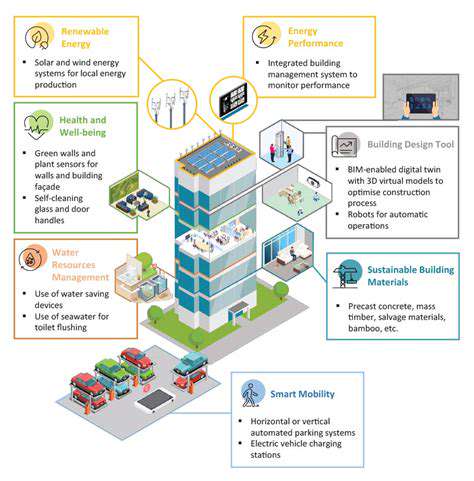
Climate Adaptation Finance for Real Estate

Innovative Financing Mechanisms for Climate Adaptation Projects
Innovative Financing Mechanisms for Climate Adaptation Projects in Developing Countries
Developing nations frequently encounter substantial obstacles when seeking adequate funding for climate adaptation initiatives. Conventional financing approaches, including grants and loans from international bodies, often prove insufficient to address the immense requirements. Creative financing solutions are indispensable for closing this financial shortfall. These approaches must be customized to match the unique circumstances and capabilities of developing nations, guaranteeing their sustainability and fairness. Potential solutions include blended finance models that combine public and private capital, alongside impact investments that balance financial gains with beneficial societal and ecological impacts.
Additionally, emerging economies should investigate opportunities within carbon markets and similar market-driven tools. These systems can promote both emission reductions and adaptation activities by offering monetary rewards to involved parties. Nevertheless, strong regulatory frameworks and clear accountability systems are vital to maintain the efficiency and fairness of these tools, preventing issues like carbon displacement or unequal benefit allocation.
Leveraging Public-Private Partnerships for Sustainable Adaptation
Collaborations between public and private entities (PPPs) present a promising method for attracting private investment toward climate adaptation efforts. By uniting government bodies, non-governmental organizations, and commercial enterprises, PPPs can access considerable resources and specialized knowledge. This strategy proves especially valuable in fields like infrastructure development, where private sector expertise and funding can substantially improve project execution and long-term viability.
Meticulous design of PPP contracts is paramount to ensure alignment with climate adaptation objectives. This involves establishing precise success metrics, reliable oversight procedures, and fair profit distribution terms. Comprehensive background checks and risk evaluations are necessary to prevent possible conflicts and confirm that ventures are both economically feasible and ecologically responsible.
Exploring Alternative Funding Sources and Mechanisms
Beyond conventional methods and PPPs, investigating supplementary funding avenues is essential for advancing climate adaptation programs. This includes examining novel financial products such as climate bonds, which can direct investments specifically toward resilience-building projects. Moreover, inventive approaches like grassroots funding and small-scale lending can enable local populations to finance their own adaptation measures. These methods offer critical assistance, particularly in regions with limited access to traditional financing options.
Equally important is the formulation of comprehensive national adaptation blueprints that explicitly outline a nation's focus areas and requirements. These plans should be incorporated into governmental budgets and developmental agendas, ensuring climate adaptation becomes an inherent component of broader national progress objectives. This holistic method will optimize resource distribution for climate adaptation purposes.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Climate Adaptation Finance
Technological Advancements in Data Collection and Analysis
Modern technological progress is transforming how we gather and interpret data essential for successful climate adaptation funding. Advanced monitoring devices, orbital imaging systems, and cutting-edge predictive models deliver unparalleled understanding of climate change effects on at-risk populations and built environments. This detailed information enables more accurate risk evaluations, helping decision-makers and financiers direct resources to locations most urgently requiring adaptation solutions. These technological tools also simplify progress tracking for adaptation projects, verifying that investments produce quantifiable outcomes.
The capacity to rapidly and precisely handle enormous datasets is fundamental. Utilizing computational intelligence and pattern recognition systems allows identification of climate data correlations that would otherwise remain hidden. This capability facilitates forecasting of future climate hazards and creation of preventive adaptation measures. Ultimately, this enhanced data processing results in better-informed choices, optimizing climate adaptation funding effectiveness while reducing economic losses.
Innovative Financial Instruments and Mechanisms
Technological innovation is also reshaping the conception and execution of financial products for climate adaptation funding. Online platforms and distributed ledger technology are facilitating novel financial offerings specifically designed to mitigate climate vulnerabilities. These encompass weather-dependent insurance policies, environmental investment bonds, and creative funding structures that encourage private sector involvement in adaptation schemes. This transition toward digital alternatives promotes improved availability and operational efficiency in the monetary transfers required for climate resilience.
Moreover, technology supports establishment of more effective and open systems for monitoring and documenting climate adaptation expenditures. This improved clarity strengthens confidence among participants, drawing additional capital and promoting cooperation. Transparent documentation also enables superior responsibility, ensuring resources are properly utilized to deliver concrete climate adaptation results.
Improving Access and Transparency in Climate Finance
Digital solutions significantly enhance availability of climate adaptation funding for emerging economies and susceptible populations. Cellular technology, online access, and intuitive digital interfaces are connecting these groups with financial opportunities. This expanded availability enables local communities to formulate and execute customized adaptation approaches, yielding more enduring and contextually appropriate answers. The capacity to serve isolated and disadvantaged groups is essential for guaranteeing equitable distribution of climate adaptation funding advantages.
Greater openness in climate funding represents another crucial element. Technology permits creation of publicly available repositories and web-based interfaces that monitor adaptation investments, offering improved visibility into resource distribution and utilization. This transparent data strategy promotes accountability and develops public confidence in the adaptation process, eventually stimulating increased investment and global participation in resilience-building activities.
Read more about Climate Adaptation Finance for Real Estate
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing