Climate Risk and Real Estate Insurance Premiums: Trends
Geographic Variations in Risk and Premium Adjustments
Geographic Variations in Flood Risk
Flooding doesn't impact all areas equally. Coastal zones, river basins, and low-lying terrains naturally face greater exposure to flood hazards, whether from storm surges or heavy rainfall. These locations typically endure more regular and intense flooding than elevated inland areas. Recognizing these differences proves vital for precise risk evaluation and customized mitigation approaches.
Several elements affect flood occurrence and intensity, including land elevation, water drainage infrastructure, and long-term precipitation trends. With extreme weather becoming more common, insurers must adapt their pricing and risk management plans to reflect local conditions accurately.
Impact of Seismic Activity on Premiums
Earthquake-prone regions present distinct challenges for property valuation and insurance. The possibility of devastating quakes demands substantially higher insurance costs in vulnerable areas. Key considerations include ground composition, construction quality, and distance from active faults - all crucial for assessing earthquake risk and determining appropriate premium levels.
Insurers thoroughly examine past earthquake records, geological studies, and regional building regulations to set fair prices for properties. Since quakes strike without warning, comprehensive risk management requires strict construction standards and effective emergency response protocols.
Influence of Climate Change on Precipitation Patterns
Global weather systems are undergoing dramatic shifts, causing more extreme rainfall in some locations. This change elevates flood and landslide risks even in traditionally safer areas. Insurers must update their risk assessment frameworks to incorporate these evolving conditions and modify pricing structures. The impact extends beyond shorelines, with many inland regions now facing unprecedented heavy rainfall episodes.
Adjustments for Wildfire Risk and Frequency
Wildfires represent an escalating threat affecting property values and insurance expenses worldwide. Areas characterized by drought-prone vegetation, strong winds, and proximity to woodlands face particularly high wildfire dangers. These variables play a central role in insurance pricing. Detailed knowledge of regional features - including plant species, prevailing winds, and fire history - proves essential for proper risk evaluation and prevention measures. The recent surge in severe wildfires highlights the importance of forward-looking risk control methods.
Variations in Hurricane Risk and Coastal Erosion
Shoreline properties confront special hazards from tropical storms, tidal surges, and beach erosion. Climate models suggest certain coastal zones will experience stronger and more frequent hurricanes, leading to increased insurance costs for oceanfront real estate. Distance from water, property elevation, and existing coastal defenses significantly affect risk exposure and insurance rates. Accelerating beach erosion due to sea level rise intensifies these vulnerabilities. Insurers must weigh all these elements to create accurate risk profiles and fair pricing models that provide sufficient protection for at-risk properties.
Predictive Analytics and Future Risk Assessment
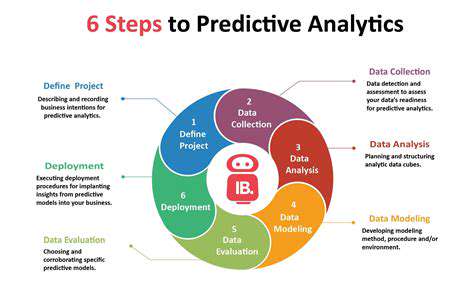
Predictive Modeling Techniques
Modern forecasting methods employ diverse analytical approaches to project future scenarios. These range from basic statistical models to advanced artificial intelligence systems, each suited to different applications. Properly understanding each method's capabilities and constraints is fundamental for reliable predictions. While linear models work well for straightforward relationships, more complex algorithms like decision trees or deep learning networks can uncover intricate patterns in multifaceted situations.
Effective forecasting depends heavily on quality data preparation. This includes selecting impactful variables, ensuring data cleanliness and accuracy, and formatting information appropriately for analysis. Data refinement often proves equally important as model selection for generating meaningful insights. Critical steps include addressing data gaps, adjusting for anomalies, and properly encoding categorical information.
Future Risk Assessment
Advanced analytics transforms how organizations evaluate potential hazards. By detecting patterns in historical information, predictive systems can reveal hidden vulnerabilities that conventional methods might miss. This includes tracking economic trends, consumer patterns, and operational metrics to anticipate problems like financial shortfalls, workflow interruptions, or security threats.
Proactive risk evaluation forms the foundation of sound business strategy. It enables companies to prepare contingency plans and defensive measures. By quantifying risk probabilities and potential impacts, enterprises can distribute resources wisely and make evidence-based choices to reduce negative consequences. This approach benefits multiple sectors, from banking to medical services, by promoting stability and sustainable growth.
Applications in Business
Predictive tools deliver value across numerous business operations. Whether projecting sales volumes, identifying at-risk customers, spotting fraudulent activity, or managing stock levels, the advantages are substantial. Companies utilize predictive systems to refine pricing models, customize client interactions, and streamline business processes. For instance, precise demand forecasting helps retailers maintain optimal inventory, minimizing surplus while meeting customer needs. Predicting customer attrition enables focused retention efforts that preserve revenue streams.
These analytical methods also inform marketing and product development decisions. By understanding consumer preferences and market shifts, businesses can craft targeted promotional campaigns and design products that better satisfy customer requirements. These capabilities ultimately strengthen market position and boost financial performance. The broad applicability of predictive analytics demonstrates its transformative potential across all business functions.
Read more about Climate Risk and Real Estate Insurance Premiums: Trends
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing