Climate Risk and Real Estate Disclosure: What You Need to Know
Identifying and Assessing Climate-Related Risks in Real Estate
Understanding the Scope of Climate Change
The Earth's climate system is undergoing profound transformations with cascading effects across all sectors. These shifts extend far beyond simple temperature increases, disrupting delicate ecological balances and human systems in interconnected ways. Coastal communities face existential threats from rising seas, while agricultural regions grapple with unpredictable growing seasons. The complexity of these changes demands comprehensive analysis to develop robust response strategies.
Primary Contributors to Climate Shifts
Human activities have become the dominant force shaping our planet's climate trajectory. The combustion of coal, oil, and gas for energy production releases unprecedented amounts of carbon dioxide, while industrial processes emit other potent greenhouse gases. Land use changes, particularly deforestation, further exacerbate these effects by removing natural carbon sinks. While natural climate variability continues, its influence has been overshadowed by anthropogenic factors since the mid-20th century.
Ecological Consequences of Climate Change
Biodiversity faces unprecedented challenges as climate patterns shift. Marine ecosystems suffer from ocean acidification and coral bleaching events, while terrestrial species struggle with habitat fragmentation. The timing of natural events like flowering and migration has become increasingly mismatched, threatening intricate ecological relationships. These disruptions ultimately affect human societies through reduced ecosystem services and food security concerns.
Societal Impacts and Vulnerabilities
Climate change manifests differently across communities, often amplifying existing inequalities. Urban heat islands intensify health risks in densely populated areas, while rural populations face agricultural disruptions. The economic costs of climate impacts could reach trillions annually by mid-century, with developing nations bearing disproportionate burdens. Infrastructure designed for historical climate conditions proves increasingly inadequate against modern weather extremes.
Emission Reduction Strategies
Transitioning to low-carbon energy systems represents the cornerstone of climate mitigation. Solar and wind power now compete favorably with fossil fuels in many markets, while energy storage technologies continue advancing. Building efficiency improvements and sustainable urban planning offer significant emission reduction potential with co-benefits for residents. Carbon pricing mechanisms and renewable portfolio standards have proven effective policy tools in various jurisdictions.
Adaptation Approaches
Climate resilience requires tailored solutions reflecting local vulnerabilities. Coastal communities implement managed retreat strategies and living shorelines, while agricultural regions adopt drought-resistant crops. Early warning systems for extreme weather have demonstrated remarkable cost-benefit ratios, saving countless lives. Nature-based solutions like urban green spaces provide multiple benefits including flood mitigation and heat reduction.
International Climate Cooperation
The Paris Agreement framework enables voluntary national commitments while facilitating technology transfer. Multilateral development banks increasingly prioritize climate-smart investments, and carbon markets continue evolving. Subnational actors like cities and corporations often lead ambitious climate action, complementing national efforts. Grassroots movements maintain pressure for accelerated decarbonization across sectors.
The Role of Disclosure in Protecting Stakeholders
Building Trust Through Transparency
Comprehensive disclosure practices serve as the foundation for stakeholder confidence in any organization. When companies proactively share both positive developments and challenges, they demonstrate accountability that resonates with investors and consumers alike. This openness frequently translates into competitive advantages during crises when trust becomes paramount. Conversely, selective disclosure often backfires, as stakeholders increasingly value authenticity over carefully curated messaging.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
Modern securities regulations increasingly mandate climate risk disclosures alongside traditional financial reporting. The SEC's proposed climate disclosure rules exemplify this trend, requiring public companies to disclose material climate risks and transition plans. Non-compliance carries not just legal consequences but also reputational damage that can persist for years. Forward-looking organizations now view disclosure compliance as strategic opportunity rather than mere obligation.
Risk Management Through Disclosure
Proactive risk communication enables organizations to shape narratives before crises emerge. By acknowledging vulnerabilities and outlining mitigation strategies, companies can maintain stakeholder confidence during challenging periods. Scenario analysis disclosures demonstrate sophisticated risk awareness that reassures investors. This approach contrasts sharply with reactive damage control that often follows undisclosed risks materializing.
Engaging Diverse Stakeholders
Modern disclosure extends beyond regulatory filings to encompass multiple communication channels. Sustainability reports, investor presentations, and digital platforms allow tailored messaging for different audiences. Interactive disclosure tools enhance understanding while demonstrating technological sophistication. This multi-channel approach meets stakeholders where they are while maintaining message consistency.
Ethical Dimensions of Disclosure
The tension between transparency and competitive sensitivity presents ongoing ethical challenges. While material information requires disclosure, companies must balance stakeholder needs with legitimate business concerns. Emerging best practices emphasize proportional disclosure - providing sufficient detail without compromising strategic positioning. Independent assurance of disclosures helps maintain credibility while addressing ethical concerns.
Reputational Capital and Disclosure
Organizations with strong disclosure track records often weather crises more effectively than peers. This reputational resilience stems from accumulated goodwill and established communication channels. Investors increasingly incorporate disclosure quality into valuation models, recognizing its correlation with strong governance. The disclosure premium manifests in lower capital costs and higher customer loyalty.
Accountability Mechanisms
Robust disclosure creates natural accountability by enabling performance tracking against stated goals. Climate transition plans with clear metrics allow stakeholders to assess progress objectively. Third-party verification enhances this accountability while reducing greenwashing concerns. Disclosure-linked compensation increasingly aligns executive incentives with long-term sustainability goals.
The Implications for Real Estate Transactions and Investments
Climate Risk and Property Valuation
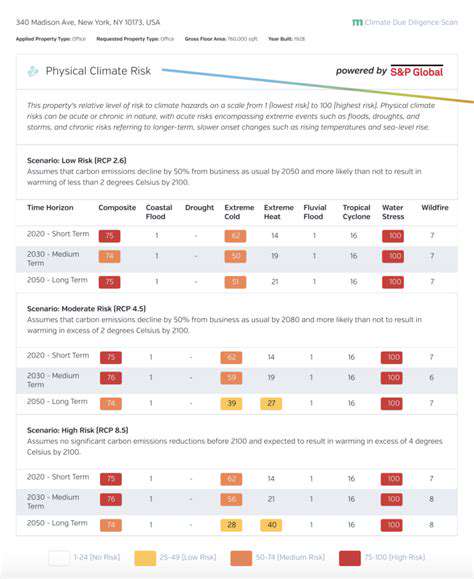
Property valuation methodologies increasingly incorporate climate risk assessments as standard practice. Appraisers now consider flood risk, wildfire susceptibility, and heat stress alongside traditional factors. Coastal properties face particular scrutiny, with some markets already pricing in anticipated sea level rise. Mortgage lenders increasingly require climate risk assessments, reflecting growing regulatory and investor expectations.
Climate-Informed Investment Strategies
Forward-thinking investors now analyze climate scenarios across multiple time horizons. Properties with superior resilience features command premium pricing, while vulnerable assets face growing discounting. Portfolio diversification strategies increasingly emphasize geographic risk spreading across climate zones. Green building certifications like LEED and BREEAM have transitioned from differentiators to baseline expectations in many markets.
Insurance Market Evolution
The property insurance landscape undergoes rapid transformation as climate risks intensify. Some regions experience private market retreat, necessitating state-backed insurance solutions. Parametric insurance products gain traction by offering predictable payouts based on objective triggers. Building resilience measures now directly influence insurability and premium calculations in many jurisdictions.
Long-Term Investment Analysis
Climate-aware underwriting now examines 30-year risk projections rather than historical data alone. Investors utilize sophisticated modeling tools to assess physical risks under various warming scenarios. Transition risks related to policy changes and technological shifts receive equal consideration. This comprehensive analysis helps identify future-proof assets likely to maintain value through the energy transition.
Policy and Regulatory Developments
Building codes evolve rapidly to address climate resilience, with material consequences for development costs. Zoning reforms increasingly restrict construction in high-risk areas while incentivizing climate-smart development. Disclosure mandates create transparency that reshapes investment flows toward resilient assets. Tax incentives for resilience upgrades and energy efficiency improvements influence investment calculus across property types.
Read more about Climate Risk and Real Estate Disclosure: What You Need to Know
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing