing units. This could involve zoning regulations that permit denser housing options and financial incentives for developers to construct more affordable housing projects.
Another critical component is increasing access to affordable mortgage financing options. This could involve government subsidies or programs that make homeownership more attainable for lower- and middle-income families. Providing financial support can ease the burden of housing costs and potentially stimulate the economy.
Analyzing the Impact of Healthcare Costs
The escalating cost of healthcare is a major concern for many individuals and families. High medical bills can quickly deplete savings and create significant financial stress. Healthcare affordability is a critical issue that needs immediate attention and innovative solutions.
Comprehensive health insurance plans and readily available preventative care services can significantly reduce the financial burden associated with unexpected illnesses or injuries. Promoting preventive care can improve overall health outcomes and reduce long-term healthcare costs.
Examining Education Costs
The rising cost of education, including tuition, fees, and living expenses, is another significant affordability concern. Many students and families find themselves burdened by substantial educational debt, which can impact their future financial stability.
Exploring alternative educational pathways, such as community colleges and vocational training programs, can provide more affordable and accessible educational options. These alternatives can provide valuable skills and training without the high cost of traditional four-year universities.
Investigating Wage Stagnation
The stagnation of wages in many sectors has contributed to the affordability crisis. When wages fail to keep pace with rising living costs, individuals and families struggle to maintain their standard of living. This leads to a decrease in purchasing power and limits opportunities for upward mobility.
Implementing policies that promote fair wages and job growth is crucial to addressing this issue. This includes advocating for living wages, supporting worker protections, and investing in economic development initiatives.
Addressing the Debt Burden
The increasing burden of debt, including student loans, credit card debt, and other forms of consumer debt, exacerbates affordability challenges. High-interest debt can quickly spiral out of control, leading to financial instability and hardship. Debt management strategies, such as budgeting, debt consolidation, and seeking financial counseling, can provide much-needed support for those struggling with debt.
Promoting Financial Literacy
Enhancing financial literacy is crucial in empowering individuals and families to make informed financial decisions. Education on budgeting, saving, investing, and managing debt can equip individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate financial challenges more effectively. By providing resources and tools, we can help individuals make sound financial choices and build a secure financial future.
Promoting financial literacy programs in schools and communities can empower future generations to make responsible financial decisions from a young age. This proactive approach can lead to long-term positive outcomes and help mitigate the effects of future financial hardships.
The Future of Housing: A Sustainable and Affordable Path
Modular Construction: Streamlining the Process
Modular construction is revolutionizing the housing industry, offering a more efficient and sustainable alternative to traditional methods. By prefabricating components in a controlled factory environment, builders can significantly reduce on-site labor, minimize waste, and accelerate construction timelines. This streamlined process not only lowers overall project costs but also contributes to a more environmentally conscious approach, as transportation distances for materials are often reduced and waste is often better managed.
Green Materials: Eco-Friendly Choices
Sustainable building practices are increasingly important, and modular homes offer excellent opportunities to incorporate eco-friendly materials. From using reclaimed wood and recycled materials in the construction process to incorporating solar panels and energy-efficient windows, these homes can significantly reduce their environmental footprint. The use of locally sourced, sustainable materials further enhances this aspect, supporting local economies and reducing the carbon emissions associated with long-distance transport.
Energy Efficiency: Reducing Operational Costs
Energy efficiency is paramount in the modern housing market, and modular homes are uniquely positioned to excel in this area. Utilizing advanced insulation techniques, high-performance windows, and smart home technologies, these homes can dramatically reduce energy consumption for heating, cooling, and lighting. This translates to lower utility bills for homeowners, a significant long-term financial benefit and a positive contribution to the fight against climate change.
Affordability: Bridging the Housing Gap
One of the key advantages of modular construction is its potential to make housing more affordable. By reducing construction time and on-site labor costs, modular homes can lower overall project expenses. This affordability is particularly crucial in addressing the current housing crisis, making homeownership a realistic possibility for a wider range of individuals and families.
Design Flexibility: Tailoring Homes to Needs
Modular construction doesn't compromise on design flexibility. Customizable layouts, personalized aesthetics, and adaptable floor plans can be integrated into these homes. This allows homeowners to tailor the living space to their specific needs and preferences, creating a home that truly reflects their lifestyle and personality. The prefabrication process allows for intricate designs and unique features to be incorporated without sacrificing speed or cost-effectiveness.
Community Impact: Fostering Sustainable Living
The widespread adoption of modular green homes can have a positive impact on communities as a whole. Reduced construction time leads to faster development and the creation of new housing options, addressing the housing shortage. The use of sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs contributes to a healthier environment for residents and the community at large. Moreover, the increased availability of housing can lead to economic growth and community development within a given region.
Read more about Modular Green Homes: Affordability and Sustainability
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
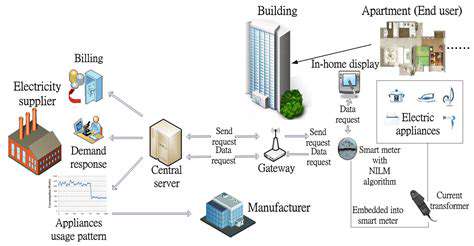
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing