Real Estate Climate Risk: Understanding the Science, Impacts, and Solutions
The financial implications extend beyond physical structures. Municipal tax bases shrink as inundation zones expand, creating feedback loops of reduced services and depreciating values. Sophisticated investors now analyze tidal gauge histories alongside construction blueprints when evaluating coastal holdings.
Extreme Weather Events and Property Damage
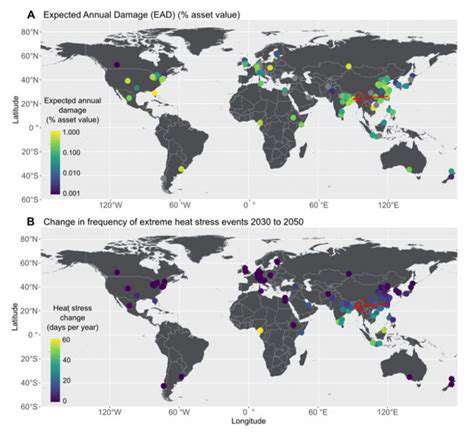
Modern climatology reveals troubling intensification patterns - hurricanes now linger longer, atmospheric rivers dump heavier precipitation, and drought conditions persist across multiple growing seasons. This volatility translates directly to claims frequency, with some insurers withdrawing coverage entirely from high-risk ZIP codes.
Changes in Precipitation Patterns and Water Scarcity
Hydrological shifts create paradoxical challenges - some regions face aquifer depletion while others contend with chronic inundation. Agricultural land values fluctuate dramatically based on irrigation access, while urban properties face new floodplain designations that trigger costly mitigation requirements.
Water rights have become critical valuation factors in western states, where changing snowpack patterns alter long-term water availability projections. Forward-thinking investors now prioritize hydrology reports alongside traditional due diligence documents.
Impacts on Infrastructure and Utility Systems
Aging civil engineering networks struggle under climate stressors - heat-buckled railways, overloaded storm drains, and overtaxed electrical grids now require climate-adjusted maintenance protocols. These systemic vulnerabilities inevitably affect nearby property functionality and operating expenses.
Resilience investments now factor prominently in underwriting criteria, with premium adjustments for properties incorporating floodproof mechanical systems or microgrid capabilities. Infrastructure degradation timelines have accelerated, necessitating revised depreciation schedules.
The Role of Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
Progressive developers now integrate climate modeling into site planning, elevating critical systems above projected flood levels and specifying impact-resistant materials. These adaptations often qualify for preferential financing through green building initiatives.
The most valuable properties now combine hazard mitigation with energy efficiency, creating circular benefits of reduced operating costs and enhanced durability. This dual approach will likely become standard practice as building codes evolve to address climate realities.
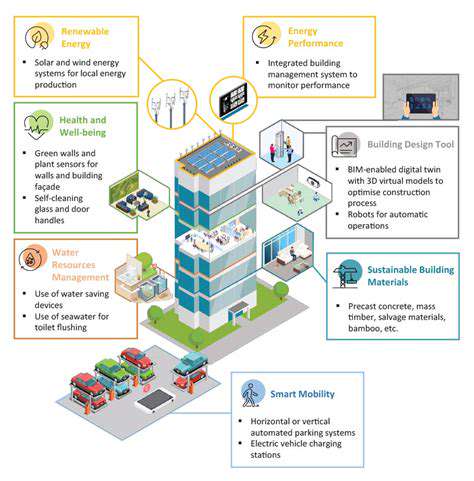
Physical Impacts on Real Estate Assets
Physical Deterioration
Structural integrity degradation occurs along a continuum from superficial blemishes to load-bearing failures. The most financially consequential issues often begin as minor concerns - a hairline foundation crack that widens with freeze-thaw cycles or attic moisture that fosters structural rot. Modern assessment protocols now employ thermal imaging and moisture mapping to detect latent problems before visible symptoms emerge.
Seasonal maintenance cycles prove more cost-effective than reactive repairs. For every dollar spent preserving roof membranes or repointing masonry, owners avoid multiples in emergency remediation costs later. This economic reality drives the professional property management sector's growth.
Environmental Factors
Microclimate exposures create distinct weathering patterns - UV degradation in desert regions, spalling from road salt in northern climates, or mold proliferation in humid zones. These geographically-specific deterioration mechanisms demand tailored maintenance approaches that local contractors best understand.
Coastal properties face particularly aggressive degradation vectors: salt corrosion attacks electrical systems and fasteners, while airborne sand abrades exterior finishes. Savvy owners in these regions implement biannual corrosion inspections and specify marine-grade materials for renovations.
Natural Disasters and Accidents
Catastrophic events expose structural vulnerabilities that routine inspections might miss - inadequate shear walls in seismic zones or undersized drainage capacity in floodplains. Post-disaster forensics often reveal how minor code deviations amplified damage severity, prompting widespread building standard revisions.
The insurance industry's evolving risk models now price these low-probability/high-consequence events differently, with some requiring mitigation retrofits for policy renewal. This creates financial incentives for proactive resilience upgrades.
Maintenance and Neglect
Deferred upkeep follows predictable deterioration pathways: leaking gutters lead to foundation erosion, unattended HVAC filters reduce system lifespan, and unsealed pavement cracks develop into trip hazards. These neglect patterns become exponentially more expensive to correct with each passing year.
Conversely, documented maintenance histories demonstrate operational discipline that translates to premium valuations during transactions. Institutional buyers particularly value properties with digitized maintenance logs and scheduled capital improvement plans.