Smart Building Security: AI Enhanced Surveillance
Predictive Analytics for Enhanced Threat Detection
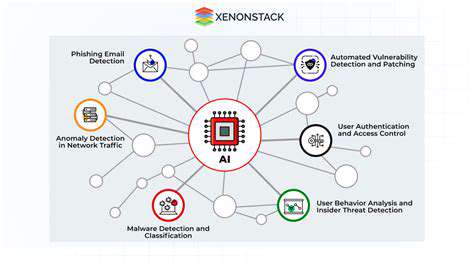
Predictive Modeling Techniques
Modern predictive analytics employs diverse statistical and computational methods to anticipate future scenarios. From straightforward linear models to intricate neural architectures, these tools empower organizations to uncover hidden trends. Grasping these patterns enables proactive strategy adjustments and evidence-based choices. Retailers, for instance, leverage such models to predict product demand, optimizing stock levels to prevent shortages or excess inventory. The foresight gained translates to operational excellence and improved margins.
Model complexity varies significantly. Elementary approaches like linear regression offer simplicity but may overlook nuanced relationships. Conversely, advanced methods such as random forests and gradient boosting machines excel at detecting subtle correlations, albeit requiring robust datasets and processing power. Selection hinges on the specific use case and available information quality.
Data Preparation and Feature Engineering
The foundation of reliable predictions lies in meticulous data preparation. This multi-stage process involves cleansing datasets by addressing incomplete records, anomalous values, and inconsistencies. Proper data sanitization forms the bedrock of trustworthy analytical outcomes. Subsequent transformation stages adapt raw information into formats suitable for algorithmic processing. Feature engineering emerges as particularly crucial - creating derived variables that better represent underlying phenomena, like extracting seasonal patterns from timestamps or crafting interaction terms between demographic factors.
When data preparation falters, predictive accuracy suffers. Substandard preprocessing can yield misleading models, resulting in flawed forecasts and misguided decisions. The painstaking attention to data quality ensures models stand on solid footing, producing dependable insights. This demands systematic approaches to missing value imputation, appropriate scaling techniques, and the development of meaningful predictors that capture complex variable relationships.
Model Evaluation and Selection
Assessing model efficacy remains paramount before deployment. Various metrics quantify prediction quality, including classification accuracy, precision-recall tradeoffs, and F-measures. The choice depends on operational priorities - in fraud screening scenarios, maximizing true positive rates often outweighs precision considerations, as overlooking fraudulent transactions proves costlier than occasional false alarms.
Selecting the optimal model involves comparative testing across multiple algorithmic approaches. This empirical process evaluates performance against validation datasets, weighing each technique's strengths against implementation constraints. Balancing model complexity, interpretability, and computational demands proves essential for practical implementation. The final selection should align with business objectives while considering maintainability and explainability requirements.
Deployment and Monitoring
Transitioning models to production environments demands careful orchestration. Integration with existing IT infrastructure presents technical challenges requiring solutions for scalability and maintainability. Successful deployment hinges on preserving model integrity while meeting real-world performance expectations. This includes addressing latency requirements, API design considerations, and failover mechanisms.
Post-deployment vigilance remains critical as data patterns evolve. Continuous performance tracking identifies concept drift - when underlying relationships change over time. Scheduled model refreshes incorporating new data prevent accuracy erosion, ensuring predictions remain relevant. This ongoing maintenance safeguards against deteriorating performance that could undermine operational decisions.
Real-World Applications of Predictive Analytics
Predictive methodologies transform operations across sectors. Healthcare systems forecast patient readmission risks, enabling preventive care interventions. Financial institutions deploy these tools for credit scoring and fraud prevention, mitigating monetary losses. Marketing teams harness predictive insights to personalize customer journeys and optimize campaign spending. The transformative potential spans industries, generating actionable intelligence from historical patterns.
Predictive analytics represents a competitive differentiator in data-driven decision environments. Organizations employing these techniques realize benefits ranging from streamlined operations to enhanced customer experiences. As technological capabilities advance, novel applications continue emerging, creating opportunities for innovation and strategic advantage across business functions.
Real-Time Threat Response and Automated Actions
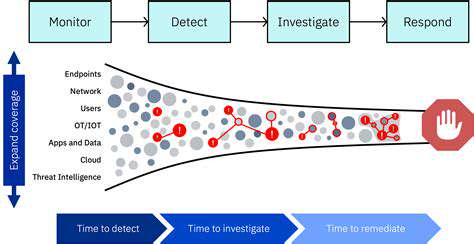
Real-Time Threat Detection
Contemporary cybersecurity strategies prioritize immediate threat identification through continuous monitoring of network traffic and system behaviors. This vigilant approach enables security personnel to intercept malicious activity during initial stages, limiting potential damage. Rapid threat containment significantly reduces operational disruptions and associated financial impacts.
Advanced detection systems employ machine learning to analyze massive data streams in milliseconds, uncovering subtle anomalies that traditional signature-based methods might miss. This capability proves invaluable against sophisticated, evolving cyber threats that constantly test organizational defenses.
Automated Response Mechanisms
Automation revolutionizes incident response by executing predefined countermeasures without human intervention. When threats emerge, these systems instantly implement containment protocols, dramatically shrinking response windows. Automated defenses provide critical speed advantages against rapidly propagating threats, minimizing potential data exfiltration or system compromise.
Typical automated actions include blocking malicious network traffic, isolating compromised endpoints, and triggering security incident workflows. This immediate response capability proves particularly valuable against ransomware and other time-sensitive attacks where minutes matter.
Integration with Existing Security Infrastructure
Effective threat management requires tight coupling with deployed security solutions. Interoperability with firewalls, SIEM platforms, and endpoint protection systems creates comprehensive visibility. Unified security ecosystems enable rapid correlation of events across attack surfaces, accelerating threat neutralization.
Siloed security tools create blind spots and delayed responses. Proper integration eliminates these gaps, providing security teams with complete situational awareness necessary for effective defense against multi-vector attacks.
Proactive Threat Intelligence
Staying ahead of adversaries demands continuous threat intelligence gathering. Security teams monitor diverse sources - from vendor feeds to dark web forums - identifying emerging attack patterns. Preemptive defense adjustments based on this intelligence significantly reduce organizational exposure to novel threats.
This forward-looking approach allows security architects to harden defenses before attacks materialize. Understanding attacker methodologies and tools enables development of targeted countermeasures, creating resilient security postures capable of withstanding evolving threats.
Future Trends and Implications for Smart Building Security

Technological Advancements and Their Impact
Artificial intelligence and automation technologies continue advancing at remarkable pace, transforming business operations. These innovations drive unprecedented efficiency gains while creating new possibilities across sectors. AI-powered solutions already optimize logistics networks, enable hyper-personalized customer interactions, and automate routine processes - delivering cost reductions and productivity improvements. The workforce implications necessitate significant retraining initiatives.
While promising, these technologies introduce challenges around workforce transitions. Organizations must implement comprehensive upskilling programs to help employees adapt to evolving job requirements in increasingly automated environments.
Economic Shifts and Global Interdependence
The global economy grows increasingly interconnected through digital commerce and international agreements. E-commerce platforms dissolve traditional geographic barriers, presenting new opportunities while complicating supply chain risk management. Market volatility, trade tensions, and global health crises demonstrate the need for agile economic strategies capable of withstanding disruptions.
Developing economies experience accelerated growth, generating increased demand for commodities and creating investment opportunities. Navigating this dynamic landscape requires businesses to develop flexible operational models that can adapt to rapidly changing conditions.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
Environmental consciousness reshapes corporate strategies worldwide. Businesses increasingly adopt sustainable practices and clean technologies to minimize ecological footprints. This shift spurs innovation in renewable energy systems, circular economy models, and environmentally responsible production methods - opening new markets for green technologies.
The transition toward sustainability requires substantial investments in research, infrastructure modernization, and policy reform. Addressing environmental challenges demands coordinated efforts across public and private sectors to ensure long-term planetary health.
Social and Cultural Transformations
Digital communication platforms fundamentally alter social dynamics and cultural norms. While enhancing global connectivity, these technologies also facilitate misinformation spread and privacy erosion. Addressing these challenges requires thoughtful policy frameworks and digital literacy initiatives.
Society must critically examine technology's societal impacts to harness benefits while mitigating negative consequences. Developing ethical guidelines and responsible usage norms will prove essential for maintaining healthy digital ecosystems.
Demographic Shifts and Workforce Dynamics
Changing population structures influence labor markets and consumer behavior. Organizations must adapt policies to accommodate multigenerational workforces and diverse consumer bases through inclusive practices and flexible arrangements. Understanding evolving demographic needs becomes crucial for business sustainability.
Aging populations present unique challenges for social systems and healthcare infrastructure. Proactive policy adjustments and innovative care models will be necessary to support changing demographic realities.
Political and Regulatory Environments
The global political landscape remains in constant flux, with policy changes impacting business operations. Navigating this complexity requires organizations to maintain regulatory agility and geopolitical awareness. Trade agreements and international relations significantly influence market access and operational considerations.
Businesses must establish robust regulatory monitoring processes to ensure compliance across jurisdictions. Developing adaptable operational models helps mitigate risks associated with changing political environments.
Emerging Technologies and their Disruptive Potential
Breakthrough technologies like quantum computing and advanced biotech promise revolutionary changes across industries. These innovations may redefine healthcare delivery, materials science, and energy systems, potentially creating entirely new economic sectors. Organizations must cultivate innovation capabilities to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
The accelerating pace of technological change demands continuous learning and adaptation. Forward-looking organizations invest in technology foresight capabilities to anticipate disruptions and position themselves advantageously in evolving markets.
Read more about Smart Building Security: AI Enhanced Surveillance
Hot Recommendations
- AI in Property Marketing: Virtual Tours and VR
- Water Management Solutions for Sustainable Real Estate
- IoT Solutions for Smart Building Energy Management
- Sustainable Real Estate: Building a Greener Tomorrow
- Sustainable Real Estate: From Concept to Community
- AI Driven Due Diligence for Large Scale Developments
- Real Estate Sector and Global Climate Agreements
- Smart Buildings: The Key to Smarter Property Management
- Zero Waste Buildings: A Sustainable Real Estate Goal
- Understanding Climate Risk in Real Estate Financing