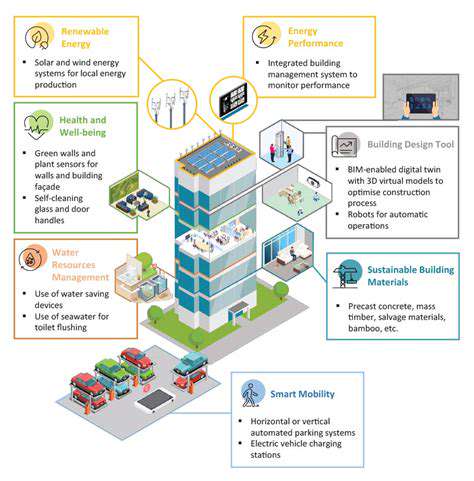
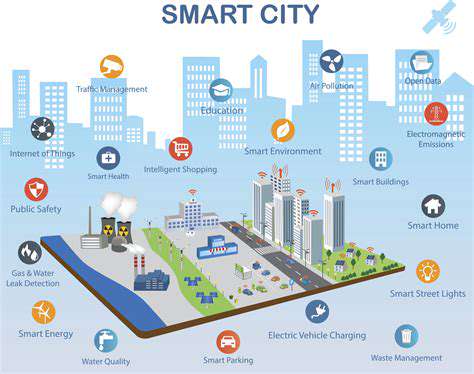
Smart Buildings and the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Rise of IoT Sensors in Building Automation
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors are revolutionizing building management systems by providing real-time data on various parameters, such as temperature, humidity, occupancy, and energy consumption. This continuous stream of information allows for proactive adjustments to optimize comfort, security, and energy efficiency. From sophisticated motion sensors that detect human presence to advanced environmental sensors that gauge air quality, IoT devices are transforming how buildings operate and interact with their surroundings.
The integration of these sensors empowers building managers with unprecedented control and visibility. Data collected from these devices can be analyzed to identify patterns and trends, leading to informed decisions about resource allocation, maintenance schedules, and overall building performance. This level of data-driven insight is crucial for achieving sustainability goals and creating more responsive and efficient spaces.
Data Collection and Transmission: The Backbone of Smart Buildings
The effectiveness of smart building technologies hinges on robust data collection and transmission protocols. High-speed networks are essential for transferring real-time sensor data to central processing units. Reliable communication channels are paramount for ensuring uninterrupted data flow, enabling continuous monitoring and control of building systems. Efficient data transmission enables the building management system to respond promptly to changing conditions, ensuring optimal performance and occupant comfort.
Secure data transmission is equally critical. Protecting sensitive building data from unauthorized access is paramount. Robust security measures are crucial to safeguard privacy, maintain system integrity, and prevent potential disruptions. This aspect of data handling is critical to the long-term reliability and trustworthiness of smart building technologies.
Connectivity Solutions for Seamless Integration
Various connectivity solutions are available to facilitate seamless integration of IoT sensors into building automation systems. From Wi-Fi and Bluetooth to cellular and dedicated low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN), these technologies offer diverse options for connecting sensors to the central control system. Selecting the appropriate connectivity solution depends on factors such as the range required, data transmission rate, and power consumption needs of the sensors.
The choice of connectivity method significantly impacts the overall performance and cost-effectiveness of the smart building system. Careful consideration of these factors is critical for creating a robust and scalable infrastructure that can support future expansion and technological advancements.
Impact on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Smart buildings equipped with IoT sensors and connectivity solutions can significantly enhance energy efficiency and sustainability. Real-time data enables optimization of lighting, HVAC systems, and other energy-consuming appliances. Predictive maintenance capabilities based on sensor data can minimize equipment failures, reduce downtime, and enhance the lifespan of building components. These advancements contribute to lower operating costs and a reduced carbon footprint.
Real-time adjustments to energy consumption patterns can be implemented based on occupancy and environmental conditions. This dynamic response to changing needs ensures significant energy savings and contributes to a more sustainable building environment. The integration of renewable energy sources can be further optimized with the data insights provided by IoT sensors.
Security and Privacy Considerations in Smart Buildings
Security and data privacy are paramount concerns in the implementation of smart building technologies. Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access and cyber threats is essential. Implementing robust security protocols and encryption methods is critical to safeguard the confidentiality and integrity of building information. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are necessary to ensure the ongoing protection of the system.
Addressing privacy concerns, especially regarding occupant data, is crucial. Transparency about data collection practices and ensuring user consent for data usage is essential for maintaining trust and upholding ethical standards. Strict adherence to data privacy regulations is paramount in safeguarding the rights and security of building occupants.
The Future of Smart Buildings: Enhanced User Experience and Operational Efficiency
The integration of IoT sensors and connectivity solutions is paving the way for future smart buildings that offer enhanced user experiences and operational efficiency. Personalized control over environmental settings, such as temperature and lighting, will be possible through intuitive user interfaces. Proactive maintenance schedules and predictive analytics will minimize disruptions and maximize building lifespan. These advancements will create more comfortable, efficient, and sustainable environments for occupants and building managers alike.
The future of smart buildings promises a seamless integration of technology and human needs. Continuous innovation in sensor technology, connectivity solutions, and data analytics will drive the evolution of smart buildings, creating spaces that are not only efficient but also responsive to the evolving demands of occupants and the environment.
Optimizing Energy Efficiency with Smart Building Technologies

Understanding Energy Consumption Patterns
Analyzing energy consumption patterns is crucial for identifying areas where energy waste occurs. This involves examining energy usage throughout the day, week, and year to pinpoint trends and anomalies. By understanding these patterns, we can pinpoint specific activities or equipment that contribute disproportionately to overall energy consumption, allowing us to target interventions effectively. For example, if a significant increase in energy use is consistently observed during peak hours, it could indicate inefficient lighting or inadequate insulation.
Regular monitoring of energy consumption data is essential to detect potential problems and adjust energy-saving strategies promptly. This data-driven approach allows for informed decisions and proactive measures to optimize energy efficiency.
Implementing Smart Technologies
Integrating smart technologies can significantly enhance energy efficiency. Smart thermostats, for example, can adjust temperatures automatically based on occupancy and external conditions, optimizing heating and cooling systems to minimize energy waste. Smart lighting systems can also be programmed to turn off lights in unoccupied areas, saving energy and reducing costs.
Improving Building Insulation
Proper building insulation is fundamental to energy efficiency. Insulating walls, roofs, and windows reduces heat transfer, minimizing energy loss in winter and heat gain in summer. This leads to lower heating and cooling costs and a more comfortable indoor environment. Well-insulated buildings require less energy to maintain a desired temperature range, directly contributing to a lower carbon footprint.
Furthermore, effective insulation enhances the overall building's structural integrity and resilience.
Optimizing HVAC Systems
Maintaining and optimizing HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems is crucial for energy efficiency. Regular maintenance checks, including cleaning filters and ensuring proper airflow, can significantly improve the efficiency of these systems. Properly calibrated HVAC systems can drastically reduce energy consumption while maintaining optimal indoor comfort. Replacing old, inefficient equipment with newer, high-efficiency models can also yield substantial energy savings over time.
Promoting Energy-Conscious Behaviors
Ultimately, promoting energy-conscious behaviors among occupants can significantly improve overall energy efficiency. Encouraging the use of energy-efficient appliances, turning off lights in unoccupied rooms, and optimizing thermostat settings are simple yet effective strategies. Educating occupants about energy conservation practices and providing clear guidelines can foster a culture of sustainability within the building. This approach not only reduces energy consumption but also fosters environmental awareness and responsibility amongst occupants.
Enhanced Occupant Experience and Building Security
Improved Safety and Security Features
Smart building technology offers a wide range of enhanced safety and security features that significantly improve the overall experience for occupants. These features go beyond basic security systems, providing proactive measures to prevent potential threats and enhance the safety of individuals within the building. This includes sophisticated access control systems, real-time monitoring of critical areas, and automated responses to emergencies, which contribute to a safer and more secure environment for everyone.
Advanced fire detection and suppression systems, integrated with building management systems, can significantly reduce response times in case of emergencies. These systems can automatically alert occupants and emergency services, minimizing potential damage and injuries. Furthermore, smart building technologies can be utilized to enhance the security of individual spaces within the building, providing personalized security measures tailored to the specific needs of each user.
Personalized and Efficient Building Management
Smart buildings allow for a personalized and efficient management of various aspects of the building. This includes optimizing energy consumption, automating routine tasks, and providing real-time feedback on building performance. By leveraging data analytics and automation, building managers can gain valuable insights into building usage patterns and make informed decisions to improve efficiency.
Real-time data on energy consumption, occupancy rates, and environmental conditions can be used to optimize resource allocation. This leads to significant cost savings and a reduced environmental footprint. Moreover, smart building systems can automate routine maintenance tasks, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing downtime.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
Smart buildings foster enhanced communication and collaboration among occupants. Integrated communication platforms allow for seamless interaction between building staff, tenants, and visitors. This can include real-time communication tools, digital signage, and interactive displays that facilitate information sharing and collaboration.
Smart building technologies can create a more connected and interactive environment for users, enabling them to easily access information, communicate with each other, and coordinate their activities. This enhanced communication can improve workplace productivity, facilitate collaboration among tenants, and enhance the overall user experience within the building.
Optimized Energy Consumption and Sustainability
Smart buildings play a crucial role in optimizing energy consumption and promoting sustainability. By integrating various building systems, smart technologies can optimize energy usage, reduce waste, and minimize the environmental impact of building operations. This includes intelligent lighting systems, automated HVAC systems, and energy-efficient appliances.
By leveraging sensors and data analytics, smart buildings can monitor energy consumption patterns in real-time. This allows building managers to identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to reduce energy consumption and lower utility costs. This commitment to sustainability makes smart buildings a more environmentally responsible option compared to traditional buildings.
Improved Accessibility and Inclusivity
Smart buildings can be designed to be more accessible and inclusive for all occupants, regardless of their abilities or needs. This can include features such as automated doors, ramps, and elevators, along with adjustable lighting and sound systems that cater to diverse needs.
By incorporating accessibility features into building design and management, smart buildings can create a more welcoming and inclusive environment for individuals with disabilities. This commitment to accessibility benefits all occupants, fostering a sense of community and belonging within the building. This improves the overall user experience, making the building more usable for a broader range of people.
Data-Driven Decision Making and Predictive Maintenance
Smart buildings utilize data analytics to enable Data-driven decision-making and predictive maintenance. By collecting and analyzing data from various building systems, building managers can identify patterns, predict potential problems, and implement proactive maintenance strategies.
This data-driven approach allows for more efficient and effective management of building resources. It can significantly reduce maintenance costs by identifying potential issues before they occur and scheduling maintenance accordingly. This proactive maintenance approach leads to improved building performance, reduced downtime, and greater overall efficiency.
Data-Driven Decision Making for Building Management
Improving Operational Efficiency
Data-driven decision-making is crucial for optimizing building operations. By analyzing energy consumption patterns, maintenance schedules, and occupancy data, building managers can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to reduce costs. This involves using sensors and IoT devices to gather real-time information about building performance, enabling proactive responses to issues like HVAC malfunctions or lighting inefficiencies. This proactive approach translates to significant savings on utility bills and reduces the environmental footprint.
Furthermore, understanding the occupancy patterns allows for dynamic adjustments to lighting and temperature settings, reducing unnecessary energy waste. Predictive maintenance models, powered by data analysis, can anticipate equipment failures, minimizing downtime and preventing costly repairs. In essence, data-driven insights empower building managers to fine-tune every aspect of building operations for maximum efficiency and sustainability.
Enhancing Tenant Satisfaction
Tenant satisfaction is directly linked to a building's comfort and functionality. Data analysis can illuminate tenant preferences and needs, enabling personalized services and tailored environments. By tracking occupancy patterns, feedback from surveys, and even social media sentiment, building managers can understand tenant preferences for temperature, lighting, and other environmental factors. This allows for the creation of a more comfortable and productive environment tailored to the needs of the occupants.
Real-time feedback mechanisms can identify and address issues quickly, maintaining high levels of tenant satisfaction. For example, if a particular area experiences consistently low temperatures, data analysis can pinpoint the problem and enable rapid corrective actions. This not only improves tenant experience but also fosters a positive perception of the building's management.
Optimizing Energy Consumption
Smart buildings leverage data to significantly reduce energy consumption. By analyzing energy usage patterns across different times of day and days of the week, building managers can identify opportunities to optimize energy use. This includes adjusting HVAC systems, controlling lighting, and implementing energy-efficient technologies. This continuous monitoring and analysis contribute to a remarkable reduction in utility costs and significantly lower the carbon footprint.
Real-time data on energy consumption allows for immediate adjustments. For instance, if a particular area of the building is consuming significantly more energy than expected, the data alerts managers to investigate the cause, such as an equipment malfunction or an inefficient control system. This proactive approach prevents waste and ensures optimal energy management throughout the building.
Improving Maintenance and Repair
Predictive maintenance, driven by data analysis, is revolutionizing building maintenance. By identifying patterns in equipment performance, managers can anticipate potential failures and schedule maintenance proactively. This minimizes costly downtime and prevents major equipment breakdowns. This data-driven approach ensures that repairs are carried out when they are most needed, avoiding unexpected disruptions. By tracking equipment performance data, building managers can predict potential problems, allowing for timely interventions and minimizing the impact on tenants and operations.
Facilitating Security and Safety
Data-driven insights are instrumental in enhancing security and safety within a building. Security systems, combined with data analysis, can provide early warnings of potential threats and improve response times. By monitoring access points, detecting unusual activity, and analyzing patterns of movement, building managers can proactively identify and mitigate potential security risks. This intelligent approach ensures the well-being of occupants and the safety of the building.
Furthermore, data analysis can help identify areas that require enhanced security measures, such as installing additional cameras or implementing access control systems. This proactive approach minimizes the likelihood of security breaches and enhances the overall sense of safety for all building occupants.
The Future of Smart Buildings: Integration and Innovation

Smart Building Technologies: Revolutionizing Design
The integration of smart building technologies is rapidly transforming the architectural and engineering landscape. These technologies encompass a wide range of systems, from automated lighting and climate control to advanced security and energy management. The design process is evolving, moving away from static blueprints to dynamic, data-driven models that adapt to real-time needs and optimize performance. This shift represents a paradigm shift in how we approach building design, construction, and operation.
Smart buildings leverage data to optimize resource utilization, resulting in significant energy savings and a reduced environmental footprint. This data-driven approach also leads to enhanced occupant comfort and well-being, creating healthier and more productive spaces. From predictive maintenance to intelligent scheduling, these systems are designed to anticipate and address potential issues before they arise.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
One of the most significant benefits of smart buildings lies in their ability to drastically improve energy efficiency. Through intelligent sensors and automated systems, energy consumption can be monitored and adjusted in real-time, leading to substantial savings. Furthermore, smart building technologies facilitate the implementation of sustainable practices, minimizing environmental impact and aligning with growing global concerns about climate change.
Smart grids and renewable energy integration are crucial components of this sustainability strategy. Buildings equipped with these technologies can generate and utilize renewable energy sources, further reducing their carbon footprint and fostering a more sustainable future for urban environments.
Improved Security and Safety
Advanced security systems are integral to smart building design. These systems incorporate sophisticated sensors, access controls, and video surveillance to monitor and protect the building and its occupants. Real-time monitoring and automated responses to potential threats can significantly enhance safety and security protocols.
The implementation of these advanced security features not only enhances physical safety but also protects sensitive data and information. Smart building technologies provide a layered approach to security, making them less vulnerable to various types of threats, from unauthorized access to natural disasters.
Enhanced User Experience and Productivity
Smart building technologies play a crucial role in enhancing the user experience for occupants. Personalized control over lighting, temperature, and other environmental factors can improve comfort and productivity. Automated systems can optimize the use of shared spaces and resources, leading to a more efficient and enjoyable work environment. Furthermore, these improvements can lead to decreased absenteeism and increased employee satisfaction.
By analyzing user behavior and preferences, smart buildings can adapt to individual needs, creating a more personalized and responsive experience. This personalized approach to building management creates a more engaging and productive environment for employees and residents, ultimately impacting the overall quality of life within the building.
Read more about Smart Buildings and the Internet of Things (IoT)
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing