Sustainable Real Estate: A Blueprint for Sustainable Communities and Regenerative Urban Growth

Sustainable Infrastructure
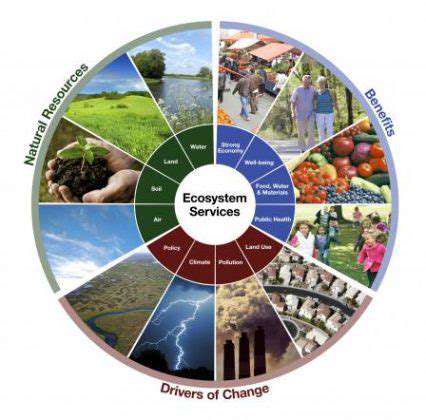
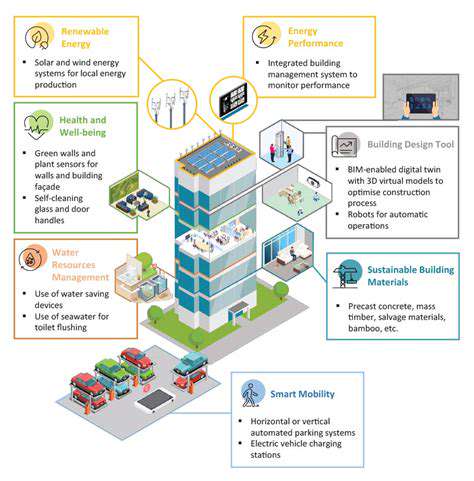
Truly green communities integrate sustainability into their very foundations. District energy systems leverage shared geothermal wells to efficiently heat multiple buildings. Permeable paving materials allow rainwater to replenish groundwater instead of overwhelming storm drains. These systemic solutions create environmental benefits that individual buildings can't achieve alone.
Transportation networks designed around people rather than cars encourage walking and cycling. Electric vehicle charging stations powered by community solar arrays complete the clean mobility ecosystem. This infrastructure planning reduces emissions while creating more livable neighborhoods.
Green Spaces and Biodiversity
Urban oases do more than beautify - they're essential for healthy communities. Native plant gardens require minimal watering while supporting pollinators. Green roofs insulate buildings while creating habitats for urban wildlife. These natural elements improve air quality and reduce the urban heat island effect.
Thoughtful landscape design connects green spaces through wildlife corridors, allowing animals to move safely through developed areas. Community gardens provide fresh produce while educating residents about sustainable agriculture practices.
Waste Management and Recycling
Zero-waste communities treat garbage as a design flaw rather than an inevitability. On-site composting transforms food scraps into nutrient-rich soil amendments. Material recovery facilities sort construction debris for reuse in future projects, closing the resource loop. These systems dramatically reduce landfill contributions while creating local economic opportunities.
Smart waste stations with sensors optimize collection routes, reducing truck emissions. Educational campaigns paired with convenient recycling options drive high participation rates among residents.
Community Engagement and Education
Sustainability succeeds when embraced as a shared value rather than imposed as a requirement. Hands-on workshops teach practical skills like energy auditing and water conservation. Neighborhood sustainability champions model green living while assisting others. These grassroots efforts create lasting behavior change.
Digital platforms share real-time environmental data, allowing residents to track their community's progress. Gamification elements like energy-saving competitions maintain engagement and motivation over time.
Economic Opportunities and Partnerships
Green communities spark innovative local businesses. Urban farms supply restaurants with hyper-local produce. Repair cafes extend product lifecycles while building community connections. These enterprises demonstrate that environmental responsibility and economic vitality reinforce each other.
Public-private partnerships accelerate sustainability initiatives. Utility companies fund energy efficiency upgrades while universities provide research expertise. This collaborative approach multiplies the impact of limited resources.
Healthy and Equitable Communities
Thoughtful design promotes wellbeing for all residents. Affordable housing units meet the same environmental standards as market-rate homes. Universal design principles ensure accessibility regardless of age or ability. These inclusive approaches create communities where everyone can thrive.
Proximity to nature, clean air, and safe walking routes contribute to better physical and mental health outcomes. Community centers offer programs that bridge socioeconomic divides while promoting environmental stewardship.
Resource Efficiency and Circularity in Construction Practices
Resource Efficiency in Construction
Modern construction techniques dramatically reduce material waste without compromising quality. Prefabricated wall panels arrive at job sites ready for installation, minimizing cut-off waste. Digital modeling optimizes material orders to within 2% of actual needs, a vast improvement over traditional estimation methods.
Water reclamation systems on construction sites recycle thousands of gallons for dust control and equipment cleaning. These innovations demonstrate that environmental responsibility can coexist with project efficiency and profitability.
Circular Economy Principles in Construction
The construction industry transforms from linear consumer to circular innovator. Modular building components designed for disassembly allow entire structures to be reconfigured rather than demolished. Material passports track components' origins and potential future uses, creating a marketplace for high-quality reclaimed materials.
Deconstruction crews trained in careful disassembly recover up to 90% of building materials for reuse. This shift from wrecking balls to surgical deconstruction represents a fundamental change in how we view building lifecycles.
Sustainable Material Selection and Sourcing
Local material sourcing reduces transportation emissions while supporting regional economies. Innovative alternatives like mushroom-based insulation and recycled glass countertops perform as well as traditional options. Lifecycle assessment tools help designers choose materials with the smallest environmental footprints.
Salvaged materials add character while reducing demand for virgin resources. Reclaimed wood flooring and antique brick walls tell stories while honoring sustainable principles.
Waste Management and Recycling Strategies
Construction sites evolve into sophisticated material recovery operations. On-site sorting stations separate metals, wood, concrete, and other materials for dedicated recycling streams. Crushed concrete becomes aggregate for new foundations, demonstrating the circular economy in action.
Digital platforms connect projects with nearby material needs, ensuring surplus supplies find new homes rather than landfills. These systems turn waste management from cost center to value opportunity.
Deconstruction and Demolition Practices
The demolition industry reinvents itself through selective deconstruction techniques. Specialized crews carefully remove reusable components before processing remaining materials. Historic building elements find new life in contemporary designs, preserving craftsmanship while reducing waste.
Advanced material separation technologies recover pure material streams from demolition debris. These innovations make recycling economically viable while conserving valuable resources.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and Building Performance
Comprehensive LCA tools now inform every design decision. Architects compare multiple material options' environmental impacts across entire building lifecycles. These analyses reveal surprising opportunities to reduce carbon footprints through smart material choices.
Operational data from existing buildings feeds back into the design process, creating continuous improvement cycles. This evidence-based approach ensures each new project builds on previous sustainability achievements.
Encouraging Equity and Accessibility in Sustainable Development

Promoting Inclusive Policies
Equitable development policies actively dismantle historical barriers to opportunity. Municipal affordable housing mandates now frequently include sustainability requirements. Community land trusts preserve affordability while implementing green building standards. These policies ensure environmental benefits reach all residents.
Transparent decision-making processes invite broad community participation. Multilingual outreach and accessible meeting formats ensure all voices contribute to shaping neighborhood development.
Investing in Infrastructure
Universal design principles transform public spaces into welcoming environments for all. Curb cuts and tactile paving assist mobility-impaired residents while benefiting parents with strollers. These inclusive features demonstrate that accessibility enhances usability for everyone.
Digital infrastructure receives equal attention, with municipal websites meeting WCAG accessibility standards. Public WiFi networks bridge the digital divide, ensuring equal access to information and services.
Providing Comprehensive Support Services
Holistic support programs address multiple barriers simultaneously. Weatherization assistance reduces energy bills while improving home comfort. Job training programs prepare workers for green economy positions, creating pathways out of poverty.
Community navigators help residents access available resources, from energy rebates to nutrition programs. This personalized assistance ensures support systems reach those who need them most.
Promoting Cultural Sensitivity
Community designs honor diverse cultural traditions through inclusive public spaces. Multilingual signage and programming reflect neighborhood demographics. Cultural competency training for staff fosters respectful service delivery across all community interactions.
Public art installations celebrate local histories and identities. These visible representations of diversity strengthen community bonds while fostering mutual understanding.
Ensuring Equitable Access to Resources
Strategic placement of essential services eliminates geographic barriers. Fresh food markets anchor transit-accessible locations in food deserts. Mobile health clinics bring preventive care to underserved neighborhoods. These targeted interventions address disparities at their roots.
Sliding-scale pricing models make sustainability upgrades accessible across income levels. Energy efficiency programs specifically designed for renters overcome split-incentive barriers.
Addressing Systemic Barriers
Data-driven equity analyses identify hidden obstacles in policies and programs. Participatory budgeting processes empower communities to direct resources to priority needs. These structural changes create more just systems.
Supplier diversity programs create economic opportunities for minority-owned businesses. Workforce development pipelines prepare local residents for construction careers on neighborhood projects.
Monitoring and Evaluating Progress
Comprehensive equity metrics track program effectiveness across demographic groups. Regular community surveys measure lived experiences of inclusion, complementing quantitative data. This feedback loop ensures interventions achieve intended impacts.
Public dashboards display progress toward equity goals, maintaining accountability. These transparent reporting mechanisms build trust while driving continuous improvement.
Read more about Sustainable Real Estate: A Blueprint for Sustainable Communities and Regenerative Urban Growth
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing