Understanding Real Estate Climate Risk: A Comprehensive Overview
The Role of Government and Regulation
Effective climate policies are essential for managing real estate risks. Updated building codes, incentives for sustainable construction, and funding for adaptation projects can significantly reduce vulnerabilities. Collaboration between government, industry, and communities is key to addressing climate challenges effectively.
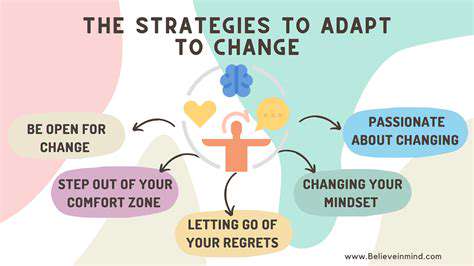
When learners actively engage with content rather than passively consume it, they form deeper connections with the material. Instead of just memorizing facts, they question, analyze, and apply concepts practically. This hands-on approach leads to significantly better retention rates and deeper conceptual understanding. The difference resembles watching a cooking show versus actually preparing the meal yourself.
Evaluating Transition Risks and Opportunities in the Real Estate Sector
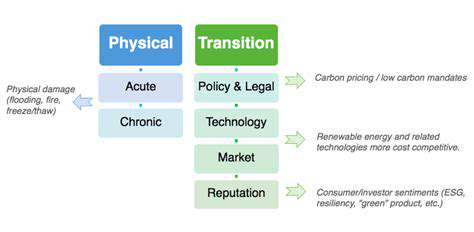
Evaluating Transition Risks in Operations
Operational transitions bring various challenges, from technological changes to shifts in market conditions. Recognizing these risks is crucial for maintaining efficiency and performance during changes. Each potential risk should be evaluated for its likelihood and potential impact on organizational goals.
Identifying Key Transition Phases
Effective transition management requires clear phase identification: planning, implementation, and review. Each stage presents unique challenges that must be addressed systematically.
Analyzing Potential Operational Disruptions
A thorough examination of possible disruptions—equipment failures, process bottlenecks, or supply chain issues—is essential. Both internal and external factors must be considered to develop comprehensive mitigation plans.
Assessing Personnel Impacts
Staff changes often create significant transition risks that organizations underestimate. Role changes, new responsibilities, or workforce reductions can disrupt operations. Proper training and communication strategies are vital for smooth transitions.
Evaluating Technological Integration Risks
New technology implementation carries risks throughout its lifecycle, from initial setup to ongoing maintenance. Compatibility issues, data migration challenges, and staff training requirements must all be addressed.
Analyzing Financial Implications
Transition risks have clear financial consequences. Quantifying potential costs from delays, equipment failures, or retraining enables better resource allocation and contingency planning.
Developing Mitigation Strategies
After identifying risks, specific mitigation plans must be developed for each one. Proactive measures significantly reduce transition-related disruptions. Ongoing monitoring allows for necessary adjustments during implementation.
Strategies for Mitigating Climate Risks in Real Estate

Understanding the Urgency of Climate Action
The escalating effects of climate change are now undeniable, affecting communities through sea level rise, extreme weather, and agricultural disruptions. Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive solutions balancing immediate needs with long-term planning.
Implementing Sustainable Energy Solutions
Shifting to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal power is essential. These alternatives reduce fossil fuel dependence while creating sustainable energy infrastructure. Improving energy efficiency in buildings and transportation further reduces carbon footprints.
Enhancing Carbon Capture and Storage Techniques
Advanced carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies can significantly reduce emissions from industrial sources. CCS prevents CO2 from entering the atmosphere, helping mitigate existing pollution levels. Continued research aims to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Promoting Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Methods like no-till farming, crop rotation, and cover cropping improve soil health while reducing chemical use. These practices enhance environmental sustainability while maintaining agricultural productivity. Support programs help farmers adopt these techniques.
Protecting and Restoring Ecosystems
Natural ecosystems serve as vital carbon sinks. Preserving and restoring forests, wetlands, and oceans is crucial for climate mitigation. This requires effective policies, sustainable land management, and international cooperation.
Encouraging International Cooperation and Policy Changes
Global collaboration is essential for effective climate action. International agreements should promote emission reduction targets and support green innovation. Policies must incentivize sustainability while discouraging environmentally harmful practices.