AI in Real Estate: Unlocking Hidden Value in Commercial Properties

Leveraging Customer Feedback for Enhanced Business Insights
Customer feedback serves as a vital tool for businesses to refine their offerings and strategies. Unlike traditional metrics, feedback provides a nuanced view of customer experiences, revealing both strengths and areas needing attention. Businesses that actively analyze feedback can uncover hidden opportunities to innovate and enhance customer satisfaction. This approach fosters stronger relationships and promotes sustainable growth.
By systematically collecting and reviewing feedback, companies gain insights into customer preferences and expectations. These insights inform product development, marketing efforts, and service improvements. Organizations that prioritize feedback often enjoy higher customer retention and brand loyalty.
Identifying and Addressing Critical Pain Points
While traditional metrics offer a high-level view, they often miss the finer details of customer experiences. Feedback, however, highlights specific issues that quantitative data might overlook. For instance, a spike in customer churn could stem from a usability problem that only becomes apparent through direct feedback.
Analyzing recurring themes in feedback allows businesses to pinpoint and resolve critical issues. Addressing these concerns can lead to improved product usability, better service, and higher overall satisfaction.
Optimizing Product Development and Innovation
Customer feedback drives innovation by informing product design and functionality. Integrating customer insights into development ensures products meet real-world needs. This customer-centric approach often results in more intuitive and valuable solutions.
Feedback helps teams focus on features and improvements that matter most to users. Iterative feedback loops ensure continuous refinement and alignment with customer expectations.
Enhancing Customer Experience and Engagement
Feedback directly shapes the customer journey. Companies that actively seek and act on feedback demonstrate commitment to their audience, building trust and loyalty. This engagement translates into measurable improvements in satisfaction and retention.
Understanding customer interactions—from initial contact to post-purchase support—enables businesses to create seamless experiences. Feedback identifies friction points, allowing for targeted improvements that strengthen customer relationships.
Predictive Modeling for Future Value Projections
Understanding the Fundamentals of Predictive Modeling
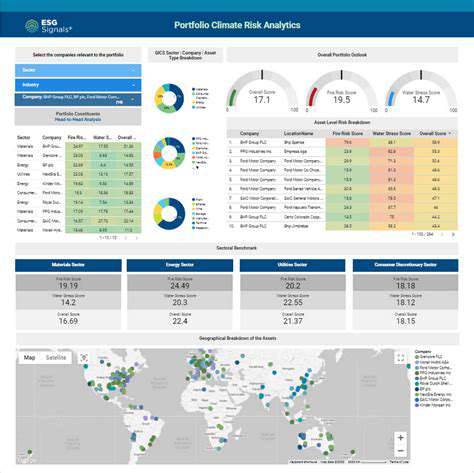
Predictive modeling uses historical data and statistical techniques to forecast outcomes. In real estate, this involves analyzing past trends, property attributes, and economic factors to predict future values. Reliable models depend on thorough data preparation and validation.
The goal is to identify patterns that inform predictions. Models range from simple regressions to advanced machine learning algorithms, depending on data complexity and accuracy requirements.
Data Sources and Feature Engineering
High-quality data is essential for accurate predictions. Real estate models draw from listings, public records, and economic reports. Feature engineering refines raw data into meaningful variables, such as price-per-square-foot or neighborhood safety metrics, enhancing model precision.
Model Selection and Training
Choosing the right model depends on the data and prediction goals. Simpler scenarios may use linear regression, while complex relationships might require neural networks. Training involves optimizing model parameters to minimize errors, with regular testing to prevent overfitting.
Evaluating Model Performance
Metrics like R-squared and mean absolute error assess prediction accuracy. These indicators help determine how well the model generalizes to new data, ensuring reliability.
Integrating Predictive Modeling into Real Estate Decision-Making
Predictive models guide investment choices, development strategies, and client advisement. Accurate forecasts empower stakeholders to make informed decisions, reducing risks and maximizing returns.
Addressing Limitations and Ethical Considerations
Models are limited by their data and external factors like economic shifts. Ethical concerns, such as bias in data or AI applications, must be addressed to ensure fair and responsible use in real estate.
Improving Portfolio Management and Decision-Making
Defining Clear Investment Objectives
Effective portfolio management starts with specific, measurable goals. These might include capital growth, income generation, or risk mitigation. Clear objectives align investments with long-term financial plans. Goals should account for timeframes, risk tolerance, and financial needs.
Quantifiable targets, like a 10% annual return, simplify progress tracking and strategy adjustments.
Assessing Risk Tolerance and Capacity
Risk tolerance reflects an investor's comfort with volatility, while risk capacity measures their ability to absorb losses. A thorough evaluation ensures portfolios match the investor's financial situation. Factors like emergency funds and debt obligations influence this assessment.
Diversification for Reduced Risk
Diversifying across asset classes, sectors, and regions minimizes risk. A balanced portfolio might include stocks, bonds, and real estate. Low-correlation assets further reduce volatility.
Strategic Asset Allocation
Allocating assets based on goals and market conditions is key. This strategy guides long-term investment decisions and rebalancing efforts. Adjustments should reflect changes in objectives or market dynamics.
Regular Monitoring and Rebalancing
Portfolios require ongoing review to stay aligned with goals. Rebalancing ensures the desired asset mix is maintained, optimizing performance and risk levels.
Tax Optimization Strategies
Tax-efficient investing, such as using retirement accounts or tax-loss harvesting, enhances after-tax returns. Understanding tax implications is critical for maximizing long-term gains.
Read more about AI in Real Estate: Unlocking Hidden Value in Commercial Properties
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing