Climate Risk Disclosure for Real Estate Funds
The Urgency of Climate Risk Disclosure in Real Estate

Understanding the Stakes
Climate change is no longer a distant threat; its impacts are being felt globally, demanding immediate attention and proactive measures. The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events, like hurricanes, floods, and droughts, are causing significant economic losses and humanitarian crises. These events disrupt supply chains, damage infrastructure, and displace communities, highlighting the urgent need for businesses and governments to understand and address climate risks.
Recognizing the interconnectedness of climate change with various sectors is crucial. From agriculture to energy, from finance to healthcare, the effects of climate change are pervasive. Understanding these interconnected risks is paramount to developing effective strategies for mitigation and adaptation.
The Financial Implications
Climate-related financial risks are substantial and pose a significant threat to businesses and investors. The potential for physical damage to assets, disruptions to supply chains, and changes in demand patterns due to extreme weather events can lead to substantial financial losses. Companies that fail to adequately assess and manage these risks are likely to face severe repercussions in the form of reduced profitability and even insolvency.
Insurance companies are also significantly impacted by the escalating climate risks. Increased payouts for claims related to extreme weather events strain their financial resources and potentially lead to rate increases, which could affect consumers and businesses. The financial sector as a whole needs to urgently incorporate climate considerations into their operations and investment strategies.
Transparency and Accountability
Transparent and comprehensive climate risk disclosure is essential for informed decision-making. Investors, businesses, and governments need access to reliable information about the potential impacts of climate change on their operations. This transparency fosters accountability, encouraging organizations to take proactive measures to mitigate their risks and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Accurate and standardized disclosure standards are critical for fostering trust and enabling effective comparisons across companies and industries. This will empower stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding investments and business strategies. By embracing transparency, the private sector can play a crucial role in accelerating the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Policy and Regulatory Responses
Governments play a critical role in addressing the urgency of climate risk disclosure. Policymakers need to implement regulations that encourage businesses to disclose their climate-related risks and opportunities. These regulations should create a level playing field, ensuring that companies are held accountable for their impact on the environment. This will also create incentives for companies to develop and implement robust climate risk management strategies.
Stronger regulations and incentives are crucial to encourage the development of innovative climate-resilient technologies and practices. This will stimulate economic growth while simultaneously reducing the risks and consequences of climate change. Ultimately, policy responses should incentivize responsible corporate actions and drive the necessary transformations to a more sustainable future.
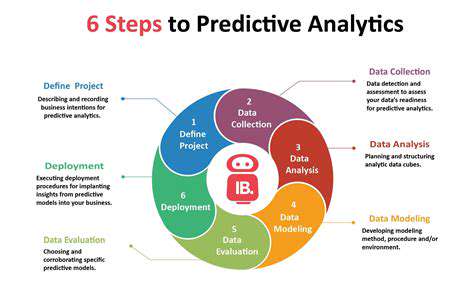
Data Collection and Reporting Standards for Effective Disclosure

Data Collection Methods
Data collection is a critical first step in any successful reporting initiative. Different methods are appropriate for different situations, and the chosen method should align directly with the specific goals and objectives of the reporting. Careful consideration must be given to the potential biases that can arise from various data collection techniques. For example, self-reported data can be prone to inaccuracies due to recall bias or social desirability bias. Observational studies, while offering a different perspective, can be influenced by the observer's presence and potential for subjective interpretation.
Employing a combination of methods can often provide a more comprehensive understanding. For instance, combining surveys with observational data can provide a richer dataset and potentially reduce the impact of individual biases inherent in each method.
Data Validation and Cleaning
Data validation is an essential step in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the collected data. This process involves scrutinizing the data for inconsistencies, errors, and missing values. Addressing these issues early on is crucial for preventing misleading conclusions later in the reporting process. Robust validation techniques are critical in maintaining data integrity and ensuring that reported findings are truly representative of the population being studied.
Cleaning the data further refines the dataset. This involves handling missing data, correcting inconsistencies, and transforming data into a suitable format for analysis. Accurate and thorough data cleaning processes are essential for generating reliable insights and avoiding erroneous interpretations.
Data Storage and Security
Secure storage is paramount for protecting sensitive data. Implementing robust security protocols is essential to safeguard confidential information and comply with relevant regulations. Data breaches can lead to significant reputational damage and financial losses. Furthermore, proper storage methods should ensure data accessibility for authorized personnel while maintaining confidentiality.
Choosing appropriate storage solutions – whether cloud-based or on-premise – depends on the volume and sensitivity of the data. Careful consideration of data backup and recovery procedures is critical to minimize disruption in the event of unforeseen circumstances.
Reporting Frequency and Format
The frequency of reporting should be determined by the nature of the data and the intended use cases. Regular reporting provides opportunities for timely identification of trends and potential issues. This allows for proactive adjustments and improvements in processes or operations.
The format of the report should be tailored to the audience. Clarity, conciseness, and visual aids are crucial for effective communication. Visualizations, such as charts and graphs, can effectively convey complex data in a readily understandable format. Clear and concise reporting language is essential for avoiding misunderstandings and ensuring that the message is conveyed accurately.
Data Analysis Methods
The choice of analytical methods depends heavily on the type of data being collected and the questions being asked. Statistical analysis is often used to identify patterns and trends in large datasets. This analysis can reveal insights that might not be apparent from simply observing the raw data. Qualitative research methods can provide valuable contextual information to complement quantitative findings.
Proper selection of appropriate analytical techniques is crucial for obtaining meaningful and reliable results. Different methods will generate different insights, and the analyst must carefully select the tools that best address the specific research questions.
Stakeholder Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication with stakeholders is vital for ensuring that the collected data and generated reports are used to inform decisions and drive action. Regular updates and reports provide stakeholders with valuable insights and allow them to participate in the decision-making process.
Collaboration among different teams and departments is crucial for ensuring that the data is utilized effectively. Open communication channels and shared access to data and reports foster a collaborative environment that leads to better outcomes. Clearly defined roles and responsibilities regarding data handling and reporting foster efficiency and accountability.
Integrating Climate Considerations into Investment Strategies
Understanding the Evolving Landscape of Climate Risk
Climate change is no longer a distant threat; its impacts are being felt globally, demanding a fundamental shift in how investors approach risk management. The frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and disruptions to global supply chains are all tangible manifestations of climate change, requiring investors to proactively consider these risks in their investment strategies. This necessitates a thorough understanding of the evolving regulatory landscape and the potential financial implications of inaction.
Recognizing the potential for significant financial losses associated with climate change is crucial. Investors must move beyond a purely financial view of investments and incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into their decision-making processes. This proactive approach ensures that long-term investment portfolios are not only financially sound but also resilient to the growing challenges of climate change.
Identifying Climate-Related Financial Risks
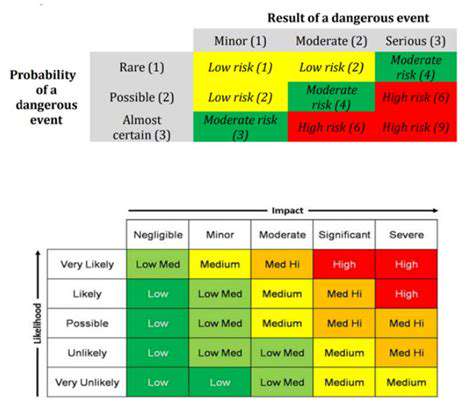
Climate-related financial risks encompass a wide range of potential threats. These include physical risks, such as extreme weather events and rising sea levels, which can directly damage assets and disrupt operations. Transition risks, stemming from the shift toward a low-carbon economy, also pose significant challenges, including stranded assets and regulatory changes that affect industries heavily reliant on fossil fuels.
Assessing these risks requires a careful analysis of individual investments and portfolios. This involves evaluating exposure to specific industries, geographical regions, and supply chains vulnerable to climate change impacts. Thorough due diligence is essential to identify and quantify these risks, enabling investors to make informed decisions about portfolio diversification and risk mitigation strategies.
Incorporating Climate Data into Investment Analysis
Integrating climate data into investment analysis is essential for a comprehensive understanding of potential risks and opportunities. Access to reliable climate data, such as historical temperature trends, projected future climate scenarios, and regional vulnerability assessments, is paramount. This data allows investors to assess the resilience of companies and projects to climate change impacts.
Utilizing climate-related scenario analysis is another critical aspect. By modeling different climate change scenarios, investors can better understand potential future impacts on investment returns and make more informed decisions about portfolio allocation. This forward-looking approach enables proactive risk management and helps to identify investment opportunities in climate-resilient sectors.
Developing Climate-Resilient Investment Portfolios
Developing climate-resilient investment portfolios requires a strategic approach to asset allocation and investment selection. This involves identifying companies and projects with strong environmental performance and a commitment to sustainable practices. Furthermore, it necessitates evaluating the carbon footprint of existing investments and considering opportunities in low-carbon sectors.
Implementing Effective Climate Risk Management Strategies
Effective climate risk management strategies go beyond simply identifying risks; they involve actively mitigating these risks and exploiting potential opportunities. This requires establishing clear policies and procedures for integrating climate considerations into investment decision-making. Robust due diligence processes, scenario analysis, and stress testing are vital tools in assessing and mitigating climate-related risks.
Regular monitoring and reporting on climate risks are crucial for tracking progress and ensuring accountability. Transparency in disclosing climate-related risks and opportunities is paramount for building investor trust and fostering responsible investment practices.
The Role of Disclosure and Transparency in Climate Risk Management
Enhanced disclosure and transparency are essential to driving effective climate risk management. Companies must be transparent in reporting their climate-related risks and opportunities, enabling investors to assess the sustainability of their investments. Clear and standardized reporting frameworks are needed to ensure comparability and reliability of climate-related information.
Stronger regulatory frameworks for climate-related disclosures will further incentivize companies to adopt sustainable practices and enhance investor confidence. By promoting transparency and accountability, investors can make informed decisions and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Read more about Climate Risk Disclosure for Real Estate Funds
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing