AI for Property Tax Optimization: Cost Savings
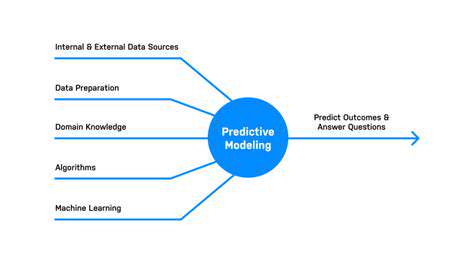
Data Analysis and Predictive Modeling for Tax Assessments

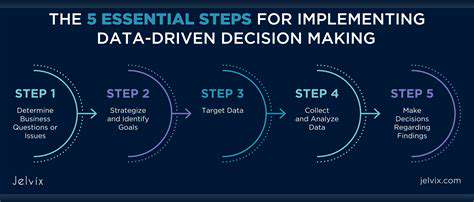
Data Collection and Preparation
A crucial first step in any data analysis project is the meticulous collection of relevant data. This involves identifying the specific data points needed to answer the research questions and determining the appropriate sources. Ensuring data accuracy and consistency is paramount for reliable results. This might involve cleaning and transforming the raw data, handling missing values, and standardizing formats to ensure compatibility with the chosen analytical tools.
The quality and representativeness of the collected data significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of the subsequent analysis. Careful consideration must be given to the potential biases inherent in the data collection process and steps should be taken to mitigate these biases. For instance, if the data is obtained through surveys, the survey design and sampling methods need to be carefully evaluated to avoid introducing any sampling bias.
Exploratory Data Analysis
Exploratory data analysis (EDA) is a vital step in understanding the characteristics of the data. It involves using various techniques to summarize and visualize the data, such as creating histograms, scatter plots, and box plots to identify patterns, trends, and outliers. This preliminary analysis helps in formulating hypotheses and uncovering hidden insights within the data. The goal is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the dataset before proceeding with more advanced modeling techniques.
Visualization plays a critical role in EDA. By visually inspecting the data, analysts can quickly identify potential relationships between variables, detect anomalies, and gain a better understanding of the data distribution. Using interactive tools and dashboards can further enhance the exploratory process by enabling analysts to drill down into specific subsets of the data and explore various perspectives.
Model Development
Selecting the appropriate predictive model is crucial for achieving accurate predictions. The choice of model depends on the nature of the data and the specific prediction task. Linear regression, logistic regression, support vector machines, and decision trees are common choices for various types of predictive modeling tasks. Factors like the size of the dataset, the complexity of the relationships between variables, and the desired accuracy of the predictions all influence the model selection process.
Careful consideration should be given to the model's assumptions and potential limitations. Understanding the underlying assumptions of each model is essential for interpreting the results accurately. It is also important to evaluate the model's performance using appropriate metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score to ensure that the model meets the required performance standards.
Model Evaluation and Validation
Evaluating the performance of the developed predictive model is essential to ensure its effectiveness. Techniques like cross-validation and hold-out samples are employed to assess the model's ability to generalize to unseen data. Accurate model evaluation helps identify areas for improvement and ensures that the model is reliable and robust. This involves examining the model's performance on different subsets of the data to assess its ability to predict outcomes accurately, and to identify any biases or overfitting issues.
Careful attention must be paid to the potential for overfitting, where the model performs exceptionally well on the training data but poorly on new, unseen data. Techniques such as regularization can help mitigate overfitting and improve the model's generalizability. By using appropriate evaluation metrics, analysts can effectively gauge the model's performance and make informed decisions about its deployment.
Deployment and Monitoring
Deploying the predictive model into a production environment is the final step in the data analysis process. This often involves integrating the model with existing systems and infrastructure to ensure seamless operation. Thorough documentation is crucial for maintaining and updating the model over time. This includes clearly defining the input variables, model parameters, and evaluation metrics used in the model. Continuous monitoring of the model's performance is crucial to ensure its continued effectiveness and adaptability to evolving data patterns.
Regularly checking for changes in the underlying data and refining the model accordingly is essential to maintaining prediction accuracy. This ongoing monitoring process ensures the model remains relevant and useful in the long run. Data drift and concept drift can affect the model's performance over time, so monitoring and adapting to these changes is key for continued success.
Automated Valuation and Assessment Processes
Automated Valuation Models
Automated valuation models (AVMs) are increasingly sophisticated tools leveraging machine learning algorithms to estimate property values. These models analyze vast datasets of property characteristics, market trends, and comparable sales data to generate highly accurate valuations. This automated approach significantly reduces the time and resources required for traditional appraisal processes, enabling faster and more consistent property assessments. AVMs can quickly process a large volume of properties, making them invaluable for jurisdictions facing substantial backlogs in property tax assessments.
A key advantage of AVMs lies in their ability to incorporate a wider range of data points. This includes factors like property size, location, age, condition, and even neighborhood characteristics, which may be missed or underrepresented in manual assessments. By considering all these variables, AVMs create a more comprehensive and reliable picture of property value, ultimately leading to fairer and more equitable property tax valuations.
Assessment Process Optimization
Beyond valuation, AVMs can streamline the entire assessment process. They can automate the data collection and processing steps, reducing errors and ensuring consistency across all assessments. This automated approach frees up assessor staff to focus on more complex tasks, such as reviewing and validating AVM outputs, addressing discrepancies, and handling appeals. This enhanced efficiency can lead to significant cost savings for jurisdictions and potentially faster turnaround times for property tax assessments.
Furthermore, the data-driven nature of AVMs allows for continuous improvement and refinement. By analyzing the performance of the model against actual market data, adjustments can be made to improve accuracy over time. This iterative process ensures that the valuations remain relevant and responsive to changing market conditions, minimizing the impact of fluctuations and ensuring that property taxes reflect current market values.
The ability to analyze large volumes of data also allows for the identification of potential anomalies or inconsistencies in the assessment data. This can lead to the detection of undervalued or overvalued properties, allowing for targeted adjustments to ensure a more equitable and accurate tax base.
Implementation of AVMs can also lead to improved transparency and accountability in the assessment process. The ability to trace the inputs and methodology used in the valuation process enhances public trust and provides a clear framework for resolving any disputes or appeals.
Finally, AVMs can aid in identifying and addressing potential bias in assessment data, which is a crucial aspect of ensuring fair and equitable property taxation. By detecting patterns and anomalies in the data, AVMs can help identify and mitigate biases, leading to more accurate and equitable valuations.
Identifying Opportunities for Tax Reduction and Appeals

Identifying Tax-Efficient Investment Strategies
Tax-efficient investment strategies are crucial for maximizing returns and minimizing your tax burden. Understanding the various tax implications associated with different investment vehicles, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, is essential. Properly structuring your investments can significantly impact your overall tax liability, allowing you to keep more of your hard-earned money. Diversification across different asset classes can also play a key role in mitigating tax risks. For example, strategically allocating funds to tax-advantaged accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs can significantly reduce your current tax obligations and boost your long-term financial security.
Furthermore, considering the tax implications of capital gains and losses is vital. Understanding the short-term and long-term capital gains tax rates can help you make informed decisions. Knowing when to sell investments to minimize capital gains taxes is an important aspect of financial planning. Tax-loss harvesting, which involves selling investments that have lost value to offset gains from other investments, can significantly reduce your tax liability. This strategy can be particularly beneficial for investors with substantial portfolios.
Leveraging Tax Credits and Deductions
Many individuals and businesses may be eligible for various tax credits and deductions. Understanding these opportunities can lead to substantial tax savings. Homeowners, for instance, can often claim deductions for mortgage interest and property taxes. This can significantly reduce the tax burden associated with homeownership, making it a more attractive investment option.
Furthermore, business owners may be able to deduct various business expenses, such as office supplies, travel, and equipment. These deductions can significantly reduce the taxable income of the business. Careful record-keeping is essential for accurately claiming these deductions. Thorough documentation of expenses can ensure that you maximize your tax deductions and minimize potential penalties.
Tax credits, on the other hand, directly reduce your tax liability dollar for dollar. These credits can be particularly beneficial for low-to-moderate-income individuals and families. Government programs often provide tax credits for energy efficiency improvements or for adoption expenses, among other things. Maximizing these opportunities can make a substantial difference in your bottom line.
Exploring available tax credits and deductions is an integral part of optimizing your tax strategy. It's important to consult with a qualified tax professional for personalized advice on how to leverage these opportunities effectively and legally.
Read more about AI for Property Tax Optimization: Cost Savings
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing