Sustainable Real Estate: A Blueprint for Sustainable Communities and Urban Growth
Prioritizing Green Spaces and Biodiversity
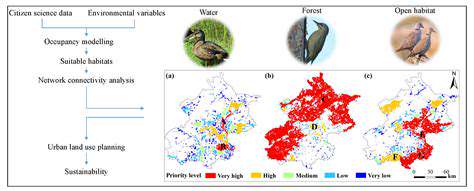
Prioritizing Urban Green Spaces for Enhanced Biodiversity
Urbanization often leads to a significant reduction in natural habitats, impacting biodiversity. Prioritizing the creation and preservation of green spaces is crucial for supporting a wider range of plant and animal life within urban environments. These spaces provide essential resources for food, shelter, and breeding grounds for various species, fostering a healthier and more diverse ecosystem.
By strategically integrating green corridors and pockets of nature, cities can promote ecological connectivity, allowing wildlife to move freely between different areas. This interconnectedness is vital for maintaining genetic diversity and resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
Designing Green Spaces for Diverse Species
Effective green spaces must go beyond simply providing areas for recreation. The design should actively consider the needs of various species, including native plants and animals. This involves incorporating diverse habitats, such as wetlands, meadows, and woodland edges, each with specific requirements for different species.
Planting native vegetation is paramount. Native plants are adapted to local conditions and provide crucial food and shelter for native insects, birds, and mammals. Introducing non-native species can disrupt the existing ecosystem and potentially lead to invasive problems.
The Role of Green Spaces in Mitigating Climate Change
Urban green spaces play a critical role in mitigating the impacts of climate change. Trees and other vegetation absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to regulate temperatures and reduce the urban heat island effect. This is important for human health and comfort, as well as for the overall well-being of the local ecosystem.
Furthermore, green spaces can help manage stormwater runoff, reducing the risk of flooding and improving water quality. This is particularly important in areas facing increased rainfall and extreme weather events.
Community Engagement and Educational Opportunities
Involving the local community in green space initiatives is essential for long-term success. Community gardens, urban farms, and nature trails can foster a sense of ownership and stewardship amongst residents. These opportunities provide valuable educational experiences for both children and adults, promoting environmental awareness and appreciation.
Educational programs focused on the importance of biodiversity and sustainability can further enhance community engagement. These programs can empower residents to become active participants in preserving and enhancing green spaces.
Sustainable Practices for Green Space Maintenance
Sustainable practices are crucial for maintaining the health and biodiversity of urban green spaces. This includes using water-efficient irrigation systems, minimizing pesticide use, and employing native plant species that require less maintenance. These measures help reduce the environmental footprint of urban green spaces while maintaining their ecological value.
Using recycled materials and composting programs in the maintenance of these spaces is essential for minimizing waste and promoting a circular economy. This can significantly reduce the environmental impact of urban green space management.
Funding and Policy Support for Green Spaces
Adequate funding and supportive policies are necessary to ensure the long-term viability of green spaces. This includes securing funding for initial development, ongoing maintenance, and potential restoration efforts. Government policies should prioritize green space development and conservation within urban planning initiatives.
Incentivizing private sector involvement in green space projects, potentially through tax breaks or other incentives, can also help to increase the funding available for these vital spaces. This will create a positive feedback loop, encouraging further investment and preservation of urban green spaces.
Read more about Sustainable Real Estate: A Blueprint for Sustainable Communities and Urban Growth
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing