Climate Risk Analytics for Real Estate Lenders: Emerging Best Practices
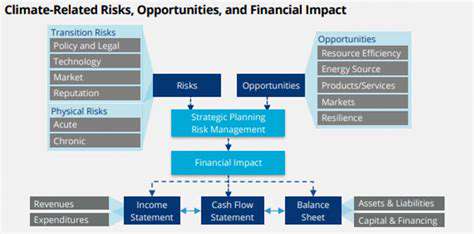
Understanding Transition Risks
Organizational transitions inherently carry risks, whether during mergers, acquisitions, or technological shifts. These challenges arise from adapting to unfamiliar processes, systems, and workplace cultures. Recognizing and addressing these risks early proves vital for smooth transitions and maintaining operational continuity. A comprehensive examination of potential transition risks forms the foundation for developing effective management approaches.
Effective analysis demands careful evaluation of multiple elements: the change's magnitude, implementation timeline, and available resources. Overlooking these critical aspects frequently results in unanticipated complications and schedule overruns.
Critical Factors in Transition Management
Several elements significantly influence transition outcomes: employee acceptance, communication effectiveness, and training adequacy. Clear communication about change rationales and addressing staff concerns often determines transition success.
Resource availability - both financial and personnel - critically impacts transition execution. Insufficient support typically leads to process breakdowns, delays, and budget overages.
Evaluating Organizational Impact
Transition risks affect organizations diversely, potentially reducing productivity, damaging morale, or harming reputation. Thorough impact analysis enables proper resource allocation and mitigation prioritization.
Department-specific transition effects require careful examination. This involves detailed process mapping and anticipating potential workflow disruptions.
Developing Risk Mitigation Approaches
Creating targeted mitigation strategies represents a crucial risk management component. These should address identified concerns through preventive measures and impact reduction tactics. Comprehensive contingency planning provides essential safeguards against unexpected challenges.
Execution and Oversight
Effective implementation demands structured planning with clear timelines and assigned responsibilities. Continuous monitoring ensures plan effectiveness and identifies necessary modifications.
Maintaining open communication channels facilitates feedback collection, issue identification, and timely corrective actions throughout the transition process.
Post-Transition Evaluation
Conducting thorough post-implementation reviews helps identify successes, improvement areas, and key learnings. Analyzing these outcomes strengthens future transition strategies and enhances organizational adaptability.
Documenting lessons learned preserves institutional knowledge and improves change management capabilities for subsequent organizational transitions.
Traditional real estate valuation approaches primarily utilized comparable property analysis, examining factors like size, location, and condition. While basic, these methods established valuation fundamentals that informed subsequent advanced techniques. Historical valuation practices provide important context for contemporary methodologies.
Advanced Analytics for Enhanced Risk Evaluation
Improving Predictive Accuracy
Machine learning applications substantially improve climate risk prediction capabilities. By processing extensive datasets including historical climate records, socioeconomic indicators, and environmental data, these systems detect emerging patterns and critical thresholds. This facilitates more sophisticated climate scenario modeling that accounts for complex system interactions. For instance, integrating precipitation history, temperature variations, and agricultural performance data enables drought-related crop failure predictions, informing mitigation planning.
Advanced analytics also pinpoint sector-specific and regional vulnerabilities. Infrastructure, energy systems, and agricultural practice analysis reveals areas most exposed to climate hazards, enabling targeted interventions and optimized resource distribution.
Data-Informed Decision Making
Analytical insights support evidence-based climate risk management decisions. Clear data visualizations and reports help stakeholders comprehend potential climate impacts, facilitating strategic resource allocation and resilience planning. For example, coastal community sea-level rise analysis enables customized adaptation measures like infrastructure elevation or early alert systems.
Beyond individual assessments, analytical platforms promote stakeholder collaboration. Shared risk analysis frameworks encourage consensus-building for comprehensive climate solutions addressing interconnected challenges.
Effective data presentation through maps, charts, and interactive displays makes complex findings accessible to diverse audiences, fostering transparency and public engagement in climate initiatives.
Developing Climate-Resilient Financing Strategies
Infrastructure Vulnerability Assessment
Creating climate-resilient portfolios begins with comprehensive infrastructure evaluation, examining location, construction materials, and design features. Identifying climate vulnerabilities enables informed financing decisions and risk mitigation. Historical weather pattern analysis provides essential context for location-specific risk assessment.
Detailed property inspections, including engineering reviews and environmental impact studies, ensure thorough resilience evaluation. Future climate projections, like sea-level rise estimates, should inform these assessments to account for evolving risks.
Climate-Adaptive Financing Terms
Loan agreements should incorporate climate resilience requirements, such as mandatory adaptation measures or performance benchmarks. This forward-looking approach reduces climate-related financial risks while promoting sustainable practices. Terms should reflect regional climate challenges and project-specific needs.
Energy efficiency mandates or green building standards in loan conditions protect assets from climate impacts while demonstrating environmental commitment.
Continuous Performance Monitoring
Ongoing evaluation ensures climate resilience measures achieve intended outcomes. Tracking asset performance relative to climate impacts and adaptation effectiveness is crucial. Regular reassessments verify risk analysis validity and borrower compliance.
Maintaining lender-borrower communication channels facilitates adaptive strategy refinement as climate conditions evolve, ensuring continued portfolio resilience.
Read more about Climate Risk Analytics for Real Estate Lenders: Emerging Best Practices
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing