Smart Building Predictive Maintenance for Fire Systems
Proactive Maintenance and Reduced Downtime
Predictive Maintenance Strategies
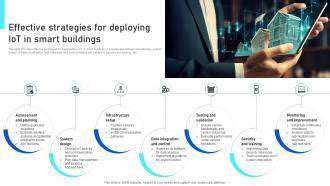
Implementing proactive maintenance strategies in smart buildings involves leveraging data analytics and machine learning to forecast potential equipment failures. This allows facilities managers to schedule maintenance before equipment breaks down, minimizing costly downtime and ensuring consistent operational efficiency. Predictive maintenance moves away from reactive maintenance, where repairs are only performed after a failure has occurred. This shift is crucial in optimizing maintenance schedules and maximizing the lifespan of building systems.
Key components of predictive maintenance strategies include analyzing sensor data from various building systems, such as HVAC, lighting, and elevators. Patterns and anomalies in this data can be identified to pinpoint potential problems before they escalate, enabling targeted interventions.
Data Collection and Analysis
A crucial aspect of proactive maintenance is the robust collection and analysis of data. Smart building technologies provide a wealth of information, including sensor readings, operational logs, and environmental data. This data must be meticulously collected, stored, and analyzed to derive meaningful insights into equipment performance and potential failure points.
Sophisticated algorithms are used to process the collected data. These algorithms identify trends, anomalies, and patterns that might signal impending equipment failures. Data visualization tools are also essential for presenting these insights in a clear and understandable manner to maintenance teams.
Early Fault Detection
Proactive maintenance hinges on the ability to detect potential equipment failures in their early stages. By identifying subtle deviations from normal operating parameters, predictive maintenance systems can alert technicians well before a major breakdown occurs. This early detection capability is critical for minimizing the impact of equipment failures on building operations.
Advanced algorithms can identify subtle changes in vibration patterns, temperature fluctuations, or energy consumption that might indicate a developing problem. This early warning system allows for timely intervention and prevents costly and disruptive breakdowns.
Optimized Maintenance Schedules
Predictive maintenance allows for the creation of optimized maintenance schedules. Instead of adhering to rigid, pre-determined maintenance cycles, proactive strategies adjust schedules based on the actual condition of the equipment. This approach reduces unnecessary maintenance tasks and ensures that repairs are performed only when necessary.
This optimization translates to significant cost savings and improved efficiency. The optimized schedules also minimize disruptions to building operations, reducing the impact on tenants and occupants.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Implementing proactive maintenance strategies in smart buildings leads to improved operational efficiency across the board. Reduced downtime translates to increased productivity and higher operational uptime. The proactive approach also minimizes the risk of unexpected equipment failures and associated disruptions.
Ultimately, the optimized maintenance schedule and reduced downtime lead to significant cost savings and enhanced tenant satisfaction. Smart building predictive maintenance is a powerful tool for maximizing building performance and minimizing operational costs.
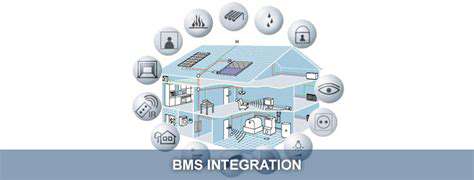
Integration with Building Management Systems
The effective implementation of predictive maintenance requires seamless integration with existing building management systems (BMS). Data from sensors and other sources needs to be seamlessly fed into the BMS platform, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis. This integration allows for the automated triggering of maintenance alerts and ensures that relevant information is readily accessible to maintenance personnel.
Integrating predictive maintenance tools with existing building management systems ensures that the insights derived from data analysis are effectively utilized to improve building operations and reduce maintenance costs. This seamless integration is key to successful implementation.
Enhancing Building Safety and Reducing Risks

Improving Fire Safety Measures
Implementing robust fire safety measures is crucial for minimizing the risk of fire-related incidents in buildings. This involves proactive measures like regular fire drills, ensuring that fire extinguishers are readily accessible and properly maintained, and installing sophisticated fire detection systems. These preventative measures significantly reduce the potential for loss of life and property damage. Further, comprehensive fire safety training for building occupants and staff is essential to ensure preparedness and rapid response in case of a fire emergency.
Strengthening Structural Integrity
Regular inspections and maintenance of structural components are vital for ensuring the building's stability and longevity. This includes checking for signs of deterioration in foundations, walls, and roofs. Properly addressing structural weaknesses can prevent catastrophic failures and ensure the continued safety of occupants. Furthermore, employing advanced structural analysis techniques allows for a deeper understanding of a building's potential vulnerabilities and enables the implementation of targeted interventions.
Enhancing Emergency Evacuation Procedures
Clearly defined and well-rehearsed evacuation procedures are paramount to a swift and safe escape in case of an emergency. These procedures must be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect any changes in the building's layout or occupancy. Effective communication during an emergency is critical, and this includes clear signage, designated assembly points, and well-trained personnel to guide occupants. Every building occupant should understand their roles and responsibilities during an evacuation.
Implementing Advanced Security Systems
Integrating advanced security systems, such as access control and surveillance, can significantly enhance the safety and security of a building. This can deter unauthorized access and provide real-time monitoring of the premises. This proactive security approach enhances the overall safety environment and facilitates quicker response times to security breaches. The use of technology can also be employed to provide real-time data on building occupancy and resource usage.
Promoting a Culture of Safety
Creating a culture of safety within a building is a fundamental aspect of enhancing overall safety. This involves fostering a sense of responsibility among occupants and staff regarding safety protocols. Regular safety awareness programs and training sessions can effectively instill safety consciousness and encourage proactive participation in safety initiatives. Encouraging open communication channels and providing a platform for feedback on safety concerns is essential in building a culture of safety.
Addressing Accessibility and Inclusivity
Ensuring accessibility and inclusivity in building design and operations is crucial for promoting safety for all occupants. This includes designing pathways and facilities that accommodate individuals with disabilities. Creating a welcoming and accessible environment promotes safety and well-being for everyone. Implementing universal design principles and providing accessible emergency exits will improve the safety of all building occupants.
Read more about Smart Building Predictive Maintenance for Fire Systems
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing