Physical Climate Risk Rating for Real Estate Assets
Evaluating Property Resilience and Adaptation Strategies
Assessing Resilience Factors
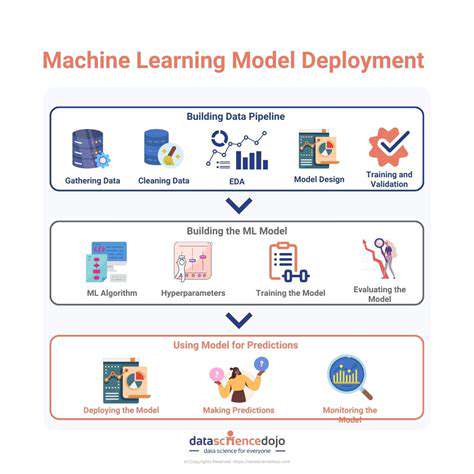
Evaluating property resilience necessitates a comprehensive assessment of various factors that influence its ability to withstand and adapt to climate-related risks. This includes considering the physical characteristics of the property, such as its construction materials, structural integrity, and location within a flood plain or high-risk wind zone. Understanding the historical patterns of extreme weather events in the area is crucial, as this data can be used to project future risks and tailor mitigation strategies accordingly. Analyzing the potential impacts of different climate scenarios, such as increased temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events, is also essential for identifying vulnerabilities and informing adaptation measures.
Furthermore, assessing the social and economic contexts surrounding the property is vital. This involves considering the community's preparedness for climate change, the availability of resources for recovery and rebuilding, and the potential for displacement or economic hardship. Identifying potential disruptions to essential services, such as water supply, sanitation, and transportation, is critical for developing comprehensive resilience strategies. A holistic approach that considers the interplay between physical, social, and economic factors is essential for creating effective and sustainable adaptation plans.
Developing Adaptation Strategies
Once the resilience factors have been assessed, developing appropriate adaptation strategies is paramount. These strategies should focus on reducing vulnerability and enhancing the property's ability to withstand and recover from climate-related impacts. This might involve implementing structural modifications, such as elevating buildings in flood-prone areas or installing reinforced roofing to withstand high winds. Implementing sustainable landscaping practices to manage stormwater runoff and reduce erosion is another crucial component of adaptation.
Beyond structural measures, non-structural strategies are equally important. These could include developing emergency preparedness plans, establishing community networks for mutual aid, and implementing early warning systems for extreme weather events. Investing in community-based education programs to raise awareness about climate risks and promote adaptive behaviors is also a crucial element of a comprehensive adaptation strategy. The goal is to create a resilient property that can not only withstand the impacts of climate change but also contribute to the overall resilience of the surrounding community.
Effective adaptation strategies also need to consider long-term sustainability. This involves exploring innovative technologies and practices that can minimize the environmental footprint of the property and promote resource efficiency. Integrating principles of green building design and sustainable land management can significantly enhance the resilience of the property and reduce its overall impact on the environment. Adapting to climate change requires a proactive and multifaceted approach, considering both short-term and long-term implications to ensure the sustainability of the property and the community.
A key element of successful adaptation is the consideration of the future. This means continuously monitoring the evolving climate risks and adapting strategies as necessary. This necessitates a commitment to ongoing research, data analysis, and stakeholder engagement to stay abreast of the latest scientific findings and community needs. This adaptive management approach is crucial for ensuring that the strategies remain relevant and effective in the face of an ever-changing climate.
Integrating Climate Risk into Portfolio Management
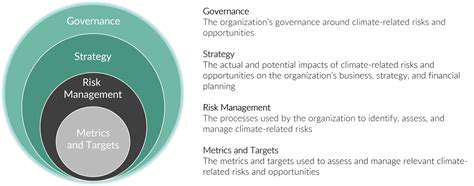
Understanding the Scope of Climate Risk
Climate change presents a multifaceted threat to port operations, impacting everything from infrastructure resilience to supply chain disruptions. Understanding the specific vulnerabilities of each port, from sea-level rise and increased storm intensity to changing precipitation patterns, is crucial. This necessitates a comprehensive assessment considering historical data, projected future scenarios, and the unique characteristics of the port's location and infrastructure.
Analyzing the potential impacts on cargo handling, vessel operations, and the surrounding community is vital. The risk assessment should identify critical assets and infrastructure, evaluate their susceptibility to various climate hazards, and estimate the potential financial and societal consequences of climate-related events.
Adapting Infrastructure to Climate Change
Adapting port infrastructure to withstand the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events is paramount. This includes upgrading existing seawalls, reinforcing docks, and implementing flood control measures. These measures require significant investment and careful planning to ensure long-term resilience and minimize disruption to port operations.
Modernizing infrastructure to improve resilience against climate change is a crucial step in ensuring long-term port sustainability. This involves incorporating climate-resilient design principles into new construction projects, and retrofits of existing infrastructure. This approach considers factors like wave heights, storm surge projections, and changes in precipitation patterns when designing and building new infrastructure.
Integrating Climate Change into Operational Plans
Port operations must be prepared for changing weather patterns. This involves developing contingency plans to mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events, including procedures for evacuations, emergency response, and the temporary suspension of operations. These plans must be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect the evolving climate risks and ensure they are effective and efficient.
Effective contingency planning requires collaboration among port authorities, shipping companies, and other stakeholders. It is crucial to establish clear communication channels and coordination mechanisms to ensure a timely and coordinated response to climate-related emergencies. Regular training and drills for personnel will help ensure preparedness and minimize disruption during events.
Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience
Climate change can disrupt supply chains, impacting the flow of goods and services through the port. A robust supply chain strategy needs to consider the potential for disruptions and the need to diversify transportation routes and sourcing options. This involves building partnerships with other ports and logistics providers to create alternative routes and enhance redundancy.
Implementing technologies and strategies that improve the forecasting and monitoring of weather patterns can help anticipate and prepare for potential disruptions. This will lead to more efficient operations and help ports and their stakeholders minimize the impacts of climate change related disruptions.
Read more about Physical Climate Risk Rating for Real Estate Assets
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing