Rainwater Harvesting: Sustainable Water Solutions
Introduction to Rainwater Harvesting Systems

Understanding Rainwater Harvesting
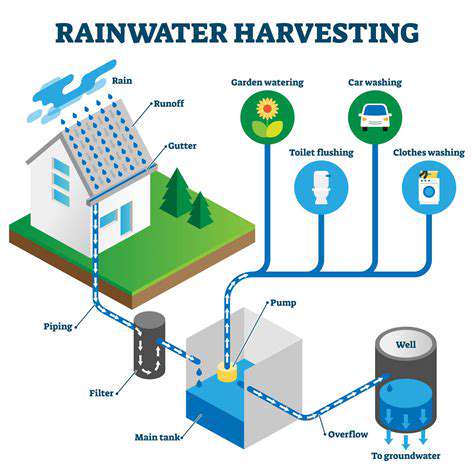
Rainwater harvesting is the process of collecting and storing rainwater for later use. This method offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional water sources, especially in areas facing water scarcity or high water costs. It's a vital practice for conserving water resources and reducing reliance on municipal water supplies. By utilizing rainwater, communities and individuals can significantly decrease their environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
The practice has ancient roots, with historical examples of rainwater collection systems used across various cultures worldwide. Modern applications of rainwater harvesting are diverse, ranging from residential rooftop systems to large-scale agricultural projects.
Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
Implementing rainwater harvesting systems provides numerous advantages. Reduced water bills are a primary benefit, as collected rainwater can be used for irrigation, toilet flushing, and other non-potable uses. This translates to significant financial savings over time, especially in areas with high water rates.
Furthermore, rainwater harvesting can enhance community resilience by creating a backup water supply during droughts or water shortages. This is particularly crucial in regions prone to water stress, making the community more self-sufficient.
Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Various types of rainwater harvesting systems are available, ranging from simple DIY solutions to complex commercial installations. Rooftop systems are a popular choice for residential applications, collecting rainwater from the roof and directing it into storage tanks or barrels. These systems are relatively straightforward to install and maintain.
Choosing the Right System
Selecting the appropriate rainwater harvesting system depends on several factors, including the specific needs and resources available. Factors such as the amount of rainfall in the region, the size of the property, and the intended uses of the collected water all play a role in determining the most suitable system.
Careful consideration of the local climate and water regulations is critical for ensuring a successful and compliant system.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation is essential for the effectiveness and longevity of a rainwater harvesting system. Professional installation ensures that the system is designed and built to meet local regulations and the specific needs of the property. A well-maintained system is crucial for preventing leaks and ensuring that the collected water remains clean and safe for intended use.
Environmental Impact
Rainwater harvesting significantly reduces the environmental impact of water consumption. By decreasing the demand for treated municipal water, it lessens the strain on water treatment plants and reduces the need for energy-intensive water pumping. This, in turn, contributes to a smaller carbon footprint and a healthier environment.
Cost and Return on Investment
The initial investment for rainwater harvesting systems can vary depending on the system's complexity and size. While the upfront cost might seem substantial, the long-term financial benefits and environmental advantages often make it a worthwhile investment. The return on investment often stems from reduced water bills and the peace of mind associated with having a reliable water source. Furthermore, many municipalities offer incentives and rebates for installing rainwater harvesting systems, which can significantly offset the initial costs.
Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Surface Runoff Systems
Surface runoff systems are the most common type of rainwater harvesting system. These systems collect rainwater that flows over the ground surface, typically from rooftops, paved areas, or other impervious surfaces. They are relatively simple to install and maintain, making them a popular choice for homeowners. This method usually involves directing the runoff into a storage tank, often located underground or on the property. The collected water can then be used for various purposes, such as irrigation, toilet flushing, or laundry.
Rooftop Collection Systems
Rooftop collection systems are designed to capture rainwater directly from the roof. These systems are efficient and can provide a significant amount of water, particularly in areas with high rainfall. They involve a network of gutters, downspouts, and pipes that channel the rainwater to a storage tank. Rooftop systems often include filters to remove debris and contaminants from the collected water, ensuring its suitability for various uses.
The water collected from rooftops is usually high in quality, making it suitable for a wide variety of applications, including drinking water in emergencies or for non-potable water uses.
Underground Storage Tanks
Underground storage tanks are a common choice for storing rainwater due to their ability to maintain a constant temperature and protect the water from contamination. They are often buried below ground level, minimizing their visual impact on the landscape. These tanks are generally made of durable materials like concrete, fiberglass, or polyethylene and are designed to hold large volumes of water.
Another benefit of underground storage is their ability to insulate the water, preventing temperature fluctuations that might affect its suitability for certain applications.
Cistern Systems
Cistern systems, a more traditional approach, typically involve collecting rainwater in large, elevated storage tanks, often called cisterns. These tanks are commonly constructed from materials like clay or concrete, and their design often incorporates features for water filtration. These systems have a long history and are a reliable way to store rainwater, offering a timeless solution to water collection. The elevated storage allows for gravity-fed distribution of the water to various points of use.
Greywater Harvesting Systems
Greywater harvesting systems collect and treat wastewater from sinks, showers, and washing machines, rather than rainwater. This water can be used for irrigation, toilet flushing, or other non-potable purposes. These systems are beneficial in areas with water scarcity or limited access to municipal water. Careful filtration and treatment are crucial in greywater systems to prevent the spread of disease and maintain water quality. Using greywater is an environmentally conscious choice, reducing the reliance on freshwater sources.
Rain Barrel Systems
Small-scale rainwater harvesting is often achieved using rain barrels. These relatively inexpensive and easy-to-install systems collect rainwater from rooftops and store it in large barrels for use in irrigation. Rain barrels are a great way for homeowners to reduce water bills and contribute to water conservation. Their simple design and accessibility make them ideal for individual property owners or small gardens. Often, these systems use a simple filtration system to remove larger debris before storage.
Combined Systems
Some rainwater harvesting systems combine different approaches, such as collecting rainwater from rooftops and using greywater for irrigation. These combined systems offer a more comprehensive solution to water conservation, maximizing the use of available resources. Such systems are particularly beneficial in areas with limited water availability or where multiple water sources are practical. The design and implementation of a combined system require careful planning and consideration of the specific needs of the property.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies

Real-World Applications of Machine Learning in Healthcare
Machine learning (ML) algorithms are revolutionizing healthcare, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes. ML models can analyze vast amounts of patient data, including medical images, lab results, and electronic health records, to identify patterns and predict potential health risks. This allows healthcare providers to proactively intervene and prevent serious illnesses, ultimately improving the overall health of the population.
From detecting cancerous tumors in medical images with high accuracy to predicting patient readmission risk, ML applications are transforming various aspects of healthcare. These applications are not just limited to diagnosis and prediction; they also play a crucial role in drug discovery, personalized medicine, and robotic surgery, opening up new avenues for improving patient care.
Case Studies Demonstrating Success
Numerous case studies showcase the successful implementation of machine learning in real-world healthcare settings. For instance, a study by Stanford University researchers demonstrated the ability of an ML algorithm to detect diabetic retinopathy from retinal images with a high degree of accuracy, potentially preventing vision loss. This type of technology can significantly reduce the burden on healthcare systems by enabling early detection and intervention. These tools can also help streamline workflows, freeing up clinicians to focus on patient care.
Another compelling example involves using ML to predict hospital readmissions. By analyzing patient data, ML models can identify high-risk patients and tailor interventions to reduce readmission rates. This not only improves patient outcomes but also saves healthcare systems substantial financial resources. This approach to preventative care is a key component of modern healthcare initiatives.
Impact on Drug Discovery and Development
Machine learning is rapidly transforming drug discovery and development, accelerating the process of identifying potential drug candidates and optimizing clinical trials. ML algorithms can analyze vast biological datasets, including genomic data and protein structures, to identify new drug targets and predict the efficacy of potential treatments. This can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with traditional drug development methods.
ML also enables the development of personalized medicine approaches, tailoring treatments to individual patients based on their specific genetic makeup and medical history. This approach promises to lead to more effective and safer treatments, improving patient outcomes and reducing adverse effects.
Future Trends and Possibilities
The future of machine learning in healthcare is brimming with exciting possibilities. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated applications in areas like personalized medicine, predictive analytics, and robotic surgery. Expect to see more integration of ML into existing healthcare systems, leading to more efficient and effective patient care.
The integration of machine learning into healthcare systems is rapidly evolving and promises to reshape the landscape of medicine in the coming years. This includes the potential for remote patient monitoring, personalized treatment plans, and proactive disease management.
Further research and development in this field will undoubtedly lead to even more innovative applications, ultimately improving the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.
Read more about Rainwater Harvesting: Sustainable Water Solutions
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing