LEED Zero Certification: Achieving Net Zero Goals
Key Components of a LEED Zero Building
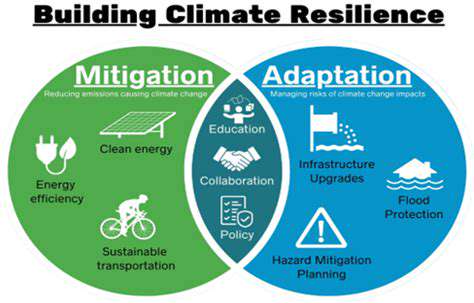
Energy Efficiency Strategies
LEED Zero buildings prioritize energy efficiency throughout their design and construction. This involves meticulous energy modeling to predict and minimize energy consumption. Advanced insulation materials, high-performance windows, and optimized building layouts all contribute to reducing the building's reliance on external energy sources. Careful attention to daylighting strategies further reduces the need for artificial lighting, showcasing a commitment to environmentally conscious design principles that directly impact energy savings.
Furthermore, the implementation of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and geothermal heat pumps, is a crucial aspect of achieving energy efficiency. These systems harness sustainable energy sources, significantly reducing the building's carbon footprint and lowering operational costs in the long run. The integration of smart building technologies enables real-time monitoring and adjustments to energy usage, optimizing performance and further enhancing energy efficiency.
Water Conservation and Management
Water conservation is a critical element of LEED Zero certification. Buildings are designed with water-efficient fixtures and appliances to minimize water usage. Rainwater harvesting systems collect rainwater for non-potable uses, reducing reliance on municipal water supplies. Greywater recycling systems further optimize water usage by reusing wastewater for irrigation or other non-drinking purposes. These strategies demonstrate a commitment to responsible water management, reflecting a holistic approach to environmental sustainability.
Material Selection and Waste Reduction
LEED Zero buildings prioritize the use of sustainable and recycled materials. This extends beyond simply using recycled content to include materials with low embodied energy, meaning they require less energy to produce. Choosing materials with low environmental impact throughout their life cycle is crucial. This conscious approach to material selection contributes significantly to minimizing the environmental footprint of the building from its inception to its eventual decommissioning. Furthermore, waste management strategies are integral to the process, from minimizing waste generation during construction to implementing effective recycling and composting programs.
Site Selection and Urban Planning Considerations
The site selection process for LEED Zero buildings is pivotal. Prioritizing locations with minimal environmental impact and readily available sustainable transportation options is key. Buildings are often sited to maximize natural light and ventilation, minimize disruption to ecosystems, and incorporate green spaces. Considering the surrounding urban environment is critical, as LEED Zero certification often involves the integration of the building into a larger sustainable urban planning framework. This includes factors such as proximity to public transportation, access to green spaces, and the overall environmental health of the immediate surroundings.

Challenges and Considerations in Achieving LEED Zero

Navigating the Complexities of A
The implementation of A presents a multitude of challenges, requiring careful consideration of various factors. Understanding the potential pitfalls and proactively addressing them is crucial for successful execution. A thorough assessment of the existing infrastructure and workflows is essential to ensure a smooth transition. This process often involves significant adjustments to existing procedures, requiring strong communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
Addressing potential resistance to change is paramount. Change management strategies should be meticulously planned and executed to ensure a positive reception and minimize disruption. Open communication and active engagement with all affected parties are critical to fostering a sense of ownership and collaboration in the process.
Evaluating Resource Allocation and Capacity
A significant consideration in implementing A is the allocation of necessary resources, including personnel, budget, and technology. Careful planning and forecasting are crucial to ensure that the project has the resources it needs to execute its objectives efficiently and effectively. This necessitates a comprehensive assessment of current capabilities and a proactive identification of any potential resource gaps.
Adequate staffing and training will be critical to success. The project team needs to be equipped with the skills and knowledge necessary to effectively implement and manage A. This often involves providing employees with training and support to help them adopt new tools and procedures.
Assessing Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Implementing A will inevitably introduce certain risks, and proactive risk management is essential to mitigate potential negative impacts. Understanding the potential challenges, such as data migration issues, system compatibility problems, and user adoption difficulties, is crucial for developing appropriate mitigation strategies. Identifying potential disruptions and developing contingency plans is imperative for maintaining project momentum.
Implementing robust data backup and recovery procedures is vital for safeguarding against unforeseen data loss. This includes establishing regular backups, testing recovery procedures, and ensuring data security measures are in place to protect against malicious activities and data breaches. A well-defined disaster recovery plan is essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
Understanding the Impact on Existing Processes and Systems
A will inevitably impact existing workflows and systems. A thorough understanding of how A will affect current processes is vital to ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruption to ongoing operations. This requires careful analysis of the current processes, identification of dependencies, and assessment of the impact on different departments and stakeholders. This will allow for the identification and mitigation of potential conflicts or inefficiencies.
Careful planning and communication are crucial in ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of the changes and how they will affect them. This includes providing training and support to help employees adapt to new processes and technologies. Addressing any concerns proactively will help foster acceptance and cooperation.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations and Standards
Adherence to relevant regulations and standards is paramount in the implementation of A. The project must comply with all applicable laws, regulations, and industry best practices. This includes data privacy regulations, security protocols, and any other relevant compliance requirements. Failure to adhere to these requirements can lead to significant legal and financial penalties.
Thorough documentation of compliance procedures is essential. This will ensure that the project team and stakeholders remain aware of their obligations and responsibilities. Regular audits and reviews are essential for maintaining compliance standards and avoiding potential issues down the line. This documentation should be easily accessible and understandable to all relevant personnel.
Read more about LEED Zero Certification: Achieving Net Zero Goals
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing