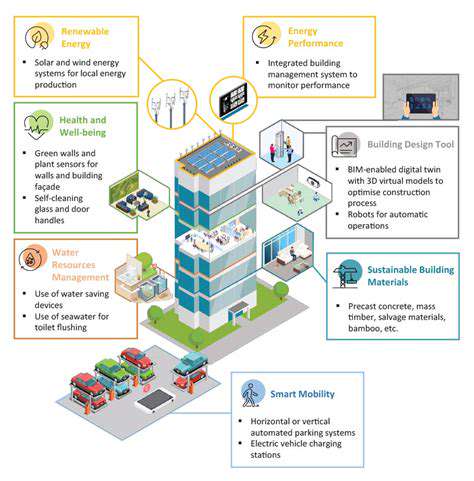
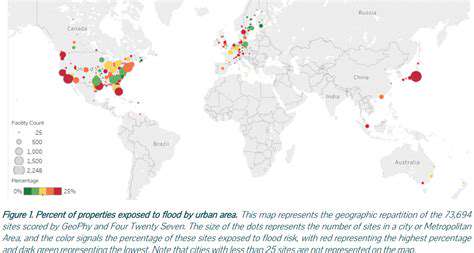
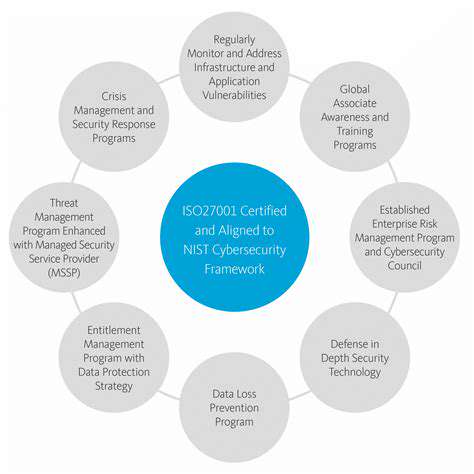
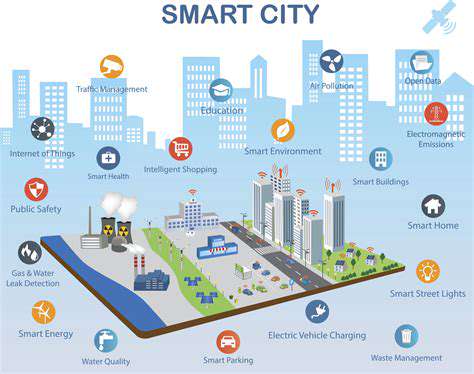
Real Estate's Response to Climate Change: Proactive Measures and Innovative Solutions for Adaptation
Ethical programming goes beyond simply writing functional code. It encompasses a broader set of considerations that address the potential societal impact of software. Developers have a responsibility to ensure their creations are not used for harm or to perpetuate biases. This responsibility extends to the design, development, and deployment phases of a software project, demanding a conscious effort to evaluate the potential consequences of their work.
Community-Based Solutions for Enhanced Climate Resilience
Community Engagement Strategies
Effective community-based solutions hinge on robust engagement strategies. These strategies should prioritize active listening and collaboration, ensuring that the needs and perspectives of all community members are heard and considered. This inclusive approach is crucial for fostering trust and buy-in, ultimately leading to more sustainable and impactful solutions. Furthermore, transparent communication channels are essential to keep the community informed about progress and challenges throughout the implementation process.
Establishing clear communication protocols and utilizing diverse channels, such as community forums, local newspapers, and social media, can significantly enhance engagement. Regular feedback mechanisms, such as surveys and focus groups, are also vital for gauging community sentiment and making necessary adjustments along the way. Building strong relationships with local leaders and community organizations is also paramount to the success of any community-based initiative.
Identifying Community Needs
A critical first step is identifying the specific needs and challenges facing the community. This requires thorough research and analysis, considering factors like economic disparities, access to resources, and existing social structures. Detailed data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, and observations, should be employed to gather comprehensive information.
Understanding the unique circumstances of the community is crucial to developing tailored solutions. For example, a community facing high unemployment may require different interventions than one struggling with inadequate access to healthcare. Careful consideration of these differing needs helps in directing resources efficiently and effectively.
Resource Mobilization and Allocation
Successfully implementing community-based solutions requires a robust strategy for resource mobilization. This includes identifying existing resources within the community, such as volunteer networks, local businesses, and non-profit organizations. Partnering with these organizations can leverage existing strengths and expertise, increasing the overall impact of the solution.
Furthermore, exploring potential external funding sources, such as grants and sponsorships, is equally important. A well-defined plan for allocating resources, ensuring transparency and accountability, is essential for maintaining community trust and maximizing the impact of the investment.
Sustainable Implementation Strategies
Sustaining the impact of community-based solutions requires carefully planned implementation strategies. This includes developing clear timelines and milestones, as well as creating mechanisms for ongoing monitoring and evaluation. Regular assessment of the program's effectiveness is crucial for identifying areas for improvement and adapting strategies to changing circumstances.
Building local capacity is vital for long-term sustainability. Training and empowering community members to take ownership of the solution, and ensuring knowledge transfer and skill development, are essential steps in creating a self-sufficient and resilient community. This empowerment fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, ensuring the longevity of the solution.
Evaluation and Feedback Mechanisms
Regular evaluation and feedback mechanisms are essential for gauging the effectiveness of community-based solutions. This includes collecting data on program outcomes, assessing community satisfaction, and identifying areas for improvement. Using various methods, like surveys, interviews, and focus groups, can provide valuable insights into the program's impact on the community.
Feedback from community members is critical for adapting the solution and ensuring it meets evolving needs. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and responsiveness to emerging challenges, making the solution more relevant and effective over time. A willingness to adapt and adjust is paramount to long-term success.
Addressing Potential Challenges
Community-based solutions, while offering great potential, may face various challenges. These challenges might include resistance from some community members, limited resources, or difficulties in coordinating efforts between different stakeholders. Addressing these challenges proactively is crucial for success.
Developing strategies to address potential conflicts, building consensus, and fostering collaboration are essential elements for achieving success. Effective communication and conflict resolution skills are vital for navigating these complexities and ensuring a positive outcome for all involved. By proactively addressing these potential issues, the likelihood of success significantly increases.
The Role of Policy and Regulation in Fostering Climate Resilience
Policy Frameworks for Climate-Resilient Development
Effective policy frameworks are crucial for guiding real estate development towards climate resilience. These frameworks should incorporate risk assessments, outlining potential vulnerabilities to climate hazards like flooding, extreme temperatures, and wildfires. Such assessments should be region-specific, recognizing that different geographic locations face varying climate risks. This necessitates a nuanced understanding of the local environment, including historical climate patterns and projected future changes. Policies should also incentivize the adoption of sustainable building practices and promote the use of climate-resilient materials, ultimately reducing the environmental footprint of new construction and renovations. Furthermore, clear regulations and enforcement mechanisms are essential for ensuring compliance and preventing environmentally damaging practices.
Integrating climate resilience into zoning regulations and building codes is another key component of effective policy. This involves establishing minimum standards for flood protection, fire resistance, and energy efficiency. Stricter enforcement of these regulations is needed, ensuring that developers and builders adhere to the guidelines and that projects are built to withstand the anticipated climate impacts. The implementation of these policies should be accompanied by public awareness campaigns to educate stakeholders, including developers, investors, and homeowners, about the importance of climate resilience in real estate development.
Regulatory Mechanisms to Drive Sustainable Practices
Regulatory mechanisms play a critical role in fostering climate resilience within the real estate sector. These regulations can include incentives for green building practices, such as tax breaks or subsidies for energy-efficient construction or the use of renewable energy sources. Such incentives encourage developers to incorporate sustainable features into their projects, ultimately contributing to a more resilient built environment. Regulations should also address the use of environmentally damaging materials, promoting the adoption of sustainable alternatives and minimizing the environmental impact of real estate development.
Mandating the use of climate-resilient building designs and materials can significantly enhance the resilience of structures. This may include specific requirements for floodproofing, wind resistance, and drought-tolerant landscaping. Clear guidelines and standards for these practices are needed, ensuring that buildings are constructed to withstand anticipated climate changes and minimizing the risk of damage. Stronger regulatory enforcement is necessary to ensure compliance and deter environmentally harmful practices. These regulations should also address the ongoing maintenance and upgrades of existing buildings, promoting their longevity and resilience in the face of changing climate conditions.
Financial Instruments for Climate-Resilient Investments
Integrating climate resilience into financial instruments for real estate development is essential. This involves developing green financing options, such as green bonds or loans specifically for climate-resilient projects. These instruments provide capital for projects that prioritize sustainable and resilient practices, encouraging investment in the sector. By incentivizing investment in climate-resilient projects, financial institutions can drive the creation of a more sustainable and resilient built environment. This could also involve the development of clear metrics and reporting standards for assessing the climate resilience of real estate investments, enabling investors to make informed decisions.
Insuring properties against climate risks is also a crucial aspect of fostering climate resilience. Insurance policies should adequately reflect and address the growing risks associated with extreme weather events and other climate change impacts. This can include incorporating climate change projections into risk assessments for insurance purposes. This can incentivize the construction and maintenance of climate-resilient structures, encouraging the adoption of sustainable practices in property development.
Community Engagement and Education
Community engagement and education are vital to building a shared understanding and commitment towards climate resilience in real estate. Public awareness campaigns can educate communities about the risks posed by climate change and the importance of climate-resilient development. This includes educating community members on how to prepare for and respond to climate-related hazards, promoting the use of sustainable practices, and fostering a sense of shared responsibility for building a resilient future. Engaging local communities in the planning and implementation of climate-resilient projects is essential to ensure that these projects are relevant, appropriate and successful.
Read more about Real Estate's Response to Climate Change: Proactive Measures and Innovative Solutions for Adaptation
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing