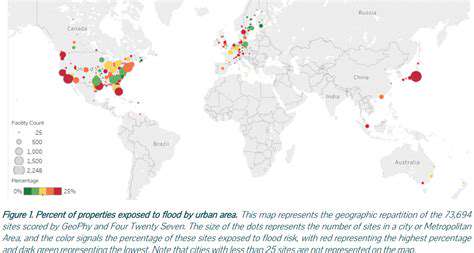
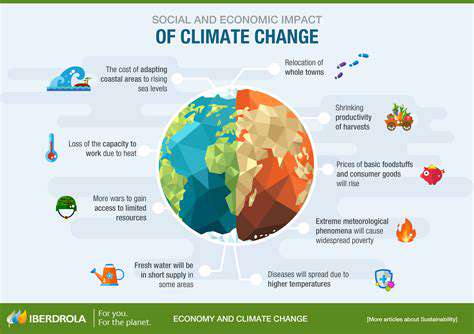
Climate Risk and Real Estate Development: Building for Resilience
Identifying Potential Climate Risks
A crucial first step in assessing climate risks in development projects is to identify the specific vulnerabilities of the project to various climate-related hazards. This involves a thorough analysis of the project's location, considering factors such as historical climate data, projected future climate scenarios, and the potential impacts of extreme weather events like floods, droughts, storms, and heatwaves. Understanding the specific climate risks relevant to the project, including their frequency, intensity, and potential impacts on project components and beneficiaries, is essential for developing effective risk mitigation strategies. This initial assessment should also consider the potential for sea-level rise, glacial melt, and changes in precipitation patterns, as these can have long-term and significant consequences.
Analyzing the vulnerability of the project's location to climate change necessitates a deep dive into historical trends. Examining past weather patterns, including extreme events, and correlating them with potential impacts on similar projects in the area allows for a more informed prediction of future risks. Furthermore, incorporating local community knowledge and traditional ecological knowledge is critical for a comprehensive understanding of the specific challenges and vulnerabilities unique to the region.
Developing Climate Risk Mitigation Strategies
Once potential climate risks have been identified, the next step is to develop tailored mitigation strategies. These strategies should encompass a range of approaches, from structural measures to policy interventions and community-based adaptation techniques. For example, building flood defenses or drought-resistant infrastructure are structural measures, while implementing sustainable land management practices or early warning systems are examples of policy and community-based adaptation strategies. A key aspect of this stage is considering the cost-effectiveness and feasibility of each mitigation option, balancing immediate needs with long-term resilience goals.
Risk mitigation strategies must consider the unique context of the project. Factors such as the local economy, social structures, and existing infrastructure will influence the most effective strategies. Engaging local communities in the planning process is essential for ensuring that solutions are relevant, practical, and culturally appropriate. Community participation can also help to build local capacity for future climate change adaptation and resilience.
Integrating Climate Considerations into Project Design
Integrating climate considerations into the very design of development projects is crucial for long-term sustainability and resilience. This means incorporating climate-resilient features into infrastructure, such as flood-resistant building designs, or incorporating drought-tolerant crops into agricultural projects. This also extends to the project's overall planning, including supply chains, resource management, and contingency plans for unexpected climate events. Incorporating these considerations early in the design phase can significantly reduce vulnerabilities and minimize potential disruptions later on.
This integration should also extend to the project's monitoring and evaluation frameworks. Effective monitoring systems can track the effectiveness of mitigation strategies and identify potential weaknesses or emerging risks. This data can then be used to refine and improve future projects, creating a cycle of continuous improvement in climate resilience.
Monitoring and Evaluating Climate Risk Management
A comprehensive approach to assessing climate risks requires a robust monitoring and evaluation framework. Regular monitoring of weather patterns, the performance of mitigation strategies, and the impacts of climate events on the project are essential for identifying areas needing adjustments or improvements. This involves collecting and analyzing data on project performance, community well-being, and the overall effectiveness of implemented measures. This data provides critical feedback for refining strategies and ensuring that interventions are having the intended positive effects.
Evaluation must encompass both quantitative and qualitative data. Quantitative data, such as rainfall records or infrastructure damage reports, can provide hard evidence of the effectiveness of mitigation measures. Qualitative data, such as community feedback and expert assessments, can offer valuable insights into the social and environmental impacts of the project and the broader context of climate change adaptation.
Integrating Climate Resilience into Design and Construction Practices

Understanding Climate Change Impacts
Climate change is no longer a future threat; its impacts are being felt globally, and the consequences are multifaceted and severe. Changes in weather patterns, including more frequent and intense heatwaves, droughts, floods, and storms, are already causing significant disruptions to ecosystems and human societies. These events often exacerbate existing vulnerabilities, disproportionately affecting marginalized communities and nations with limited resources.
Understanding the specific impacts of climate change in a given region is crucial. This involves analyzing historical data, projecting future scenarios, and identifying the most vulnerable sectors and populations. Such analysis allows for the prioritization of adaptation strategies and the development of targeted interventions that build resilience.
Developing Climate-Resilient Infrastructure
Modern infrastructure must be designed and built with climate change in mind. This includes considering extreme weather events like hurricanes, wildfires, and sea-level rise when constructing buildings, transportation networks, and utilities. The incorporation of climate-resilient design principles can significantly reduce the risk of damage and disruption.
Examples of climate-resilient infrastructure include flood-resistant drainage systems, elevated roads and buildings in coastal areas, and drought-resistant water management strategies. Implementing these measures can help protect communities and critical infrastructure from the escalating impacts of climate change.
Strengthening Community Preparedness
Community preparedness is essential for building climate resilience. This involves educating communities about the risks associated with climate change, providing access to early warning systems, and empowering individuals and groups to take proactive steps to mitigate the effects of extreme weather events.
Community-based disaster preparedness programs, including evacuation plans, resource sharing, and community-led response mechanisms, are vital for effective disaster response. Promoting community engagement and knowledge sharing will enhance the collective capacity to respond to and recover from climate-related disasters.
Implementing Sustainable Land Management Practices
Sustainable land management practices play a crucial role in climate resilience. These practices focus on protecting and restoring ecosystems, such as forests and wetlands, which act as natural buffers against extreme weather events. They also include promoting sustainable agricultural practices that enhance soil health and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Reforestation efforts, sustainable agriculture techniques, and improved water management systems are key components of sustainable land management. These initiatives not only enhance climate resilience but also contribute to biodiversity conservation and improved livelihoods for local communities.
Integrating Climate Considerations into Policy and Decision-Making
Integrating climate considerations into policy and decision-making processes is critical for long-term climate resilience. This requires incorporating climate projections into national and local development plans, creating incentives for climate-friendly investments, and enacting regulations that promote sustainable practices.
Policymakers and planners must consider the potential impacts of climate change on all sectors of society, from infrastructure development to public health. This proactive approach ensures that the needs of future generations are taken into account and that long-term resilience is built into every aspect of society.
Promoting International Cooperation and Knowledge Sharing
Climate change is a global challenge that requires a global response. International cooperation and knowledge sharing are vital for building climate resilience. This includes collaboration on research, development, and technology transfer to facilitate the implementation of effective solutions.
Sharing best practices, exchanging lessons learned, and fostering partnerships between nations will accelerate the development and deployment of climate-resilient technologies and strategies. This will ultimately enable a more coordinated and effective global response to the escalating threat of climate change.
Financial Considerations and the Role of Insurance in Climate-Resilient Development

Investment Strategies for Retirement
Planning for retirement requires a multifaceted approach, and one of the crucial aspects is developing sound investment strategies. This involves understanding your risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals. Diversification is key to mitigating risk, spreading your investments across different asset classes like stocks, bonds, and real estate. A well-diversified portfolio can help to weather market fluctuations and protect your capital over the long term. Different investment vehicles, such as mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and individual stocks, offer various levels of risk and potential returns. Carefully evaluating these options based on your personal circumstances is essential for achieving your retirement objectives.
Understanding the interplay between investment strategies and your retirement goals is critical. For example, if your retirement goal is to maintain a specific lifestyle, your investment strategy should be aligned with that goal. This means considering the potential for inflation and adjusting your investments accordingly to ensure that your retirement income remains sufficient to meet your needs. Proper planning should also involve regular reviews and adjustments to your investment strategy as your financial situation and goals evolve. This process allows for adapting to market changes and ensuring your investments remain aligned with your long-term objectives.
Tax Implications and Financial Planning
Tax implications are an undeniable part of financial planning, especially for retirement. Understanding how your investments are taxed, including capital gains and dividends, is crucial to maximizing your returns. Federal and state tax laws can significantly impact your overall retirement savings and the effectiveness of your chosen investment strategy. Careful consideration of these tax implications is essential to avoid unnecessary tax burdens and ensure that your retirement funds are managed effectively.
Proper tax planning can lead to substantial savings, helping to stretch your retirement funds further. Consulting a qualified financial advisor can provide valuable insights into navigating the complexities of tax laws and optimizing your investment strategy for maximum returns while minimizing tax liabilities. This proactive approach can safeguard your financial well-being and ensure that your retirement savings are used most effectively.
Estate planning is often a crucial component of comprehensive financial planning, particularly as it relates to retirement. Proper legal documentation and strategic asset allocation can help manage the transfer of assets to beneficiaries, minimizing potential tax liabilities and ensuring a smooth transition. This aspect of planning often requires guidance from legal professionals to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations. Understanding the legal and tax aspects of estate planning is essential for securing a comfortable retirement for yourself and your loved ones.
Promoting Community Resilience through Sustainable Development Practices
Building Community Capacity for Climate Change Adaptation
Empowering communities with the knowledge, skills, and resources necessary to adapt to climate change impacts is crucial for building resilience. This involves training programs focused on climate-smart agriculture, water management techniques, early warning systems for extreme weather events, and disaster preparedness. By equipping community members with practical skills and fostering a sense of collective responsibility, we can enhance their ability to withstand and recover from climate-related challenges.
Sustainable Infrastructure for a Resilient Future
Investing in resilient infrastructure is paramount for safeguarding communities from climate change impacts. This includes constructing buildings and infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events like floods, storms, and heatwaves. Using sustainable materials and design principles, we can create structures that are not only durable but also contribute to a lower carbon footprint. This long-term approach ensures community safety and minimizes future vulnerability.
Promoting Climate-Smart Agriculture and Food Security
Climate change poses significant threats to food security, impacting crop yields and livestock production. Transitioning to climate-smart agricultural practices is vital for preserving food production systems. This involves promoting drought-resistant crops, implementing water-efficient irrigation techniques, and integrating climate-resilient livestock management strategies. These practices not only enhance food security but also reduce the carbon footprint of agriculture.
Enhancing Water Management and Resource Conservation
Sustainable water management is essential for community resilience in the face of changing climate patterns. Implementing water-saving technologies and promoting efficient water use practices within households and communities are crucial steps. Furthermore, developing rainwater harvesting systems and exploring alternative water sources can ensure a reliable water supply during periods of drought. This proactive approach ensures long-term water security and reduces vulnerability to water scarcity.
Fostering Community Engagement and Collaboration
Community engagement and collaboration are essential elements in promoting resilience. Active participation from community members in decision-making processes related to climate change adaptation and mitigation strategies is crucial. This participatory approach ensures that solutions are tailored to the specific needs and priorities of the community. Building strong partnerships between local communities, government agencies, and non-governmental organizations facilitates the effective implementation of climate-resilient initiatives.
Promoting Sustainable Energy and Reducing Emissions
Transitioning to renewable energy sources is vital for mitigating the effects of climate change and building community resilience. Promoting the use of solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance energy security. Investing in energy efficiency measures in buildings and transportation systems can further contribute to reducing the community's carbon footprint. This shift towards sustainable energy practices not only protects the environment but also fosters economic growth and community well-being.
Read more about Climate Risk and Real Estate Development: Building for Resilience
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing