Sustainable Real Estate: Designing for the Next Generation
The Imperative for Sustainable Real Estate Practices
Embracing Eco-Conscious Design
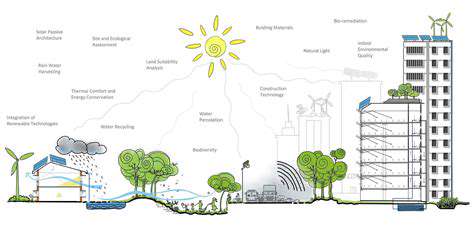
Sustainable real estate practices are no longer a niche concept but a crucial element in the design and development of modern properties. Integrating environmentally friendly materials and minimizing the environmental footprint throughout the building lifecycle are paramount. This involves careful consideration of the sourcing of materials, aiming for locally sourced, recycled, and renewable options whenever possible. Innovative design strategies, such as passive solar design and natural ventilation, can drastically reduce energy consumption and reliance on fossil fuels. The long-term cost savings and reduced environmental impact of these choices make them increasingly attractive to both developers and tenants.
Furthermore, incorporating green spaces and biodiversity into the design enhances the overall well-being of the occupants and the surrounding ecosystem. Creating vertical gardens, rooftop terraces, and integrated green roofs not only provides aesthetic appeal but also contributes to air purification, temperature regulation, and improved water management. These design elements demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, fostering a healthier environment for both people and the planet. By prioritizing these eco-conscious approaches, the real estate industry can lead the way in creating a more harmonious and sustainable future.
Optimizing Operational Efficiency for Reduced Environmental Impact
Beyond the initial design phase, sustainable real estate practices extend to the operational management of buildings. Implementing energy-efficient lighting systems, smart thermostats, and optimized HVAC systems can significantly decrease energy consumption and operating costs. These technologies not only contribute to a smaller carbon footprint but also offer significant financial advantages for property owners and managers. Strategic water conservation measures, such as low-flow fixtures and rainwater harvesting systems, are essential to minimizing water usage and promoting responsible resource management.
Waste management strategies are also critical components of sustainable operations. Implementing recycling and composting programs, reducing single-use plastics, and promoting responsible waste disposal practices are essential steps in minimizing landfill waste and promoting a circular economy. By actively seeking opportunities to minimize waste throughout the building's operational lifecycle, property owners can contribute to a more environmentally responsible future. These operational efficiencies not only benefit the environment but also demonstrate a commitment to responsible business practices, attracting environmentally conscious tenants and investors.
Finally, fostering a culture of sustainability within the building's community is crucial. Educating tenants about energy and water conservation practices and promoting sustainable transportation options can empower residents to actively participate in reducing the building's environmental impact. By working together, building owners, managers, and tenants can create a truly sustainable and responsible community.
Embracing Passive Design Strategies for Energy Efficiency

Passive Solar Design Principles
Passive solar design strategies leverage the sun's energy to heat and cool buildings naturally, reducing reliance on mechanical systems and lowering energy consumption. This approach considers the building's orientation, window placement, and thermal mass to optimize natural light and temperature regulation. By strategically placing windows and using appropriate materials, passive solar design can significantly reduce energy bills and minimize environmental impact.
Understanding the sun's path and the building's relationship to it is crucial for effective passive solar design. The goal is to maximize solar gain in the winter and minimize it in the summer. This requires a careful analysis of the local climate, including the sun's angle and intensity throughout the year.
Natural Ventilation Techniques
Natural ventilation systems utilize wind patterns and building design to circulate air and improve indoor air quality. These techniques can significantly reduce the need for mechanical ventilation, leading to substantial energy savings and improved comfort. Properly designed natural ventilation systems can create a healthier and more comfortable indoor environment, potentially reducing the risk of respiratory issues and mold growth.
Strategies like operable windows, windcatchers, and courtyards can be incorporated into the design to maximize natural airflow. Careful consideration of prevailing wind directions and building layout is paramount for effective natural ventilation design.
Thermal Mass Strategies
Utilizing thermal mass in building design involves incorporating materials with high heat capacity, such as concrete, stone, or water features. These materials absorb and release heat, creating a more stable indoor temperature and reducing the need for heating and cooling. This approach helps to regulate temperature fluctuations throughout the day and season, creating a more comfortable and energy-efficient environment.
Daylighting Strategies
Maximizing natural daylighting is a crucial element of passive design. Strategic window placement and the use of light shelves or light pipes can bring natural light deep into the building, reducing the need for artificial lighting and improving visual comfort. Natural light improves mood, reduces eye strain, and promotes a healthier indoor environment.
Careful consideration of window placement, glazing type, and interior finishes is essential to maximize daylight penetration while minimizing glare and heat gain.
Building Orientation and Site Analysis
The orientation of a building in relation to the sun significantly impacts passive design strategies. Analyzing the site's topography, prevailing winds, and sun paths is fundamental to optimizing solar gain in winter and minimizing it in summer. Careful consideration of these factors ensures that the building is positioned to maximize natural light and minimize heat gain, directly impacting energy efficiency.
By understanding how the sun moves throughout the year, architects and builders can position windows and walls to capture the maximum amount of solar energy during the colder months and minimize it during the warmer months. This careful analysis is crucial for achieving optimal energy performance and comfort.

Read more about Sustainable Real Estate: Designing for the Next Generation
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing