Climate Finance for Real Estate Resilience
Green Bonds and Their Role in Real Estate Resilience
Understanding Green Bonds
Green bonds are a specific type of bond issued by governments, corporations, or other entities to finance projects with environmental benefits. These projects typically focus on renewable energy, energy efficiency improvements, sustainable transportation, waste management, and other initiatives aimed at mitigating climate change and fostering environmental sustainability. By investing in these bonds, investors contribute to a healthier planet while also earning a return on their investment.
Understanding the mechanics of green bonds is crucial. Investors scrutinize the projects funded by these bonds, ensuring they align with predefined environmental criteria. This due diligence process helps to prevent greenwashing and maintain the integrity of the market. Transparency in reporting the environmental impact of funded projects is also a key feature of this bond type, ensuring accountability and investor confidence.
Green Bonds and Real Estate Resilience
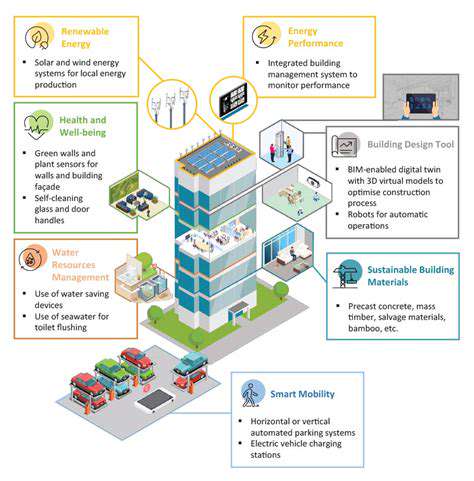
Real estate is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, from construction materials and energy consumption to waste generation during its lifecycle. Green bonds can play a pivotal role in enhancing the resilience of the real estate sector by funding projects that improve energy efficiency, reduce carbon footprints, and adapt to climate change impacts. This includes investments in sustainable building materials, smart grids, and climate-resilient infrastructure within real estate developments.
The integration of green technologies and practices in real estate projects, financed through green bonds, can lead to significant long-term cost savings for building owners and tenants. This includes reduced energy bills and lower maintenance costs, making sustainable development not just environmentally responsible but also economically viable.
Financing Sustainable Building Practices
Green bonds can directly fund the implementation of sustainable building practices, such as using recycled materials, incorporating renewable energy sources (solar panels, wind turbines), and implementing energy-efficient designs. These investments can result in buildings with lower operating costs and a reduced environmental footprint throughout their lifespan, contributing to a healthier and more sustainable urban environment.
Furthermore, the use of green bonds can incentivize developers and property owners to adopt sustainable practices. By offering attractive financing options, green bonds can make sustainable building choices more accessible, driving a significant shift towards environmentally conscious real estate development.
Enhancing Climate Change Adaptation
Climate change presents significant risks to real estate assets, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and changing precipitation patterns. Green bonds can support projects that enhance the resilience of real estate to these threats. This includes funding infrastructure improvements, such as flood defenses, and investments in climate-resilient building designs.
Promoting Sustainable Urban Development
Green bonds can play a crucial role in promoting sustainable urban development by funding projects that improve urban environments and enhance the quality of life for residents. This includes investments in green spaces, urban farming initiatives, and sustainable transportation systems. By fostering sustainable urban development, green bonds contribute to creating healthier, more resilient, and more livable cities.
Measuring and Reporting Impact
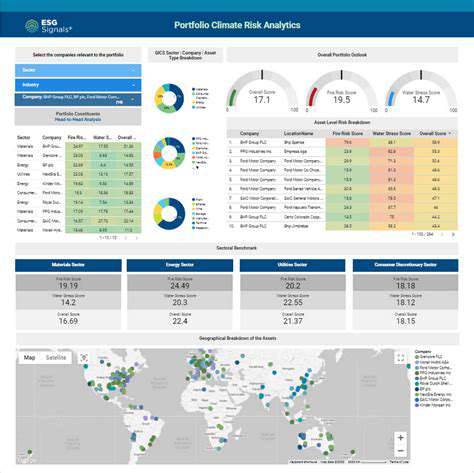
Measuring and reporting the environmental impact of green bond-financed projects is critical for maintaining transparency and accountability. Standardized metrics and reporting frameworks are essential to ensure that the investments are truly achieving their environmental goals. This data allows stakeholders to assess the effectiveness of green bonds and make informed decisions regarding future investments.
Strong reporting frameworks also encourage continuous improvement in environmental performance, pushing the sector towards more sustainable practices and fostering innovation in climate-resilient real estate development.
Beyond Funding: Policy and Regulatory Support for Resilience
Policy Frameworks for Resilience
Effective climate resilience requires more than just financial resources; it necessitates comprehensive policy frameworks that integrate climate considerations into all relevant sectors. These frameworks should establish clear targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, adapting to unavoidable climate impacts, and building societal resilience. Policies must address vulnerabilities across different sectors, from infrastructure and agriculture to health and human settlements, and foster innovation in climate-friendly technologies and practices. The development and implementation of such policies are crucial for ensuring that financial investments in resilience are impactful and sustainable.
Policymakers need to recognize the interconnectedness of climate change with other societal challenges, like poverty and inequality. Policies should aim to promote equity and ensure that the benefits of climate resilience initiatives reach all members of society, particularly the most vulnerable.
Regulatory Incentives for Green Technologies
Regulatory support plays a vital role in fostering the development and adoption of climate-resilient technologies. Incentives, such as tax breaks, subsidies, and streamlined permitting processes, can encourage businesses and individuals to invest in green technologies and practices. These incentives should be designed to stimulate innovation, accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy, and create new jobs in the green sector. Such policies can significantly increase the efficiency of climate finance investments by facilitating the deployment of effective resilience solutions.
Streamlining Permitting Processes
Bureaucratic hurdles and lengthy permitting processes often hinder the implementation of climate resilience projects. Simplifying and accelerating these processes can significantly expedite the deployment of climate-resilient infrastructure and technologies. Streamlined procedures can reduce costs, reduce delays, and foster a more conducive environment for private sector investment in resilience solutions. This is crucial to maximizing the impact of climate finance and ensuring that projects are implemented effectively and efficiently.
Transparent and predictable regulations provide crucial certainty to investors and help unlock private sector capital for climate resilience initiatives.
Building Capacity for Climate Resilience
Effective climate resilience requires strong institutional capacity at all levels, from local communities to national governments. Investing in training, education, and knowledge sharing is essential to build the skills and expertise needed to develop, implement, and manage climate resilience strategies. Capacity building initiatives should focus on providing technical expertise and fostering collaboration among different stakeholders, including local communities, civil society organizations, and the private sector.
Addressing Equity and Social Inclusion
Climate resilience efforts must prioritize equity and social inclusion, recognizing that climate change disproportionately affects vulnerable populations. Policies and regulations should actively address the specific needs of marginalized communities, ensuring that climate resilience initiatives are designed and implemented in ways that benefit all members of society. This may include targeted support for marginalized communities, community engagement initiatives, and culturally sensitive approaches to climate action.
International Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Climate resilience is a global challenge that requires international collaboration and knowledge sharing. International cooperation can facilitate the exchange of best practices, technologies, and financial resources to support climate resilience initiatives worldwide. Strengthening partnerships and fostering knowledge transfer among nations can accelerate the development and implementation of effective climate resilience strategies and ensure that solutions are adapted to local contexts.
Monitoring and Evaluation Frameworks
Robust monitoring and evaluation frameworks are essential to assess the effectiveness of climate resilience policies and projects. These frameworks should track progress towards established targets, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that resources are allocated efficiently. Regular evaluation and reporting mechanisms can provide valuable insights into the impact of policies and inform adjustments to improve future outcomes. Transparent and accessible data is essential for effective accountability and learning.
Read more about Climate Finance for Real Estate Resilience
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing