Physical Climate Risk Assessments for Asset Management
Developing Climate-Resilient Asset Management Strategies
Understanding the Urgency of Climate Resilience
Climate change is no longer a distant threat; its impacts are being felt globally, across diverse sectors, and with increasing frequency. The imperative to build climate-resilient assets is paramount to safeguarding communities, economies, and ecosystems. This urgency stems from the escalating intensity and unpredictability of extreme weather events like hurricanes, floods, droughts, and wildfires, which are directly impacting infrastructure, agriculture, and human well-being.
Recognizing this crucial need, governments, businesses, and individuals are increasingly focusing on developing strategies and implementing measures that bolster the resilience of their assets against the changing climate. This proactive approach is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring long-term sustainability.
Assessing Vulnerability and Identifying Risks
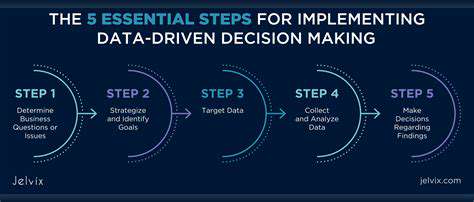
A critical first step in developing climate-resilient assets is a thorough assessment of vulnerability and risk. This involves identifying specific assets, such as buildings, infrastructure, and agricultural lands, and evaluating their susceptibility to various climate-related hazards. This process necessitates a comprehensive analysis of historical data, including weather patterns, extreme event occurrences, and societal impacts.
Detailed risk assessments provide crucial insights into potential damages and losses, allowing for informed decision-making in the design and implementation of adaptation measures. These assessments should also consider the social and economic implications of different climate scenarios.
Integrating Climate Change Considerations into Design and Construction
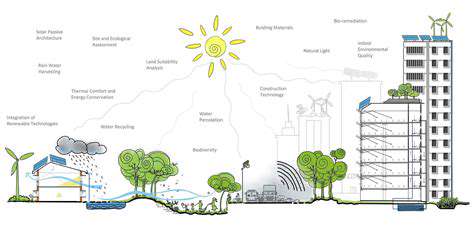
Integrating climate change considerations into the design and construction phases is essential for building resilience into assets from the outset. This includes incorporating design elements that can withstand extreme weather events, such as elevated structures, reinforced materials, and enhanced drainage systems. Implementing these measures upfront is far more cost-effective than trying to retrofit existing assets later.
Sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies should also be prioritized to reduce the environmental footprint of new developments and minimize ongoing energy consumption, especially in high-risk areas. This approach not only enhances asset resilience but also promotes environmental stewardship.
Implementing Monitoring and Evaluation Systems
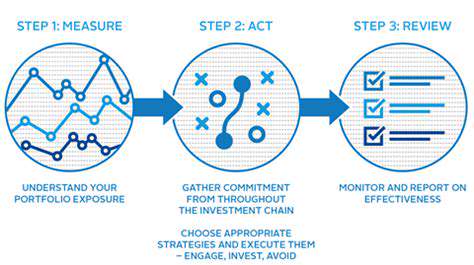
Robust monitoring and evaluation systems are crucial for tracking the performance of climate-resilient assets and assessing their effectiveness over time. This involves establishing clear metrics to measure the impact of adaptation measures on reducing vulnerability and increasing resilience. Collecting and analyzing data on asset performance in response to climate-related events is essential for continuous improvement and adaptation.
Regular monitoring also allows for adjustments to strategies and interventions as needed, ensuring that assets remain resilient to evolving climate conditions. These systems ensure that investments in climate resilience are not only effective but also sustainable in the long run.
Promoting Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Developing climate-resilient assets requires a collaborative approach involving various stakeholders. This includes governments, businesses, researchers, and communities. Collaboration facilitates the sharing of best practices, knowledge, and resources, leading to more effective and comprehensive strategies. International cooperation is also vital to address the global nature of climate change and its impacts.
Sharing lessons learned from successful implementation in different contexts allows for the adaptation and refinement of strategies, enhancing the overall effectiveness of climate-resilient asset development. This knowledge sharing is essential for a rapidly evolving global challenge.
Read more about Physical Climate Risk Assessments for Asset Management
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing