Vertical Forests: Sustainable Urban Real Estate
Introduction to Vertical Forests

Vertical Forest Design Principles
Vertical forests, also known as green skyscrapers, are innovative architectural designs that integrate vertical greenery into high-rise buildings. These structures aim to bring the benefits of nature into urban environments, improving air quality, reducing the urban heat island effect, and providing aesthetic beauty. Careful consideration is needed in the design process to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the green spaces. This includes selecting appropriate plant species that can thrive in the specific microclimates created within the building's structure and considering the necessary irrigation, drainage, and maintenance systems. The structural design must also accommodate the weight of the plants and the added complexity of the vertical gardens.
A critical aspect of vertical forest design is the integration of different plant species. The choice of plants should be carefully considered to maximize biodiversity, attract pollinators, and create a visually appealing and healthy ecosystem. Careful selection of plants ensures the long-term viability of the vertical forest. This includes considering factors such as light availability, humidity levels, and the specific needs of different plant types. The arrangement of the plants should also be thoughtfully planned to optimize light penetration and airflow, ensuring the health and growth of the entire ecosystem.
Benefits of Vertical Forests
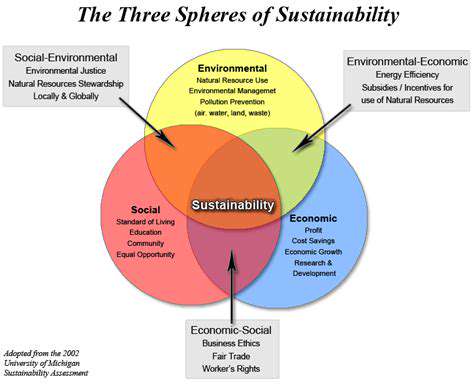
Vertical forests offer a multitude of benefits, extending far beyond their aesthetic appeal. By incorporating green spaces into urban environments, these structures contribute to improved air quality, reducing pollutants and enhancing the overall health of the surrounding community. The increased green cover significantly mitigates the urban heat island effect, lowering temperatures in urban areas and creating a more comfortable environment for residents.
Furthermore, vertical forests offer significant environmental benefits. They help improve biodiversity by providing habitats for various species of plants and animals, increasing the ecological balance in urban areas. They are a significant step toward creating more sustainable and resilient urban landscapes. They also contribute to a healthier environment for residents, improving air quality and reducing the urban heat island effect. The presence of vegetation can lead to a reduction in noise pollution and create a more peaceful and tranquil atmosphere.
The aesthetic value of vertical forests is undeniable. They transform urban landscapes into vibrant and inviting spaces, adding a touch of natural beauty to the concrete jungle. These structures enhance the visual appeal of buildings and surrounding areas, improving the overall quality of life for residents and visitors alike.
Moreover, vertical forests can serve as educational and recreational spaces, providing opportunities for community engagement and environmental awareness. They can act as living classrooms, showcasing the importance of biodiversity and sustainable practices.
Environmental Benefits of Vertical Forests

Reduced Urban Sprawl
Vertical farming significantly reduces the need for expansive horizontal agricultural land, thus minimizing the conversion of natural habitats and green spaces into agricultural areas. This conservation of natural ecosystems is crucial for biodiversity and maintaining healthy environmental balances, ultimately benefiting the planet. Urban sprawl often leads to habitat fragmentation, impacting local wildlife and increasing the risk of pollution and other environmental problems. Vertical farming helps mitigate these issues by concentrating agricultural activity within urban areas.
Water Conservation
Vertical farms can drastically reduce water consumption compared to traditional agriculture. By controlling the environment within the farm, vertical farms can optimize irrigation systems, minimizing water waste and maximizing efficiency. This efficient water use is particularly important in arid and semi-arid regions where water scarcity is a significant concern. Utilizing hydroponics and aeroponics, vertical farms can significantly decrease water usage compared to conventional farming methods, contributing to water conservation efforts.
Reduced Transportation Emissions
Transporting food from rural agricultural areas to urban markets contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Vertical farms, situated within or near urban centers, drastically shorten the transportation distance of produce. This reduces the carbon footprint associated with food transportation and contributes to a cleaner environment. By bringing production closer to consumption, vertical farms also reduce the need for long-distance transport, leading to lower emissions and a healthier environment.
Minimized Pesticide Use
Vertical farms often use controlled environments, allowing for more precise and targeted pest control methods. This minimizes the need for widespread pesticide applications, which can harm beneficial insects, pollinator populations, and contaminate the surrounding environment. Using integrated pest management strategies within controlled environments is a key benefit of vertical farming, promoting healthier ecosystems and reducing the environmental impact of pesticides.
Enhanced Food Safety and Security
Vertical farms can be designed to minimize contamination risks, reducing the potential for foodborne illnesses. By controlling the environment and growing conditions, vertical farms can create a more hygienic and secure food production process. This enhanced food safety is particularly valuable in urban areas with limited access to fresh, locally-sourced food. Vertical farming can also contribute to food security by providing a consistent and reliable source of fresh produce, regardless of weather patterns or seasonal variations.
Reduced Use of Fertilizers
Vertical farms can employ nutrient-rich solutions specifically tailored to the needs of the crops, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. This reduces the environmental impact of fertilizer runoff and its contribution to water pollution. By optimizing nutrient delivery, vertical farms can enhance crop yields while minimizing the use of potentially harmful chemicals, promoting a more sustainable agricultural system.
Lower Energy Consumption
Vertical farms can be designed with energy-efficient lighting and climate control systems. This reduces the overall energy consumption compared to traditional agriculture. By optimizing energy use, vertical farms can significantly reduce their environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable food system. Renewable energy sources can be integrated into vertical farm designs to further minimize their carbon footprint and promote environmentally friendly practices.
Design Considerations and Technological Advancements

Design Considerations for User Experience
A crucial aspect of any successful product design is prioritizing the user experience. Careful consideration must be given to intuitive navigation, clear information architecture, and aesthetically pleasing visuals. Creating a seamless user journey, from initial interaction to final completion, is paramount. This involves understanding user needs and pain points, and designing solutions that address them effectively. The goal should be to make the product not only functional but also enjoyable to use.
User interface (UI) design plays a vital role in this process. A well-designed UI ensures that users can easily find what they need and complete tasks with minimal effort. This includes aspects like button placement, visual hierarchy, and overall aesthetic appeal. A user-friendly UI fosters positive user interactions and contributes significantly to overall product satisfaction.
Technological Advancements in Design
Rapid advancements in technology have significantly impacted design methodologies. Tools like 3D modeling software, interactive prototyping platforms, and augmented reality (AR) tools allow designers to create more sophisticated and immersive experiences. These advancements allow for more realistic simulations and user testing, enabling designers to identify and address potential issues before launching a product.
The rise of machine learning and artificial intelligence is also transforming the design process. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of user data to identify patterns and preferences, helping designers make informed decisions about design choices that maximize user engagement and satisfaction. This data-driven approach to design is becoming increasingly important for creating products that truly resonate with their target audience.
Material Selection and Durability
Choosing the right materials is critical to ensuring the durability and longevity of a product. The selection process must consider the intended use case, environmental factors, and cost constraints. Robust materials are essential for products that will endure significant wear and tear, while lighter materials may be preferred for portability and ease of use.
Sustainability is also an increasingly important factor in material selection. Designers should consider the environmental impact of their choices and prioritize materials that are recyclable or biodegradable. This not only benefits the environment but also enhances the brand image and resonates with environmentally conscious consumers. Using sustainable materials is an important factor in creating environmentally responsible products.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Designing for accessibility and inclusivity is crucial to ensure that products are usable by a diverse range of users. This includes considering users with disabilities, different cultural backgrounds, and varying levels of technical expertise. Prioritizing accessibility ensures that the product is usable by the widest possible audience and enhances its overall impact.
Implementing features like adjustable font sizes, alternative text descriptions for images, and keyboard navigation options are all important considerations in creating an inclusive design. These seemingly small details can significantly improve the user experience for a wider range of users and contribute to the overall success of the product.
Read more about Vertical Forests: Sustainable Urban Real Estate
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing