Sustainable Real Estate: Driving Innovation and Economic Resilience

The Rise of Green Building Technologies
Modern real estate development is embracing cutting-edge green building solutions that go beyond basic environmental compliance. Builders now prioritize materials like aerogel insulation and triple-glazed windows, which slash energy use by up to 40% compared to traditional options. What's particularly exciting is how solar arrays are being seamlessly integrated into building facades rather than just rooftops, while greywater recycling systems are becoming standard in forward-thinking developments. These innovations demonstrate how sustainability and functionality can work hand-in-hand.
Smart Building Management Systems
Today's intelligent building systems do much more than simple automation - they're evolving into self-learning ecosystems. Using networks of IoT sensors, these platforms can predict occupancy patterns and adjust HVAC systems accordingly, often achieving 15-30% greater efficiency than scheduled operations. The real breakthrough comes from AI-driven diagnostics that can spot failing equipment weeks before human operators would notice, preventing both costly repairs and unnecessary energy waste. Some systems even negotiate real-time energy pricing with local utilities to optimize consumption during peak and off-peak hours.
Emphasis on Material Sourcing and Recycling
The construction industry is undergoing a materials revolution that extends far beyond basic recycling programs. Innovative projects now incorporate surprising elements like mushroom-based insulation and concrete mixed with recycled industrial byproducts. Perhaps most impactful is the growing practice of urban mining - salvaging high-quality materials from demolition sites for reuse in new constructions, which can reduce a project's embodied carbon by as much as 60%. Architects are also designing with future deconstruction in mind, using reversible connection systems that allow buildings to be disassembled rather than demolished.
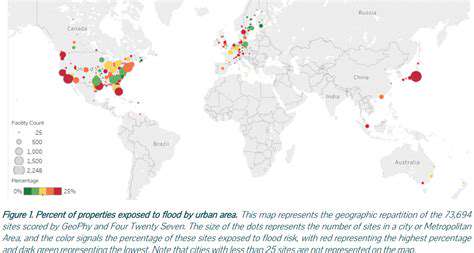
Adapting to Climate Change Impacts
Forward-looking developers aren't just planning for today's climate - they're designing for projected conditions decades into the future. In coastal areas, this means elevating critical infrastructure and incorporating amphibious foundation systems that allow buildings to float during floods. In urban heat islands, we're seeing innovative solutions like phase-change materials in walls that absorb excess heat during the day and release it at night, reducing cooling demands by up to 35%. Even landscaping is being reimagined, with drought-resistant native plants replacing water-intensive lawns and green roofs providing natural insulation.
The Role of Urban Planning and Design
Truly sustainable development requires thinking beyond individual buildings to entire neighborhoods. The most successful projects integrate mixed-use zoning that puts residences within a 15-minute walk of essential services, dramatically reducing car dependence. Clever urban design techniques like cool corridors - tree-lined pathways that channel breezes through dense developments - can lower local temperatures by several degrees during heat waves. Digital twin technology is now allowing planners to simulate how proposed developments will perform across multiple sustainability metrics before construction even begins.
Investment in Sustainable Infrastructure
The shift toward sustainable real estate demands equally innovative supporting infrastructure. Microgrid systems are proving particularly valuable, allowing clusters of buildings to share renewable energy resources and backup power. Perhaps the most transformative investments are in district energy systems, where centralized heating and cooling plants serve entire neighborhoods at far greater efficiency than individual building systems. These solutions require unprecedented cooperation between public entities and private developers, but the payoff comes in significantly lower lifetime costs and reduced environmental impact.
Community Engagement and Education
The human element remains crucial to sustainable development's success. Progressive projects now include living labs where residents can interact with building systems and track their environmental impact in real-time. Some communities have implemented gamified energy-saving programs that reward efficient behavior with credits redeemable at local businesses, achieving participation rates over 80%. Perhaps most importantly, sustainability education is being woven into building operations through interactive displays and mobile apps that make complex systems accessible to all residents, creating a culture of environmental stewardship that extends far beyond the property lines.
Read more about Sustainable Real Estate: Driving Innovation and Economic Resilience
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing