Regenerative Real Estate: Principles and Practice
Defining Regenerative Real Estate

Defining Regenerative Real Estate
Regenerative real estate represents a fundamental evolution beyond conventional sustainability efforts. This innovative framework focuses on comprehensive environmental health, community vitality, and architectural integrity. Rather than merely reducing harm, this methodology actively cultivates ecological and social capital for generations to come. It represents a transformative mindset shift - from damage control to active restoration of our living environments.
Core Tenets of Regeneration
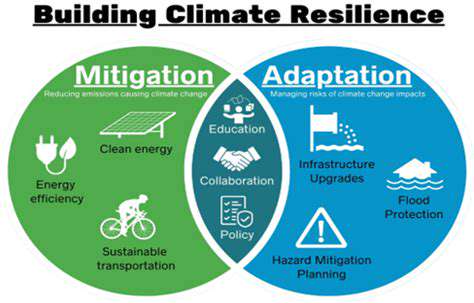
Regenerative real estate operates through several foundational pillars. These include dramatically reducing ecological footprints, revitalizing local ecosystems, fostering meaningful community participation, and developing inclusive economic models. The approach creates self-sustaining systems that strengthen both natural environments and human communities against future disruptions.
Ecological Stewardship
These developments prioritize carbon-negative operations through renewable energy integration and indigenous landscaping. Every material selection considers complete lifecycle impacts, with emphasis on closed-loop systems and waste elimination. Strategic resource conservation and innovative water reclamation systems form the backbone of these ecological interventions. The ultimate objective is creating buildings that actively enhance surrounding natural systems.
Community Empowerment
True regeneration demands equitable community benefits through inclusive housing models, local economic stimulation, and accessible public spaces. Successful projects intentionally redistribute benefits across socioeconomic groups while preserving cultural heritage. This often involves collaborative design processes that incorporate resident input from initial planning stages.
Economic Sustainability
Financial viability remains essential for scaling regenerative models. Creative financing mechanisms and cross-sector partnerships help maintain fiscal health. These projects frequently stimulate neighborhood economies through skilled job creation and support for minority-owned enterprises. The economic model proves that environmental responsibility and profitability can coexist.
Future-Proof Design
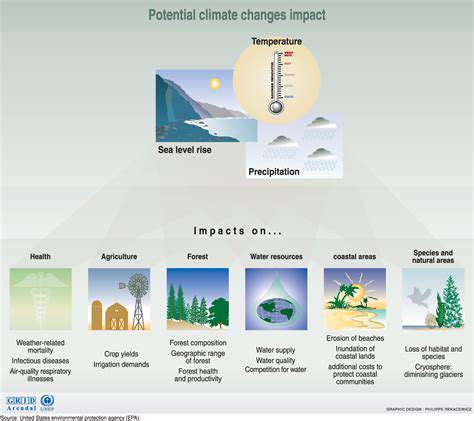
Regenerative developments incorporate climate resilience into their DNA through adaptive infrastructure and flexible spaces. This forward-looking perspective ensures buildings remain functional and valuable despite shifting environmental conditions. Design teams analyze multiple climate scenarios to create structures that evolve with changing needs.
Impact Verification
Rigorous measurement protocols validate regenerative claims through environmental, social and governance metrics. Comprehensive disclosure builds stakeholder trust while enabling continuous operational refinement. Standardized reporting frameworks allow for meaningful comparison across projects while accommodating local priorities.
Measuring and Reporting Progress
Holistic Performance Indicators
Regenerative projects demand multidimensional success metrics beyond financial KPIs. Evaluation frameworks assess ecological restoration, social cohesion, and governance quality simultaneously. This includes measuring energy efficiency gains, water conservation achievements, waste diversion rates, and emissions reductions alongside community health indicators, local hiring statistics, and accessibility improvements.
Comprehensive Baseline Assessment
Establishing detailed pre-development conditions forms the foundation for impact measurement. Teams document existing ecological systems, infrastructure conditions, and community demographics. This reference point enables accurate attribution of project outcomes and prevents greenwashing claims. Baseline studies typically include microclimate analysis, biodiversity inventories, and socioeconomic surveys.
Environmental Monitoring
Continuous tracking systems measure resource flows through the development. Smart meters track real-time energy and water usage patterns, while waste audits quantify diversion from landfills. Carbon accounting extends beyond operational emissions to include embodied carbon in building materials and transportation impacts. These systems often integrate with building automation for immediate performance optimization.
Community Impact Analysis
Qualitative and quantitative methods assess social outcomes through resident surveys, focus groups, and economic data. Key metrics track changes in neighborhood walkability, access to fresh food, educational opportunities, and healthcare services. Longitudinal studies measure generational impacts on community wealth and environmental justice indicators.
Financial Health Indicators
While prioritizing broader impacts, projects must maintain sound financials through diversified revenue streams and value capture mechanisms. Performance tracking includes traditional real estate metrics alongside innovative measurements like social return on investment (SROI) and ecosystem service valuations that quantify natural capital benefits.
Transparent Reporting
Regular impact reports utilize visual storytelling and plain language to engage diverse stakeholders. Digital dashboards provide real-time access to performance data, while annual sustainability reports contextualize achievements within broader climate goals. Third-party verification ensures credibility and prevents impact inflation claims.
Adaptive Management
Data insights drive continuous improvement through regular strategy reviews. Performance trends inform operational adjustments, while emerging technologies enable new solutions. This learning-oriented approach transforms each project into a living laboratory for regenerative innovation. Post-occupancy evaluations particularly valuable for refining future developments.
Read more about Regenerative Real Estate: Principles and Practice
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing