Climate Change and Real Estate Due Diligence: New Standards
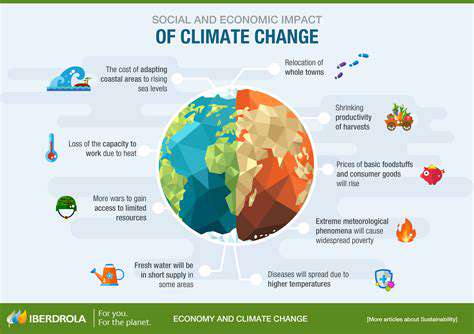
Flooding and coastal erosion pose significant risks to coastal properties and are becoming increasingly prevalent due to rising sea levels and more intense storm surges. The potential for damage from these events, as well as the regulatory and financial implications of dealing with these issues, is a major factor affecting real estate investments in vulnerable areas. These risks are driving insurers to adjust their policies and pricing models, making it more costly and potentially difficult to secure adequate insurance coverage for affected properties.
The Importance of Adaptability and Resilience
Real estate investors and developers must now prioritize adaptability and resilience in their strategies. This involves incorporating climate-conscious design principles, such as energy efficiency and water conservation, into new construction and renovations. Furthermore, assessing the long-term risks associated with climate change and developing mitigation strategies are essential to ensure the longevity and profitability of real estate investments.
Green Building Practices and Sustainable Investments
The increasing awareness of climate change has spurred the adoption of green building practices, leading to a rise in demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly real estate. This includes the incorporation of renewable energy sources, energy-efficient materials, and water conservation measures. Investors who prioritize sustainable development are likely to attract a broader range of tenants and buyers, while also potentially mitigating the financial risks associated with climate change.
The Role of Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations and policies related to climate change are increasingly impacting the real estate market. Regulations related to emissions, energy efficiency, and adaptation measures are influencing the types of properties that can be developed and the investments that are deemed acceptable. Investors must stay informed about and adapt to these changing regulations to ensure compliance and maximize returns.
The Shifting Demographics and Housing Preferences
Climate change is also influencing the shifting demographics and evolving housing preferences of potential buyers and renters. People are increasingly seeking properties in cooler climates, areas with access to green spaces, and those that offer greater resilience to extreme weather events. Understanding these evolving preferences is vital for real estate professionals to effectively market and position properties in the changing climate landscape. This understanding can significantly impact investment strategies and property valuations.

Financial Implications of Climate Change Risks

Economic Impacts of Rising Temperatures
The escalating global temperatures are having a profound effect on various sectors of the economy. Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as floods and droughts, directly impact agricultural yields and infrastructure, leading to substantial economic losses. These disruptions ripple through supply chains, increasing production costs and potentially triggering inflation. Businesses face higher insurance premiums and operational costs, which can ultimately translate into reduced profits and job losses.
Climate change also presents risks to financial institutions, as they face greater exposure to climate-related financial losses. The potential for physical damage to assets, alongside transition risks associated with the shift towards a low-carbon economy, creates a complex landscape for investment and lending decisions. Assessing and managing these risks requires a sophisticated understanding of climate science and economic modeling.
Investment in Green Technologies
While climate change presents significant economic challenges, it also fosters opportunities for investment in green technologies and sustainable practices. Government incentives and private sector initiatives are driving innovation in renewable energy sources, energy efficiency, and sustainable agriculture. These investments can create new jobs, boost economic growth, and potentially lead to long-term cost savings.
The transition to a low-carbon economy presents a significant investment opportunity. Investors are increasingly seeking opportunities in sustainable technologies and practices, potentially leading to substantial returns for those with foresight and expertise. This shift is not without challenges, but the potential rewards are substantial, both for individual investors and for the global economy as a whole.
Adaptation Strategies and Costs
Adapting to the inevitable impacts of climate change will require significant investments in infrastructure and risk management strategies. Coastal communities, for example, will need to invest in flood defenses and seawalls, while agricultural regions will need to develop drought-resistant crops and water management systems. These adaptations, while necessary, will incur substantial costs, potentially straining public budgets and increasing the burden on taxpayers. Understanding the long-term costs and benefits of these adaptation strategies is crucial for effective policymaking.
The costs associated with adapting to climate change are not evenly distributed. Developing nations often bear a disproportionate burden, lacking the resources to implement effective adaptation measures. International cooperation and financial assistance are essential to support these efforts and ensure a more equitable distribution of the burden and benefits of adaptation.
Insurance and Financial Risk Management
The rising frequency and severity of extreme weather events are significantly impacting the insurance industry. Increased payouts for claims related to flooding, wildfires, and storms are putting pressure on insurers' financial stability. This necessitates the development of more sophisticated risk assessment models that take into account climate change projections. Insurers will need to adjust their pricing structures and coverage options to reflect the evolving risk landscape, potentially leading to higher premiums for some.
Beyond the direct financial impacts on insurance companies, climate change poses broader risks to the financial system. The potential for large-scale losses from extreme weather events can trigger cascading effects throughout the economy, potentially leading to financial crises. Effective risk management strategies are crucial for mitigating these risks and ensuring the stability of the financial system.
Data-driven insights are crucial for any organization, and particularly vital for an Asset Valuation Management (AVM) system. Data allows for a more precise and objective assessment of asset values, minimizing subjective biases. By leveraging historical transaction data, market trends, and other relevant information, AVM systems can provide a more accurate reflection of current market conditions.
Regulatory and Policy Considerations
Environmental Regulations and Compliance
Assessing potential environmental liabilities is a crucial aspect of real estate due diligence in the context of climate change. Properties located in floodplains, coastal areas vulnerable to rising sea levels, or areas with high historical pollution levels may face increased regulatory scrutiny and potential remediation costs. Understanding local and national environmental regulations, including zoning ordinances, permitting requirements, and environmental impact assessments, is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring compliance. This includes researching historical contamination, assessing the property's proximity to sensitive ecosystems, and identifying potential future environmental regulations that might impact its value and use.
The impact of climate change on infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and utilities, also needs thorough investigation. Identifying potential vulnerabilities to extreme weather events, like hurricanes, droughts, or wildfires, is critical. Analyzing historical weather patterns and projections for future climate scenarios is vital to understanding the potential for damage to the property and surrounding infrastructure. This due diligence should also include a review of insurance policies and potential coverage gaps related to climate-related risks, as well as an assessment of the property's resilience to future changes in weather patterns.
Policy Implications and Future Trends
Climate change policies, both at local, state, and federal levels, are rapidly evolving, and these policies can significantly impact property values and investment decisions. Understanding potential future zoning restrictions, building codes, and incentives for sustainable development is vital for anticipating the long-term implications of climate change on a property. For instance, policies promoting renewable energy adoption or restricting fossil fuel use may affect the viability of certain types of real estate investments.
The increasing focus on sustainability and climate resilience is creating new market trends. Investors are increasingly prioritizing properties that demonstrate a commitment to environmental responsibility. This includes properties with energy-efficient features, access to public transportation, and proximity to green spaces. Understanding these trends and anticipating future regulations and policies will be crucial for successful real estate due diligence in a changing climate.
Furthermore, the potential for governmental intervention in the form of carbon pricing mechanisms, emissions trading schemes, and other climate policies should be considered. These policies could significantly impact the cost of development, operation, and maintenance of a property, especially if the property is heavily reliant on fossil fuel-based infrastructure or contributes to significant greenhouse gas emissions.
Evaluating the potential for future litigation related to climate change impacts is also a critical component of due diligence. Understanding the potential legal liabilities associated with climate-related damages is essential to mitigating risk.
Analyzing the long-term implications of climate change policies on property values, investment returns, and the overall market is crucial for making informed decisions in a rapidly evolving environment.