The Business Case for Climate Resilient Real Estate

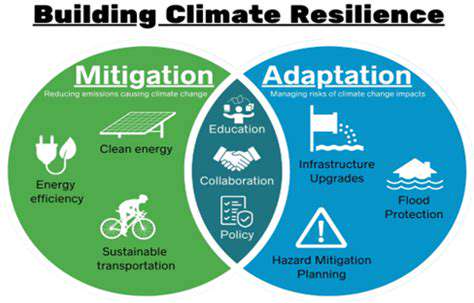
Climate Change and its Impacts
The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts, pose significant risks to infrastructure, agriculture, and human health. These events can disrupt supply chains, damage critical infrastructure, and lead to economic losses on a massive scale. The long-term impacts of climate change, including sea-level rise and altered precipitation patterns, will further exacerbate these risks and require substantial adaptation efforts.
Climate change is not just a distant threat; it's a present reality impacting communities across the globe. The consequences of unchecked greenhouse gas emissions are becoming increasingly evident, and the need for proactive mitigation and adaptation strategies is paramount. Understanding the complex interplay between climate change and other societal risks is crucial for effective risk management.
Geopolitical Instability and Conflict
Geopolitical tensions and conflicts can significantly impact the risk landscape, creating instability and uncertainty in various sectors. The competition for resources, especially water and fertile land, can escalate tensions and lead to conflicts. These conflicts can disrupt trade, displace populations, and create humanitarian crises, all of which have significant economic and social consequences.
The rise of nationalism and protectionism can also lead to trade wars and economic sanctions, hindering global economic growth and increasing vulnerability to external shocks. The interconnected nature of the global economy makes it susceptible to cascading effects from geopolitical events, highlighting the need for international cooperation and diplomacy.
Technological Disruptions and Cyber Threats
Rapid technological advancements, while offering numerous opportunities, also introduce new vulnerabilities. The increasing reliance on interconnected systems makes us susceptible to cyberattacks, which can disrupt critical infrastructure, compromise sensitive data, and cause significant economic damage. Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, requiring continuous adaptation and investment in robust security measures.
The development of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and autonomous systems, also presents ethical and security concerns. These advancements require careful consideration of their potential impact on society, including employment, privacy, and human rights. This necessitates a proactive approach to anticipate and mitigate the risks associated with these transformative technologies.
Economic and Financial Instability
Fluctuations in global markets, economic recessions, and financial crises can create significant risks for individuals, businesses, and governments. Economic downturns can lead to job losses, reduced consumer spending, and decreased investment, impacting various sectors of the economy. The interconnected nature of global financial markets means that economic instability in one region can quickly spread to others.
The increasing complexity of financial instruments and markets can also create new vulnerabilities. The potential for systemic risks, such as a collapse in the value of assets, can have devastating consequences. Effective regulation and oversight are crucial to mitigating these risks and maintaining financial stability.

The Future of Real Estate: A Climate-Conscious Approach
Embracing Sustainable Building Practices
The future of real estate hinges on a fundamental shift towards sustainable building practices. This involves incorporating environmentally conscious design elements from the initial planning stages, using eco-friendly materials, and prioritizing energy efficiency. By prioritizing renewable energy sources like solar panels and geothermal systems, developers can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of their projects and contribute to a healthier planet. This approach not only aligns with environmental responsibility but also often leads to long-term cost savings due to lower utility bills and increased property value.
Sustainable building materials, like reclaimed wood and recycled concrete, are becoming increasingly prevalent. These choices minimize the environmental impact of construction and reduce reliance on virgin resources. Implementing smart building technologies, including advanced insulation and automated lighting systems, further enhances energy efficiency and reduces operating costs for tenants and owners.
The Rise of Green Financing
Investors are increasingly recognizing the financial viability of sustainable real estate. Green financing mechanisms, such as green bonds and sustainability-linked loans, are gaining traction, providing dedicated capital for environmentally friendly projects. These specialized financial instruments incentivize developers and investors to prioritize projects with demonstrable environmental benefits.
Government incentives and tax credits for sustainable real estate development are also playing a significant role in driving this trend. These measures not only encourage environmentally responsible practices but also stimulate economic growth within the green building sector.
Climate Resilience in Real Estate Design
Adapting to the changing climate is crucial in the future of real estate. Designing buildings that withstand extreme weather events, such as floods, droughts, and heat waves, is becoming a critical factor in project planning. This includes implementing flood-resistant foundations, drought-tolerant landscaping, and incorporating strategies for managing extreme heat in building design.
The Impact of Shifting Consumer Preferences
Modern consumers are increasingly demanding environmentally responsible products and services. This shift in consumer preference is impacting the real estate market, influencing the types of properties that are in demand. Properties with sustainable features, green certifications, and a demonstrable commitment to environmental responsibility are more likely to attract buyers and renters.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Real Estate
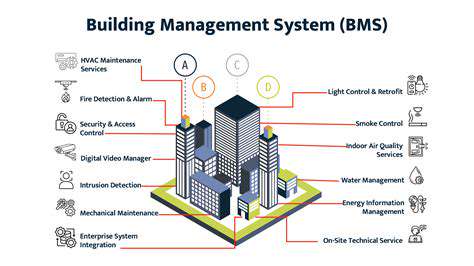
Technological advancements are revolutionizing the way real estate is developed and managed. Smart home technologies, building management systems (BMS), and data analytics are transforming how energy is consumed and managed within buildings. These tools enable real-time monitoring of energy usage and the identification of areas for improvement, ultimately leading to significant energy savings and a reduced carbon footprint.
Quantifying Environmental Impact
Accurate and transparent measurement of a project's environmental impact is becoming paramount. Implementing robust systems for calculating and reporting carbon emissions, water usage, and waste generation is essential for assessing the overall sustainability of a project. This data-driven approach allows stakeholders to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and demonstrate a commitment to environmental responsibility.
The Importance of Collaboration and Education
Successfully transitioning to a climate-conscious real estate sector requires collaboration across various stakeholders. This includes developers, investors, policymakers, and the broader community. Promoting education and awareness about sustainable practices is vital to ensuring that the necessary knowledge and expertise are widely available. Partnerships between educational institutions and real estate professionals can foster a skilled workforce equipped to design, build, and manage sustainable properties in the future.
Read more about The Business Case for Climate Resilient Real Estate
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing