Assessing Climate Vulnerability in Real Estate Assets

Identifying Key Climate Change Threats to Real Estate Assets
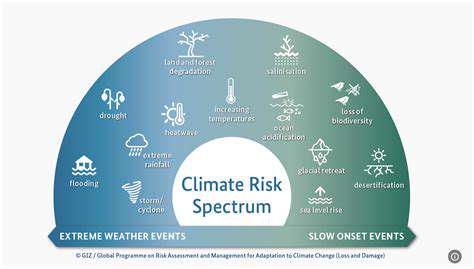
Understanding the Scope of Climate Change Threats
Climate change is no longer a distant threat; its impacts are being felt globally, across various sectors, and are increasingly affecting daily life. From rising sea levels threatening coastal communities to more frequent and intense extreme weather events, the consequences are substantial and require immediate attention. Understanding the wide-ranging and interconnected nature of these threats is crucial for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
The scope of these threats extends beyond environmental concerns. Economic instability, social unrest, and geopolitical tensions can all be exacerbated by climate change impacts, highlighting the interconnectedness of environmental, economic, and social issues. Addressing these challenges necessitates a comprehensive and integrated approach that acknowledges the broader implications.
Rising Temperatures and Extreme Weather Events
One of the most visible and impactful consequences of climate change is the rising global average temperature. This warming trend is contributing to a significant increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, and wildfires. These events cause widespread damage and displacement, and they are becoming more unpredictable, making it harder for communities to prepare and adapt.
The increasing intensity of hurricanes and typhoons is a particularly serious concern, as they can cause devastating damage to coastal infrastructure and communities. More frequent and intense storms will undoubtedly pose a significant challenge to vulnerable populations and require proactive measures to minimize their impact.
Impacts on Water Resources and Food Security
Climate change is significantly altering water resources across the globe. Changes in precipitation patterns, including increased droughts in some regions and floods in others, are affecting water availability and quality. This directly impacts agriculture, threatening food security and potentially leading to widespread food shortages in vulnerable regions.
Decreased water availability also affects human health and sanitation, increasing the risk of waterborne diseases and exacerbating existing inequalities in access to essential resources. The interconnectedness of these issues highlights the urgent need for sustainable water management practices and climate-resilient agriculture.
Impacts on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
Climate change is impacting biodiversity and ecosystem services in profound ways. Shifting temperatures and precipitation patterns are forcing species to migrate or adapt, with some facing extinction as their habitats are altered or destroyed. The loss of biodiversity directly impacts the provision of essential ecosystem services, such as pollination, water purification, and carbon sequestration.
The degradation of ecosystems also has a cascading effect on human well-being, impacting livelihoods, health, and the overall stability of communities. Conserving and restoring biodiversity is crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change and ensuring the resilience of ecosystems in the face of future challenges.
Geopolitical Implications and Social Disruptions
Climate change is not just an environmental issue; it has significant geopolitical implications and can exacerbate existing social inequalities. Competition for dwindling resources, such as water and arable land, can fuel conflict and displacement. Climate-induced migration and displacement can lead to social unrest and instability in affected regions, potentially destabilizing entire nations. Addressing climate change necessitates international cooperation and a commitment to equitable solutions.
The complex interplay of environmental, social, and economic factors requires a holistic approach to understanding and addressing the multifaceted challenges of climate change. This includes empowering vulnerable communities, fostering international cooperation, and implementing sustainable solutions that consider the needs of all stakeholders.
Integrating Climate Risk into Real Estate Investment Decisions

Understanding the Scope of Climate Risk
Integrating climate risk into real estate investment strategies is no longer a matter of preference, but a critical necessity. The implications of climate change, from rising sea levels to more frequent extreme weather events, are undeniably impacting property values and long-term investment returns. Understanding the full scope of these risks is the first step toward developing robust and resilient investment portfolios.
This involves analyzing specific climate vulnerabilities for different geographic locations. Factors such as floodplains, wildfire risk zones, and drought-prone areas need to be meticulously assessed. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for accurate risk assessment and informed decision-making.
Identifying and Assessing Physical Risks
Physical risks directly impact property values and operational viability. Flooding, droughts, and extreme temperatures are all examples of events that can cause significant damage to buildings and infrastructure, leading to financial losses for investors. Analyzing historical climate data, projections of future trends, and local building codes is critical for evaluating physical risks.
Evaluating Regulatory and Policy Risks
Government regulations and policies surrounding climate change are increasingly impacting real estate development and investment. Building codes often incorporate climate resilience standards, and new policies may restrict development in high-risk areas. Investors must stay informed about evolving regulations to avoid significant financial penalties and maintain compliance.
Understanding the potential for future regulations and policy changes is crucial for long-term planning. Staying informed about proposed legislation and its potential impact on your investments is a key step in mitigating regulatory risks.
Analyzing Financial and Market Risks
Climate change can disrupt real estate markets in various ways. Decreased property values in vulnerable areas, increased insurance premiums, and reduced rental demand can all contribute to financial losses. Assessing the potential financial ramifications of climate change is critical.
Understanding the potential for decreased demand and reduced rental yields in areas susceptible to climate-related events is essential for informed investment decisions. This analysis must consider the potential for increased costs associated with insurance and maintenance, both of which can significantly impact profitability.
Developing Climate-Resilient Investment Strategies
Developing strategies that mitigate climate risk is essential for long-term investment success. This includes diversifying investments across different geographic locations and property types, incorporating climate-resilient design features, and actively seeking opportunities in climate-friendly infrastructure projects.
Implementing Adaptation and Mitigation Measures
Investing in climate-resilient projects, such as flood defenses, drought-resistant landscaping, and energy-efficient buildings, can help to mitigate future risks. Integrating climate resilience into the design and construction process can reduce the vulnerability of properties to climate change impacts. Adopting strategies that minimize environmental impact, such as using sustainable building materials and promoting energy efficiency, can also help reduce operational costs.
Monitoring and Evaluating Performance
Continuous monitoring and evaluation of climate risk is vital for adaptive investment strategies. Tracking the performance of climate-resilient investments, assessing the effectiveness of mitigation measures, and adapting strategies based on evolving climate data are crucial for long-term success.
Regularly reviewing your investment portfolio in the context of changing climate conditions is key to adjusting to evolving risks and ensuring continued profitability. This includes analyzing the performance of your investments in relation to climate change impacts and adapting your strategies accordingly.
Read more about Assessing Climate Vulnerability in Real Estate Assets
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing