Understanding Climate Change Impacts on Property Values
Impacts on Coastal Communities
Coastal erosion, primarily fueled by rising sea levels, presents a growing danger to shoreline communities across the globe. Residential properties, commercial establishments, and vital infrastructure face increasing risks from flooding and storm surges. The forced relocation of residents combined with economic losses from damaged properties and shuttered businesses creates lasting consequences. These displacements also threaten cultural traditions and community bonds that have developed over generations.
Additionally, the disappearance of natural coastal buffers like beaches and wetlands worsens erosion's effects. These ecosystems normally absorb storm energy, so their loss leaves properties more vulnerable to flood damage. The financial burden of constructing protective measures like seawalls often overwhelms municipal budgets, creating difficult choices for local governments.
Environmental Consequences of Coastal Erosion
Erosion's impact extends far beyond human settlements, disrupting delicate marine ecosystems. Critical habitats including mangrove forests, salt marshes, and coral reefs are disappearing at alarming rates. These areas serve as nurseries and feeding grounds for countless marine species, and their decline threatens entire aquatic food chains. The sediment and pollutants released during erosion further degrade water quality, potentially contaminating seafood supplies and creating health risks.
Mitigation Strategies and Adaptation Measures
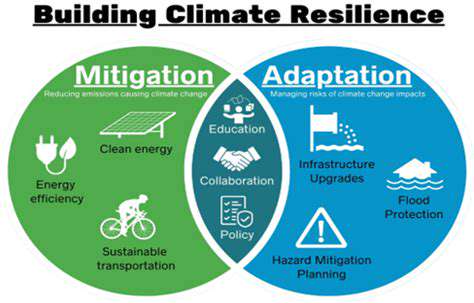
Combating coastal erosion demands a dual approach: reducing climate change's progression while adapting to its current effects. Global cooperation to limit greenhouse gases addresses the root cause, while local projects like wetland restoration provide immediate protection. Strategic relocation plans for vulnerable communities represent difficult but necessary long-term solutions. Sustainable development policies must balance economic needs with environmental realities.
Technological Advancements and Monitoring
Modern tools like satellite imaging and LiDAR provide unprecedented erosion tracking capabilities. Advanced modeling software helps predict future scenarios, allowing for precisely targeted protection strategies. These technologies enable communities to make data-driven decisions about their most vulnerable areas.
Extreme Weather Events and Their Property Value Implications

Extreme Weather Events and Climate Change
The increasing severity of weather extremes - from heatwaves to hurricanes - demonstrates climate change's tangible effects. Scientific evidence clearly links these changes to human activities, particularly fossil fuel consumption. Warmer atmospheric conditions create ideal circumstances for weather volatility, including more intense droughts through increased evaporation rates.
The Impact on Human Health
Weather extremes create multiple health hazards - from heatstroke during temperature spikes to waterborne illnesses after floods. The psychological toll of weather disasters often goes overlooked, with many survivors experiencing lasting trauma. Vulnerable populations including the elderly and economically disadvantaged face disproportionate risks.
Economic Consequences of Extreme Weather
The financial impacts ripple across multiple sectors. Infrastructure repairs, agricultural losses, and insurance claims strain local and national economies. Developing nations bear particular burdens, often lacking resources for adequate preparation or recovery. These costs highlight the need for proactive investment in resilient infrastructure.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Effective solutions require global cooperation and local implementation. Emission reduction remains critical, while adaptation measures like flood-resistant construction offer immediate protection. Knowledge sharing between nations can accelerate the development of effective solutions. Community-based preparedness programs help bridge gaps in formal response systems.
The Impact of Shifting Climate Patterns on Agricultural Lands
Changes in Precipitation Patterns
Unpredictable rainfall creates dual challenges - drought-stricken regions struggle with water scarcity while others face destructive floods. Farmers require support to implement adaptive strategies like drought-resistant crops and efficient irrigation. Government policies must incentivize sustainable practices to ensure long-term food security.
Temperature Extremes and Crop Yields
Heat stress reduces both crop quantity and quality while increasing pest pressures. Unexpected cold snaps further complicate agricultural planning. Research into resilient crop varieties offers hope for maintaining production levels. Soil cooling techniques and adjusted planting schedules provide additional adaptation options.
The Role of Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
A combination of immediate adaptations and long-term emissions reduction forms the most effective approach. International research collaboration accelerates the development of climate-smart agriculture techniques. Farmer education programs ensure successful implementation of new methods.
Beyond the Immediate: Long-Term Considerations and Investment Strategies

Long-Term Considerations in Project Management
A well-conceived project integrates future-proofing from inception. Strategic alignment ensures initiatives support organizational goals beyond immediate deliverables. Comprehensive documentation and knowledge transfer protocols preserve institutional memory.
Adapting to Future Needs and Technological Advancements
Flexible project designs accommodate emerging technologies and evolving requirements. Continuous skills development ensures workforces can leverage new tools effectively. Scenario planning helps organizations prepare for multiple potential futures.
Read more about Understanding Climate Change Impacts on Property Values
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing