Financing Sustainable Real Estate Projects
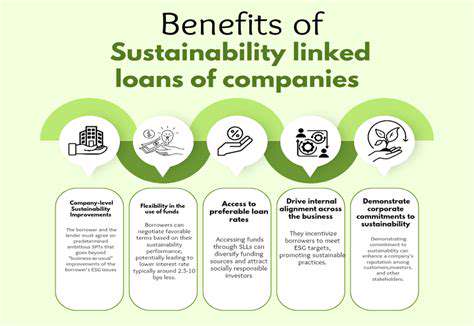
Sustainability-linked loans, on the other hand, represent a different approach to financing sustainable real estate projects. These loans often tie the interest rate or the loan terms to the achievement of predefined environmental, social, or governance (ESG) performance targets. This incentivizes borrowers to improve their sustainability profile over time, creating a dynamic link between financial performance and environmental responsibility.
The performance targets are usually measurable and verifiable, ensuring that the lender can assess the borrower's progress towards sustainability. This allows for a more flexible and tailored financing approach compared to green bonds, potentially making it more suitable for a wider range of projects and borrowers.
The Role of Green Finance in Real Estate
Green finance, encompassing both green bonds and sustainability-linked loans, plays a crucial role in driving the transition to a more sustainable real estate sector. By providing access to capital for environmentally friendly projects, these instruments incentivize the development of energy-efficient buildings, the use of renewable energy sources, and the implementation of sustainable construction practices. This shift towards sustainable building practices and infrastructure is essential for mitigating the environmental impact of the real estate industry and promoting long-term economic growth.
Furthermore, the increased demand for green finance instruments drives innovation and the development of new technologies and solutions that enhance sustainability in the real estate sector. This fosters a virtuous cycle of investment, innovation, and environmental improvement, ultimately benefitting both the planet and the bottom line of real estate investments.
Key Considerations for Investors and Borrowers
Investors looking to incorporate sustainability into their portfolios need to carefully evaluate the specific projects and initiatives funded by green bonds or sustainability-linked loans. Thorough due diligence and verification of environmental claims are essential to ensure alignment with their sustainability goals. Transparency and accountability are critical for both investors and borrowers in this area. It's important to understand the specific terms and conditions of the financing instruments to ensure that they meet their investment criteria and that the loan terms are aligned with their long-term objectives.
Borrowers seeking financing for sustainable real estate projects should carefully consider the potential benefits and drawbacks of green bonds and sustainability-linked loans. Understanding the performance targets and the potential impact on their financial position is crucial. A robust environmental impact assessment and a clear plan for achieving sustainability targets are vital for securing favorable financing terms and ensuring project viability.
The Role of Sustainability-Linked Loans in Green Financing
The Growing Importance of ESG Factors
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors are increasingly influencing investment decisions, with investors actively seeking companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. This heightened awareness reflects a broader societal shift towards responsible business practices and a recognition of the long-term value of sustainability-linked initiatives.
Companies that effectively integrate ESG considerations into their strategies often experience improved financial performance and enhanced brand reputation. These factors are no longer just nice-to-haves but are becoming critical components of a company's overall value proposition.
Defining Sustainability-Linked Finance
Sustainability-linked finance encompasses a range of financial instruments and strategies that tie financial returns to environmental, social, and governance performance. This approach moves beyond traditional investment models by explicitly linking financial incentives to the achievement of specific sustainability targets.
This innovative approach fosters a direct correlation between financial performance and positive societal impact, driving positive change.
Types of Sustainability-Linked Instruments
Various instruments exist within the realm of sustainability-linked finance. These include sustainability-linked loans, bonds, and other financial products, each designed to incentivize specific sustainability improvements. For example, a loan might be tied to a company's reduction in carbon emissions, while a bond might be linked to a commitment to diversity and inclusion initiatives.
Understanding the nuances of different sustainability-linked instruments is crucial for investors seeking to align their portfolios with their values.
Benefits for Companies
Implementing sustainability-linked initiatives can provide significant benefits to companies. These initiatives can enhance their brand reputation, attract environmentally conscious investors, and improve operational efficiency through the adoption of sustainable practices.
Companies that proactively address sustainability challenges can often gain a competitive advantage and position themselves for long-term success in a changing market. This is a critical step in the evolution of corporate responsibility, moving beyond compliance to a proactive approach to sustainability.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the numerous advantages, implementing sustainability-linked initiatives also presents certain challenges. Measuring and verifying sustainability performance accurately and consistently across different sectors is crucial, and developing robust reporting frameworks is essential.
Establishing clear and measurable targets for sustainability improvements is essential for the success of these initiatives. This requires careful planning and collaboration among stakeholders, including investors, companies, and regulatory bodies.
Investor Perspectives on Sustainability-Linked Investments
Investors are increasingly seeking opportunities to align their investments with their values. Sustainability-linked investments offer an avenue to achieve both financial returns and positive societal impact.
Investors are increasingly recognizing the long-term value proposition of sustainable investments and are seeking instruments that directly reward positive environmental, social, and governance performance. This is a significant shift in the investment landscape, signifying a growing demand for responsible and sustainable practices.
The Future of Sustainability-Linked Finance
The future of sustainability-linked finance looks promising. As ESG factors continue to gain prominence, the demand for these instruments is expected to grow, driving further innovation in the development of new financial products and frameworks.
With increasing regulation and public pressure, the adoption of sustainability-linked finance is likely to become the norm rather than the exception. This will create a more sustainable and equitable financial system, benefitting both businesses and society.
Public-Private Partnerships and Government Incentives

Public-Private Partnerships: A Catalyst for Growth
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) represent a powerful mechanism for leveraging the strengths of both the public and private sectors to achieve shared goals. By combining the public sector's mandate for societal benefit with the private sector's expertise in efficiency and innovation, PPPs can unlock substantial opportunities for economic development and improved service delivery. These partnerships often lead to projects that are more ambitious and impactful than either sector could achieve alone.
These collaborations often result in innovative solutions to complex problems, fostering a more dynamic and responsive approach to public service provision. The potential benefits are significant, spanning from infrastructure development and healthcare improvements to environmental protection and social welfare programs.
Exploring the Dynamics of Go
The term Go in the context of public-private partnerships often refers to a specific approach within the partnership structure. It can signify a focused strategy for achieving specific goals or a particular methodology for project implementation. Understanding this specific application is crucial for evaluating the potential effectiveness of the partnership model.
Further research into the specific Go strategies employed in these partnerships is essential for a more complete understanding of their impact.
Key Considerations for Successful PPPs
Successful public-private partnerships hinge on a number of critical factors. These include clear definitions of roles and responsibilities, robust legal frameworks, effective risk allocation strategies, and strong communication channels. Transparency and accountability are paramount to building trust and ensuring the partnership operates fairly.
Careful consideration must be given to long-term sustainability and the potential for unforeseen circumstances to affect the viability of the project.
Financial Implications and Investment Strategies
Financial modeling and investment strategies play a significant role in the success of PPPs. Precise projections of costs, revenue streams, and potential risks are crucial for attracting private sector investment and ensuring the financial viability of the project. This is especially important in long-term projects where financial fluctuations can significantly impact outcomes.
Understanding the financial implications and developing appropriate investment strategies are paramount to achieving a successful partnership.
Governance Structures and Regulatory Frameworks
Robust governance structures and clear regulatory frameworks are essential to manage the complexities of a public-private partnership. These frameworks should include mechanisms for dispute resolution, performance monitoring, and accountability. Establishing transparent processes for decision-making and conflict resolution is critical for maintaining harmony and ensuring the partnership's long-term success.
Risk Management and Mitigation Strategies
Identifying and mitigating risks is a crucial aspect of any PPP. Careful analysis of potential challenges, including market fluctuations, technological obsolescence, and regulatory changes, is necessary. Developing proactive risk management strategies can help mitigate potential downsides and ensure the project stays on track.
Implementing comprehensive contingency plans can help to minimize disruptions and ensure the continuation of the project even in the face of unexpected hurdles.
Evaluating Outcomes and Long-Term Impact
Evaluating the outcomes and long-term impact of a public-private partnership is crucial for learning and improving future collaborations. This includes assessing the project's economic impact, social benefits, and environmental consequences. Regular performance monitoring and independent evaluations are critical for ensuring the partnership remains aligned with its initial objectives.
Data collection and analysis are essential for understanding the success of the Go strategy and informing adjustments or improvements for future projects.