Climate Risk Analytics in Real Estate Due Diligence: A Comprehensive Guide
Physical climate risks pose significant threats to critical infrastructure. Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events can lead to substantial damage to buildings, roads, bridges, and other vital infrastructure components. This damage can disrupt essential services and result in substantial economic losses.
Damage to infrastructure, particularly in vulnerable communities, can have devastating long-term impacts on the population's well-being and economic stability. The disruption of essential services such as transportation and communication can severely hinder recovery efforts.
Transition Risks: Adapting to a Low-Carbon Economy
Transition risks are related to the shift towards a low-carbon economy. This transition necessitates significant changes in energy production, transportation, and industrial processes. Businesses and governments must adapt to these changes, which can involve significant investments and adjustments in their operations.
The transition to a low-carbon economy presents both opportunities and challenges. Companies that anticipate and adapt to these changes have the potential to gain a competitive advantage. However, those who fail to adapt may face substantial financial and operational difficulties.
Climate Risk Assessment and Modeling
Accurate climate risk assessment involves employing sophisticated modeling techniques to understand the potential impacts of climate change on specific locations and sectors. These models incorporate historical data, climate projections, and socioeconomic factors to estimate the likelihood and severity of future climate-related events.
Accurate modeling helps in identifying vulnerable areas and developing targeted mitigation strategies. A thorough understanding of these risks is essential for effective resource allocation and policy development.
Climate Risk Management Strategies
Effective climate risk management requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing various strategies. These strategies include adaptation measures to adjust to the impacts of climate change, mitigation measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and resilience-building initiatives to enhance community preparedness and recovery.
Robust strategies for climate risk management must incorporate a holistic perspective, recognizing the interdependence of various sectors and the need for collaborative efforts between governments, businesses, and communities.
Financial Implications of Climate Risk
Climate change poses significant financial implications for businesses, governments, and individuals. The costs associated with damage from extreme weather events, adaptation measures, and transition to a low-carbon economy can be substantial. Understanding these financial implications is crucial for developing effective risk management strategies.
Failing to adequately address climate risk can lead to substantial financial losses and disrupt economic stability. Proactive measures for managing these risks are essential for long-term economic sustainability.
Climate Risk and Societal Impacts
Climate risk extends beyond economic impacts and has profound implications for society as a whole. Displacement, food insecurity, and health issues can arise due to climate change. Understanding the societal impacts is crucial for comprehensive risk assessment and management.
Climate change disproportionately affects vulnerable populations, exacerbating existing inequalities. Developing equitable and inclusive risk management strategies is essential for building a resilient and sustainable future for all.
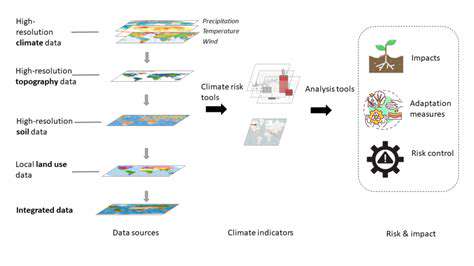
Integrating Climate Risk into Investment Strategies
Understanding the Significance of Climate Risk
Climate change is no longer a distant threat; it's a present-day reality impacting businesses and investment portfolios worldwide. Understanding and quantifying the financial risks associated with climate change is crucial for investors seeking long-term stability and returns. This involves recognizing the potential for physical risks like extreme weather events, sea-level rise, and changing precipitation patterns, as well as transition risks associated with the shift to a low-carbon economy. Ignoring these risks could lead to substantial losses down the line.
Climate change's effects are becoming increasingly apparent, with more frequent and intense extreme weather events causing disruption to supply chains, infrastructure damage, and increased insurance costs. Recognizing these phenomena as integral components of investment analysis is paramount.
Identifying Climate-Related Financial Risks
Integrating climate risk into investment strategies requires a comprehensive assessment of potential financial impacts. This process involves identifying specific climate-related risks relevant to each investment. For example, a company heavily reliant on fossil fuels faces significant transition risks as the world moves towards renewable energy. Similarly, a real estate investment in coastal areas is exposed to physical risks from sea-level rise. A thorough risk assessment must consider both the likelihood and potential magnitude of these risks.
Incorporating Climate Data into Investment Models
Modern investment models need to be augmented with climate data to provide a more complete picture of potential risks and opportunities. This includes incorporating climate projections, historical climate data, and scientific insights into valuation methodologies. Advanced analytics, including scenario planning, stress testing, and portfolio diversification strategies, can help investors effectively manage climate-related risks and capitalize on emerging opportunities within the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Developing Climate-Resilient Investment Portfolios
Creating climate-resilient investment portfolios involves actively selecting investments with lower climate-related risks. This may involve favoring companies with strong sustainability practices and exposure to renewable energy sectors. Diversifying across various asset classes and geographies can also help mitigate potential climate risks. Further, incorporating climate-focused ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors into portfolio construction and management can lead to portfolios that are not only more resilient to climate change but also better aligned with long-term sustainability goals.
Implementing Effective Monitoring and Reporting Mechanisms
To ensure the effectiveness of climate risk integration, robust monitoring and reporting mechanisms are essential. Regularly reviewing and updating climate-related risks in investment portfolios is crucial. This includes ongoing analysis of climate change impacts on specific holdings. Transparency and clear communication regarding climate risk management practices are vital for building investor trust and demonstrating responsible investment principles. This also involves reporting on the portfolio's alignment with climate goals and any associated financial impacts.