Affordable Green Housing: Policy and Innovation

Financial Models for Sustainable Housing Development
Evaluating Investment Opportunities
One critical factor in sustainable housing projects is pinpointing financially sound ventures. Financial frameworks help gauge potential returns and overall project viability. These models must consider initial expenses like land purchase, construction materials, labor, permits, and recurring costs such as maintenance, utilities, and taxes. Thorough analysis of these factors allows developers to assess feasibility and profitability with greater confidence.
Various financial approaches suit different project phases. For instance, discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis estimates future cash values to determine overall profitability. Sensitivity testing refines this further by illustrating how changes in construction costs, interest rates, or energy savings impact outcomes. This dual approach helps mitigate risks while creating effective backup strategies when market conditions shift unexpectedly.
Analyzing the Environmental and Social Impacts
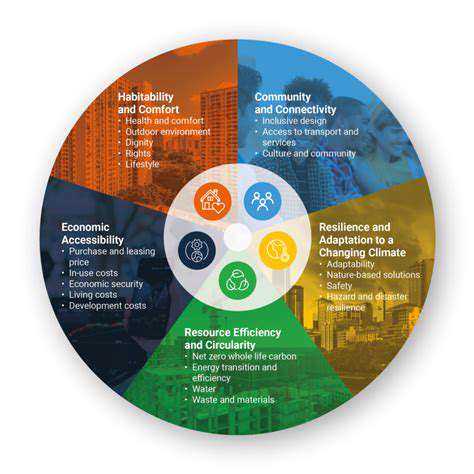
Truly sustainable housing extends beyond profits—it builds eco-conscious communities with social equity. Financial planning should therefore include environmental and social dimensions alongside monetary metrics. Key considerations include carbon reduction, water efficiency, and local job creation. Incorporating these elements demonstrates the lasting value of green housing beyond immediate financial gains.
Measuring these benefits presents challenges but remains essential. Calculating savings from energy efficiency or evaluating how affordable units improve underserved neighborhoods requires meticulous data analysis. Some models assign monetary values to environmental benefits (like carbon offsets) and social improvements (such as healthcare savings from cleaner air). This holistic approach balances financial success with environmental stewardship and community wellbeing.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methods offer additional insights by evaluating material impacts, construction processes, and long-term building performance. This data informs design choices that minimize ecological footprints throughout a project's lifespan.
When financial models incorporate these multifaceted considerations, they showcase sustainable housing's true societal value—attracting investors who recognize projects delivering both returns and positive community transformation.
Community Engagement and Education
Community Involvement
Successful green housing initiatives thrive on active community participation—engaging residents, businesses, organizations, and local governments. Genuine collaboration helps identify unique community needs and potential obstacles. This inclusive process ensures projects reflect local contexts while fostering resident ownership and long-term sustainability.
Educational initiatives complement this involvement by teaching residents to maintain green features like efficient appliances and water systems. Equipping communities with practical knowledge promotes lasting environmental benefits through daily habits.
Educational Outreach
Effective awareness campaigns must target diverse audiences—future residents, developers, builders, and policymakers alike. Demonstrating green construction's financial and environmental perks encourages broader adoption through success stories, technical support, and incentives.
Outreach materials should accommodate various learning styles via digital resources, workshops, and interactive presentations. Accessible education empowers stakeholders to understand and implement sustainable housing principles effectively.
Policy Support for Green Initiatives
Government policies fundamentally shape affordable green housing development. Tax incentives or subsidies for sustainable features motivate developer participation, while clear efficiency standards ensure quality. Policies must specifically address low-income populations to guarantee equitable access to eco-friendly living spaces.
Innovation in Green Housing Design
Creative design solutions are revolutionizing affordable green housing. From recycled/local materials reducing construction footprints to flexible layouts adapting to changing needs, innovation drives accessibility. Smart technologies like efficient lighting and thermostats slash energy use while lowering resident costs—making sustainability both practical and economical.
Read more about Affordable Green Housing: Policy and Innovation
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing